Year 2 unit overview — Australian Curriculum: Mathematics
advertisement

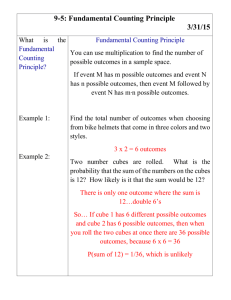
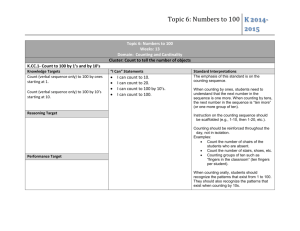
Year 2 unit overview — Australian Curriculum: Mathematics School name Unit title Duration of unit Coolkids School Term 2 Mathematics 10 weeks Unit outline In this unit students will apply, explore and develop a variety of mathematical concepts on number sequences, measurement, time, months, seasons and the use of the calendar. Through content strands – Number and Algebra, Measurement and Geometry and Statistics and Probability students will be provided with opportunities to develop understanding of: Number and place value – Investigate number sequences, initially those increasing and decreasing by twos threes, fives and tens from any starting point, the moving to other sequences. Number and place value – Recognise, model, represent and order numbers to at least 1000 Using units of measurements – Compare and order several shapes and objects based on length, area, volume and capacity using appropriate uniform informal units. Using units of measurements – Tell time to the quarter-hour, using the language of ‘past’ and ‘to”. Using units of measurements – Name and order months and seasons. Using units of measurements – Use a calendar to identify the date and determine the number of days in each month. Data representation and interpretations – Create displays of data using lists, table and picture graphs and interpret them. Students will be provided with opportunities to access ICTs during this unit as a whole class, in group work and as individuals. Achievement standard Identify curriculum By the end of Year 2, students recognise increasing and decreasing number sequences involving 2s, 3s and 5s. They represent multiplication and division by grouping into sets. They associate of Australian coins with their value. Students identify the missing element in a number sequence. Students recognise the Content descriptions to be collections taught General capabilities and cross-curriculum features of three-dimensional objects. They interpret simple maps of familiar locations. They explain the effects of one-step transformations. Students make sense priorities Number and Algebra Measurement and Geometry Statistics and Probability of collected information. Number and to place Using units of measurement representation and of strategies. TheyLiteracy Students count andvalue from 1000. They perform simple addition and subtractionData calculations using a range divide collections and shapes into interpretation halves, quarters and eighths. Students order shapes andand objects using several informal units. They tell time to the quarter hour and use a calendar to identify the date and Investigate number sequences, Compare order Develop the language of fractions the months seasons. They dimensional shapes. Theyon describe outcomes for everyday events. initially included those in increasing and draw twoshapes and objects based Create displays of data using lists,Students collect data from relevant questions to create lists, tables picture graphs. Numeracy decreasing by and twos, threes, fives length, area, volume and capacity table and picture graphs and and ten from any starting point, using appropriate uniform interpret them (ACMSP050) Apply concepts of equal portions Proficiencies then moving to other sequences. informal units (ACMMG037) ICT capability Opportunities (ACMNA026) to develop proficiencies include: Problem Solving Tell time to the quarter-hour, digitaltotechnologies to create online Understanding Uses objects, technology andUse diagrams solve mathematical using the language of 'past' and and pictographic representations and problems. Recognise, andwith counting 'to' (ACMMG039) Connecting model, numberrepresent calculations sequences glossaries of fractions least 1000 Name and order months and Reasoning order Identifynumbers a date into theatcalendar (ACMNA027) Critical and creative thinking seasons (ACMMG040) Compare results from data collection. Identify the months in the year. Useas reasoning to explain how to create fair Compare the changes to the climate the months and season change. Identify and describe the seasons. Use a calendar to identify the date and determine the number shares Fluency of days in each month Personal and social capability Counting numbers in sequence easily. (ACMMG041) Develop the notion of a fair share Describe and use mathematical language for units of measurement and number sequences. Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures Interpret data and describe the results Describe and order time durations to the quarter hour. Describe, order and identify the months and seasons of the year. Demonstrate alternative ways of knowing and sharing Sustainability Assessment Describe the assessment Develop the notion of a fair share of resources Make judgments Assessment date Relevant prior curriculum Curriculum working towards In the Australian Curriculum: Mathematics at Year 1 Number and Algebra Number and place value Develop confidence with number sequences to and from 100 by ones from any starting point. Skip count by twos, fives and tens starting from zero In the Australian Curriculum: Mathematics at Year 3 (ACMNA012) Number and Algebra Number and place value Investigate the conditions required for a number to be odd or even and identify odd and even numbers (ACMNA051) Recognise, model, represent and order numbers to at least 10 000 (ACMNA052) Recognise, model, read, write and order numbers to at least 100. Locate these numbers on a number line (ACMNA013) Measurement and Geometry Using units of measurement Measurement and Geometry Using units of measurement Measure, order and compare objects using familiar metric units of length, mass and capacity (ACMMG061) Tell time to the minute and investigate the relationship between units of time Measure and compare the lengths and capacities of pairs of objects using uniform informal units (ACMMG019) (ACMMG062) Tell time to the half-hour (ACMMG020) Statistics and Probability Describe duration using months, weeks, days and hours (ACMMG021) Data representation and interpretation Collect data, organise into categories and create displays using lists, tables, picture Statistics and Probability graphs and simple column graphs, with and without the use of digital technologies (ACMSP069) Represent data with objects and drawings where one object or drawing represents one data value. Describe the displays (ACMSP263) Bridging content In the Essential Learnings by the end of Year 2 Links to other learning areas Number Number sequences both increasing and decreasing by twos, threes, fives and tens from any starting point. Recognise, describe and order number to 1000 Measurement Tell time, describe and order the duration of events to the quarter hour. Name and order the months of the year Recognise and describe the characteristics of the seasons of the year. Identify a day and date on a calendar. Technology: This occurs in online matching games and online research for origins of the month’s extension task. English: This occurs through understanding and completing activities worksheets, word walls and written responses to topics. Week 1 By the end of week 1 Observe and note students ability to count forward and backward to 100 Observe students understanding and ability to complete the ‘Help the frog catch the fly’ activity by counting in 2s Observe and note students’ ability and understanding on number patterns in 5s starting from different points. Observe and note student’s ability to complete the number patterns quickly and accurately. Anecdotal notes on student ability to complete a number pattern and understand how to use number patterns outside the classroom. Week 2 Observation and note students ability to investigate pattern sequence using By the end of week 2 hundreds board. Observe and note student’s participation and ability in a Pattern Game Observe and note student contribution during group activity. Week 3 Observe and note student contribution during brainstorming and group work Observe students understanding and ability to complete the cut and paste activity on the months of the year. Observe and note student’s ability and understanding of tallying and graphing birthdays. Collect student work. Observe and note student’s input and accuracy when identifying AM and PM and work samples of the completion of the timeline event. By the end of week 3 Week 1 Content descriptors addressed: Unit of Number patterns (ACMNA027) & (ACMNA026) Understanding: Recognition of numbers up to 1000 The concept of a number pattern Skills: Able to read, write and verbalize ascending and descending number patterns (including 1s,2s & 10s) Create ascending and descending number patterns Week 2 Content descriptors addressed: Unit of Number patterns (ACMNA027) & (ACMNA026) Understanding: Number pattern 5s & 10s have overlapping units Skills: Able to read, write and verbalize ascending and descending number patterns (including 5s & 10s) Create ascending and descending number patterns (starting from various number points) Week 3 Content descriptors addressed: Units of measurements (ACMMG040) (ACMMG041) Understanding: Participates in brainstorming and group discussions. Describes and orders events using the calendar. Skills Uses objects and diagrams to explore months and seasons. Uses Graphs and timeline to collect and investigate data. Collection of activities and quiz shows correct answers. Uses mathematical language for calculation of time. Anecdotal notes on students understanding and abilities to copy times and tell the time using their own interactive clock face. Anecdotal notes on students understanding and abilities to display and tell the time. Week 4 By the end of week 4 Understanding: Understands clocks have 60 minutes Each hour number represents 5 minutes Clock contains an hour and a minute hand Skills: Can tell the time in a variety of ways Ability to arrange events sequentially Determine the hour hand from the minute hand Observe and note student contribution during brainstorming and group activity. Work samples – AM/PM activity of matching picture with time of day to assess students understand of time language. Work sample – creation of analogue clock By the end of week 5 Week 5 Observe and note student contribution during brainstorming and creation of word wall. Observe and note students understanding of time language using the terms ‘past’ and ‘to’ Observe and note participation in group activities. Work sample – completion of matching game online – analogue and digital. Week 4 Content descriptors addressed: Unit of time (ACMMG039) Week 5 Content descriptors addressed: Unit of time (ACMMG039) Understanding: Concept terms of ‘past’ and ‘to’ in relation to time Skills: Represent times on an analogue clock. Identify and verbalize 15,30 and 45 on an analogue clock Week 6 Content descriptors addressed: By the end of week 6 Week 6 Observe and note student understanding of Tally Marks Work Samples – Collection of activity of ‘Tally the toys” picture graph and column graph. Collection of work – Class survey results and development and understand of pie chart. Observe and note student contribution to group activity to create column graphs. By the end of week 7 Week 7 Observe and note student contribution during brainstorming and group activity. Monitor students’ accuracy for measuring with cubes Observe and note student understanding and ability during informal measuring with ribbon Anecdotal notes about students’ involvement and ability to use hands accurately to measure each other. Record students’ accuracy and understanding of their ‘big’ and ‘small’ tables. Observe students’ understanding of area measurement. Observe students contribution in pair work and accuracy when measuring area with counters. By the end of week 8 Week 8 Observe and note student contribution during brainstorming and group activity. Observe and note students understanding of capacity and capability to estimate and record new information. Unit of Data (ACMSP069) Understanding: Information can be calculated using tally marks Information can be depicted in various graphs (pie, picture, column) Skills: Calculate surveys using tally marks Convert data into graphs (pie, picture and column) Week 7 Content descriptors addressed: Units of measurements (ACMMG037) (ACMSP069) Understanding: Participates in brainstorming and group discussions. Understands that the largest measurement is the longest. Understands that the smallest measurement is the shortest. Measurement involves cm, mm etc. Skills: Use every day items to measure objects with informal units. Record data in a table to compare and order measurement. Make predictions on measurement of height. Identify size in order of small, medium and big. Week 8 Content descriptors addressed: Units of Measurement: (ACMMG037) Understanding: Collect student work: Check for accuracy in recording findings. Work samples – worksheet and picture activity By the end of week 9 Week 9 Observation and note students ability during written/verbal/hands on tasks Collect students work – Mark practice quiz Observation of student’s participation is group activities. By the end of week 10 Week 10 Assessment Week Collect student work – written test on number recognition, number patterns, data and time Collect students work- verbal/physical response on measurement and time Measurement consists of different units depending on the object (such as; cm, L, Kg etc.) Capacity is the space that needs to be filled Skills: Read/interpret capacity measurements of an object Ability to compare various quantities of object capacity Able to visual estimate capacity levels Record information in relation to measurement Week 1: Counting Patterns • Counting on activities (1s, 2, 10s) • Number recognition to 100 (Hundreds board) • Complete the hundreds board and colour the patterns Week 1: Considerations (learning and assessment) Students may count on by including the original number instead of tapping the next number (e.g. Count on 2 from 33, students taps 33 then 34 but answer is 35) Loses track when counting in 10s Videos- Counting 100s, Counting 1000s, patterns, ways to count • Show-me boards • Whiteboard pens • 100’s board print out- Individual Introducing counting by 2s & 10s- visual/verbal aide of songs Week 1: Adjustments (student’s needs): • Interactive Whiteboard (Hundreds board) Modification: • Counters (various colours) • Focusing on counting by 2s using number linesFind the missing number • Group rotation activities & manipulates • Buzz Game using 2s – Whole class activity • Work sheets in relation to counting by 2s & 10s -Worksheet • Small Group rotations each afternoon- focusing on Patterns • Large hundreds board (2 colours) • Hand display • Number cards • • • • • • • • • • Whiteboard pens Show-me boards 100’s board print out- Individual Interactive Whiteboard (Hundreds board) Counters (various colours) Group rotation activities & manipulates Work sheets in relation to counting by 5s Large hundreds board (2 colours) Chalk Large concreted area • Model counting patterns while students are individually working. Extra time for students would still grasping concept of 1s and 2s- counting forwards and backwards before moving onto 10s Scaffold learners with accuracy techniques (explicit instruction- counting on and backwards) Extension: Week 2: Counting Patterns • Counting by 2s, 5s, 10s- visual/verbal aide of songs • Investigating pattern sequences using hundreds board • Pattern Game- Create a life size hundreds board on concrete (chalk), students explore 2s, 5s & 10s patterns Students count by 2s & 10s but starting with an alternate number (e.g. count in 2s from 5) Week 2: Considerations (learning and assessment) Students may count on by including the original number instead of tapping the next number (e.g. Count on in 2s from 33, students taps 33 then 34 but answer is 35) Loses track when counting in 5s or 10s Misconceptions of all 10s are multiple of 5s so all 5s must be multiples of 10s. Week 2: Adjustments (student’s needs): Modification: • • • Focusing on counting by 5s & 10s using hundreds boards- Compare the number patterns Small Group rotations each afternoon- focusing on Patterns Collect formative assessment informationCounting patterns 2s, 5s & 10s Model counting patterns while students are individually working. Extra time for students would still grasping concept of 1s and 2s- counting forwards and backwards before moving onto 10s Scaffold learners with accuracy techniques (explicit instruction- counting on and backwards) Extension: Explore patterns of 5s & 10s starting from a different number (e.g. 8). Compare patterns to 100s chart with patterns starting at 0. Investigate/explain similarities Week 3: Months/Seasons Week 3: Considerations (learning and assessment) • Whiteboard • • • Days of the week: YouTube Clip • 12 months in a year: YouTube Clip • Months of the year cut and paste activity • Classroom calendar • Evaluate students’ prior knowledge by brainstorming to assess understanding of months, seasons, and calendars. Establish the characteristics of each month and season. • Discuss the task and outcomes of how we might understand the calendar. • Cut and paste activities identifying the months and seasons of the year. • Activity to order events in a timeline. • Collect data of students birthdays, then a bar graph using the calendar as a reference and discuss order and least and most common terms. • Students may have trouble remembering the order of the months. Student may have trouble with an analogue watch as today’s technology is digital. Week 3: Adjustments (student’s needs): Modification: • Include mnemonic devices that will help student remember the order such as the month of the year song. • Include concrete materials such as interactive clock to provide a hands on approach in order to facilitate learning. Extension: • Calendar/Date activity- Find dates through-out the year (Extension- Linking seasons) • Students could investigate the origins of the months. • Students could log the times of their favourite TV shows. Week 4: Time Week 4: Considerations (learning and assessment) • Large Interactive analogue clock face • • Student Interactive analogue clocks – Paper cut outs • What’s the time? YouTube Clip • Small group activities & Manipulates Week 4: Adjustments (student’s needs): • Images (Timeline activity) Modification: • Whiteboard • AM/PM worksheet • Time definition cards (e.g. of ‘half past’ & ‘ 10 to’ • Large Interactive analogue clock face • Student Interactive analogue clocks – Paper cut outs Explore Various types of clocks (analog/digital)discussing attributes & prior knowledge (personal) • AM/PM activities- matching pictures and time of day • Hourly timeline- Discussing/Creating their day • Activity to order events in a timeline (within 24hr period). • Create their own analog clock- Paper manipulate • Small Group rotations/games each afternoonfocusing on Time Students may confuse the hour hand and minute hand. (use clock with colour coded hands) Use worksheets as formative assessment (does the students understand am/pm in 24hour period) Be mindful of students who may have different structure within a day (may have dinner before shower or only brush teeth at night time etc.) Extension: Using 24hour time to arrange timelines Investigate timeframe (e.g. how long are we at school?) Week 5: Time Week 5: Considerations (learning and assessment) • Brainstorming word wall- language and meaning previous (o’clock, thirty) introducing ‘past’. Using large colour coded hands Clock to demonstrate, Using (individual) paper manipulates to reciprocate Students may confuse the hour hand and minute hand. (use clock with colour coded hands) Confusion may arise from exposure to 24 digital clocks Focus on the term ‘past’- make connection to numbers 1-5 (5, 10, 20, 25) • Focus on the term ‘to’- make connection to numbers 7-12 (35, 40, 50, 55) Week 5: Adjustments (student’s needs): • Small Group rotations/games each afternoonfocusing on Time • Matching game online- analog & Digital Formative assessment • Explicit teaching on when to use terms ‘to’ and ‘past’ Modification: Focus on mastering half past first before moving on Use of a verbal clock my assist students with learning difficulties • Small group activities & Manipulates • Whiteboard • AM/PM worksheet • Internet- Link to Matching online game ‘Stop the clock’ • Video: Telling the time • Small group activities & Manipulates Extension: Apply new knowledge: ordering of clocks that include concepts of ‘to’ and ‘past’ (20 to 5, 5 past 5 etc.) Include AM/PM into ordering activities Week 6 Data Week 6: Considerations (learning and assessment) Whiteboard Butcher paper Numeracy wrap Activity Picture (represent various factors compare) Small group activities & Manipulates Demonstrating Tally marks- Class Survey of Birthday (Months) - Discuss terms such as ‘Compare’, ‘Sort’ etc. Create a Numeracy wrap Activity: Tally the toysDisplay your data in a picture graph and then a column graph. Class survey results- Develop a pie chart with tally marks from previous lesson Small Group rotations on data Ability group activity- explore/compare (2, 3 & 4 factors) Create basic column graphs using cut out pictures Students to understand pie charts can be used as fractions (divide whole number into multiple parts) and to display data information (multiple grouping) Week 6: Adjustments (student’s needs): Modification: Students may find it difficult to draw charts (blank templates will eliminate time being lost) Extension: Provide extension questions to assess students skills in Interpreting data Week 7: Measurement Week 7: Considerations (learning and assessment) • • Evaluate students’ prior knowledge by brainstorming to assess understanding of what measurement means. • Students may not know how to repeat units and may leave gaps when measuring with non-standard units. E.g. Ribbon or cubes. • Establish the characteristics of measurement e.g. small, medium and big. • Students may have trouble comparing lengths and heights. Provide opportunities to use mathematical terms of measurement. • • Discuss the task and outcomes of how we might understand how to measure • Use concrete materials to demonstrate explain measurement • • • • Polar bear song Week 7: Adjustments (students’ needs): • 1m length Ribbons Modification: • Objects around the room • • Recording sheet. • Butchers paper for graph • Big and small video • Shapes song • Magazines • Large paper for tables • Pens, scissors, glue • Use problem solving questions. “How many ribbons/cubes/counters bigger is ____ than ____? Shape bag with 30 different sized cardboard shapes. • Coloured counters. Week 8: Considerations (learning and assessment) Transition game Small group activities & Manipulates Demonstrate and provide opportunities for students to measure items that are longer than the ribbon so that students move the ribbon repeatedly to measure the length of an item. • Use ribbons to measure objects in the classroom. Provide modeling and examples to help scaffold learning. • Provide measuring equipment that is easy to use. Make predictions on height of students and record in a bar graph. Discuss the results to see if their predictions were correct. • Use magazines to find pictures for small, medium and big objects and glue the items into the correct columns • Use coloured counters to measure the area of a shape. Week 8: Capacity Rubix cubes Videos: counting by 2’s, counting by 5’s, counting by 10’s Whiteboard • Discuss which objects they found longest and shortest. Use a table to record and compare results collected. • Mystery bag with items varying in length Extension: • Predict & investigate activity- arrange in order (unknown capacities) Transition game – Which cup hold the most Investigate how to record capacity (various types of containers) Language specific to capacity: litre, millilitre (word wall & term cards) Measurement representation activity Worksheets- Capacity (formative assessment) Group investigation activities (estimate/record/evaluate) Week 8: Adjustments (student’s needs): Revision lessons on required topics that need assistance (evaluate formative assessment) Provide opportunities to revise content using written/verbal/hands on tasks Practice quiz Group rotation in afternoon vary according to lesson content in the morning session (Patterns/Time/Measurement/Data) Measuring jugs Measurement representation activity Worksheets IWB Containers Provide modeling and examples to help scaffold learning. Trough Video on capacity • Provide measuring equipment that is easy to use. Extension activities Extension: Modification: Week 9 Revision Students may make misconceptions with mm and ml- make specific reference which each measuring unit is referring to (length or capacity) Students may be able to make connections between ml & L (1800mls = 1.8 L). Have students arrange in order (Container holding the least to the most amount of liquid) with different base units. Week 9: Considerations (learning and assessments) Students are giving extra guidance based on where they are having difficulties understanding. (formative assessment to provide information) Week 9: Adjustments (student’s needs): Modification: Extra teacher aide time or one on one teacher time if available for students requiring extensive assistance. Peer tutoring activities would also help students struggling to grasp certain concepts. Extension: Provide opportunities for activities to extend beyond basic topics (such as counting patterns in 3s, 4s & 7s, comparing different Practice quiz Small group activities (Pattern/Time/Data/Measurement) Measuring equipment (rulers etc.) Clocks Test sheets Manipulates Objects to measure (e.g. liquids, toys etc.) Teacher aide Stationary measuring units (ml & L), interpretation questions on data etc. Week 10: Assessment Week 10: Considerations (learning and assessment) Provide the class with hands on tests based on measurement and separate one on time. Students demonstrate understanding of measuring and recording various items (using mms, cms & ml, Ls) Interpret digital time and display on analog clocks, verbalizing various times displayed Written test on number recognition, number patterns, Months/seasons and data. Students who have reading process issues, fine motor skills issues or learning difficulties- aide guidance & extra time. Provide time to explain and model the test before students proceed on their own to ensure understanding Students who struggle with writing based test may verbally respond with teacher/aide assistance Provide students with manipulates to assist in the test (e.g. counters, rulers etc) Measuring tapes Rulers Measuring jugs Clocks Test sheets Manipulates Objects to measure (e.g. liquids, toys etc.) Teacher aide Stationary Formative assessment Use feedback Ways to monitor learning and assessment • • Feedback to students • • • Reflection on the unit plan • • • • • • Teachers meet to collaboratively plan the teaching, learning and assessment to meet the needs of all learners in each unit. Teachers create opportunities for discussion about levels of achievement to develop shared understandings; co-mark or cross mark at key points to ensure consistency of judgments; and participate in moderating samples of student work at school or cluster level to reach consensus and consistency. Teachers strategically plan opportunities and ways to provide ongoing feedback (both written and informal) and encouragement to children on their strengths and areas for improvement. Children reflect on and discuss with their teachers or peers what they can do well and what they need to improve. Teachers reflect on and review learning opportunities to incorporate specific learning experiences and provide multiple opportunities for children to experience, practise and improve. Identify what worked well during and at the end of the unit, including: activities that worked well and why activities that could be improved and how assessment that worked well and why assessment that could be improved and how common student misconceptions that need, or needed, to be clarified.