Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers
advertisement

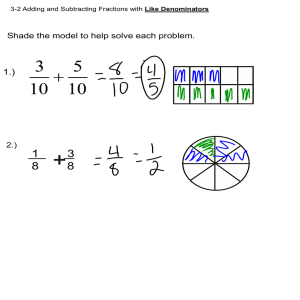
Name: Date: Unit 3: Fractions (Part 2) Fractions in simplest form Fractions are in simplest form when the only common factor of the numerator and denominator is 1. Divide the numerator and denominator by common factors Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers Improper fractions have a larger numerator than denominator Mixed Numbers have a whole number and a fraction Convert improper fractions to a mixed numbers by dividing and using DOWN Convert mixed numbers to improper fractions by multiplying whole number and denominator and adding the numerator Adding Fractions With like denominators: o Add the numerators and keep the denominator the same o Then simplify With unlike denominators: o Use the butterfly method or equivalent fraction method to add. o Be sure to simplify. Subtracting Fractions With like denominators: o Subtract the numerators and keep the denominator the same o Then simplify With unlike denominators: o Use the butterfly method or equivalent fraction method to subtract. o Be sure to simplify. Adding mixed numbers With like denominators: o Add the numerators and keep the denominator the same. o Then add the whole numbers. o Be sure to change improper fractions into mixed numbers. o Simplify. With unlike denominators: o Use the butterfly method or equivalent fraction method to add. o Then add the whole numbers. o Be sure to change improper fractions into mixed numbers. o Simplify your answer. Subtracting mixed numbers Before subtracting mixed numbers: STOP: Compare the fractions, then proceed With like denominators and a bigger starting fraction: o Subtract the numerators and keep the denominator the same. o Subtract the whole number. o Simplify. With like denominators and a smaller starting fraction: o Regroup one whole from the whole number to add to the fraction. This will give you an improper fraction which is fine! o Subtract the numerators and keep the denominator the same. o Subtract the whole number. o Simplify. With unlike denominators and a bigger starting fraction: o Use the butterfly method or equivalent fraction method to subtract the fractions o Then subtract the whole numbers o Be sure to simplify With unlike denominators and a smaller starting fraction: o Regroup one whole from the whole number to add to the fraction. This will give you an improper fraction which is fine! o Use the butterfly method or equivalent fraction method to subtract the fractions o Then subtract the whole numbers o Be sure to simplify Multiplying Fractions Put your whole number over one if necessary Look across the fractions to see if there are any common factors and simplify Multiply your numerators Multiply your denominators Simplify Dividing Fractions Put your whole number over one if necessary Follow KCF: o Keep the first fraction o Change the sign to a multiplication sign o Flip your second fraction Then simplify, multiply, simplify Multiplying and Dividing Mixed Numbers Change all mixed numbers into improper fractions Then follow the steps above to multiply or divide. Estimating with fractions and mixed numbers Determine if the fraction is less than ½ or equal to or greater than ½ If it is less than ½- round the fraction to 0 If it is more than ½- round the fraction to 1 Problem solving key terms Addition: in all, altogether, joined, combined, added, total, both, more, together, sum, increase Subtraction: difference, fewer, less than, how many more, how much more, remains, left over, decreased, take away, minus, -er words (longer, shorter, smaller, wider, etc.) Multiplication: of, twice, each, increased/decreased by a factor of, in all, multiplied by, times, area, multiple Division: per, a, share, distribute, quotient, each, divide equally, equal pieces, split, separate, cut up, half