Class XII (PHYSICS)
advertisement

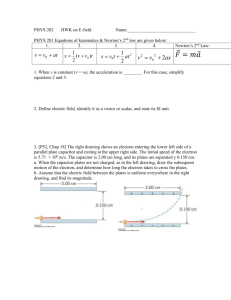
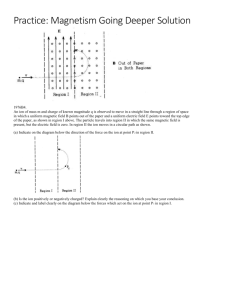
SUMMER HOLIDAY HOMEWORK D-II, Vasant Kunj, New Delhi - 110070 Session 2013-14 Name: _____________________ S.No. : 1 Date: _______/ 05______/ 2013____ Class: XII-A Subject: Physics Topic: Unit1, Unit2 & Unit3 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS: A: The numerical are based on application of theory content. Attempt them in your physics notebook as practice assignment. B: Do all questions in sequence. UNIT –I: ELECTROSTATICS 1. Three identical charges each +q are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side d cm. Calculate the force on a +ve charge +2q at the centroid of the triangle. 2. Force acting on a charged particle kept between the pair of plates, having equal and opposite charge, is F. If one of the plates is removed, find the force acting on the same particle. 3. The plates of a parallel plate system are charged up to 100V. A 4mm thickness dielectric slab is inserted between the plates. Then to maintain the same potential difference, the distance between the systems plates are increased by 2mm. find the dielectric constant. 4. A point charge placed at any point on the axis of an electric dipole at some large distance experiences a force F. Find the force acting on the point charge when its distance from the dipole is quadrupled. 5. In the electric field of a point charge ‘q’, the four points A,B,C and D are equidistant from q, however AB>AC>AD. Calculate the work done in taking a unit charge along AB, AC and AD. 6. N identical spherical drops charged to the same potential ‘V’ is combined to form a big drop. Find the potential of the new big drop formed. 7. An electron is projected with an initial speed of 25×105 m/s directly towards a proton which is at rest. Initially the electron is supposed to be at a fairly large distance from the proton. Find the distance of the electron from the proton when its instantaneous speed becomes twice the initial speed. 8. Two conducting spheres one of radius 6cm and the other of radius 12cm each carrying 3×10-8C are placed very par apart. If these spheres are connected by a conducting wire, find the direction of motion and the magnitude of charge transferred. THS, VK, Cl. XII Physics Topic: Summer HHW Session: 2013-14 Page 1 9. A solid metal disc of radius ‘R’ rotates with constant angular velocity about its axis. Calculate the electric field ‘E’ at a distance ‘x’ from the axis and the potential difference ‘V’ between the centre and the edge of the disc. 10. Three charges of +0.1C each is placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle, 1m side. If energy is supplied at the rate of 1kW, how many days would be required to move one of the charges to the midpoint of the line joining the other two? 11. A parallel plate capacitor is made by stacking ‘n’ equally spaced plates connected alternatively. If the capacitance between any two plates is ‘C’, determine the resultant capacitance of the combination. 12. Can a metal sphere of radius 1cm hold a charge of 1coulomb? Justify your answer. 13. When two capacitors are connected in series, the effective capacitance is 2.4μF and when connected in parallel, the effective capacitance is 10μF. Calculate the individual capacitances. 14. Two fixed charges -2Q and Q are located at the points with co-ordinates (- 3a,0) and (+3a,0) respectively in the x-y plane. Show that all the points in the x-y plane where the electric potential due to the two charges is 0, lie on a circle. Find its radius and location of its centre. 15. Two square metallic plates of side 1.5m are kept 0.015m apart like a parallel plate capacitor, in air in such a way that one of their edges is perpendicular to an oiled surface in a tank filled with insulating oil. The plates are connected to a battery of EMF 600V. The plates are then lowered vertically into the oil at a speed of 0.002m/s. Calculate the current drawn from the battery during the process(dielectric constant of oil=12) 16. A charged particle is free to move in an electric field. Will it always move along the electric lines of force? 17. Two point charges ‘+q’ and ‘-q’ are placed at a distance ‘d’ apart. What are the points at which the resultant field is parallel to the line joining the two charges? 18. Two copper spheres of same radii, one hollow and the other solid are charged to the same potential. Which of the two will have same charge? 19. You are given three capacitors of value 2μF, 3μF, 6μF. How will you connect them to a resultant capacity of 4μF? 20. Can you create an electric field in which all the lines of force are parallel but their density increases continuously in a direction perpendicular to the lines of force? Give reason. 21. Can you suggest an arrangement of three point charges separated by some finite distance that has zero electric potential energy? 22. Calculate the work done by the electric field of the nucleus in a complete circular orbit of an electron. Is there any change in this work if the orbit is elliptical? 23. The given graph shows the variation of charge ‘q’ verses potential difference for two capacitors C1 and C2 .The capacitors have same plate separation, but the plate THS, VK, Cl. XII Physics Topic: Summer HHW Session: 2013-14 Page 2 area of C2 is double that of C1.Identify the line in the graph corresponding to C1 & C2 and why? Unit-II: Current Electricity 1. In a hydrogen atom, an electron moves in an orbit of radius 4.8 x 10-11m with a speed of 2.5 x 10 6 m/s. Find the equivalent current. 2. Amount of charge passing through the cross section of a wire is q (t) =at2+bt+c.Write the dimensional formula for a, b and c. If the values of a, b and c in SI unit are 6, 4, 2 respectively. Find the value of current at t=6 seconds. 3. One metre long metallic wire is broken into two equal parts P and Q. The part ‘P’ is uniformly extended into another wire R. Length of R is twice the length of P and the resistance of R is equal to that of Q. Find the ratio of the resistances of P and R and also the ratio of lengths of P and Q. 4. The area of cross section, length and density of a piece of a metal of atomic weight 60 are 10-6 m2, 1.0 m and 5 x 103 kg/m3 respectively. Find the number of free electrons per unit volume of every atom that contributes one free electron. Also find the drift velocity of electron in the metal when a current of 16A passes through it. Avogadro no.=6x1023 per gram per mole. 5. An n-type Silicon sample of width 4x 10-3 m thickness 25x10-4m and length 6 X 10-2 m carries a current of 4.8mA.When the voltage is applied across the length of the sample what is the current density? If the free electron density is 1022 /m3 then find how much time does it take for the electrons to travel the full length of the sample? 6. The length and radii of 3 wires of same metal are in the ratios 2:3:4 and 3:4:5 respectively. They are joined in parallel and included in a circuit having 5A current. Find the current in each case. 7. A galvanometer together with an unknown resistance in series is connected across 2 identical cells each of emf 1.5V. When the cells are connected in series the galvanometer records a current of 1A and when the cells are connected in parallel the current is 0.6 A .What is the internal resistance of each cell? 8. An electric bulb rated for 500 Watt at 100 V is used in circuit having a 200 V supply. Calculate the resistance R that must be put in series with the bulb s that the bulb delivers 500 watt. THS, VK, Cl. XII Physics Topic: Summer HHW Session: 2013-14 Page 3 9. A heater is designed to operate with a power of 1000 watt in a 100 V line. It is connected in combination with a resistance of 10 and a resistance R, to a 100 V mains in series. What should be the value of ‘R’ so that the heater operates with a power of 62.5 watt? 10. An electric kettle has 2 heating coils. When one of the coils is switched on , the kettle begins to boil in’6’ min and when the other coil is switched on , the boiling begins in 8 min. In what time will the boiling begin if both the coils are switched on simultaneously: a) in series b)in parallel 11. One kilowatt electric heater is to be used with 220 V d.c supply. a)What is the current in the heater? b) What is its resistance? c) What is the power dissipated in the heater d) how much heat in calories is produced per second? e) How many grams of water at 1000C will be converted per minute into steam at 1000C with the heater? Radiation losses are negligible. Latent heat of steam = 540 cal /g. 12. A potentiometer wire of length 100 cm has a resistance of 100 ohm. It is connected in series with a resistance and a battery of emf 2V and of negligible internal resistance. A source of emf 10mV is balanced against a length of 40cm of the potentiometer. What is the value of the external resistance? 13. Two wires A and B of the same material and having same length have their cross sectional area in the ratio1:4. What would be the ratio of heat produced in these wires when same voltage is applied across each? 14. Two wires of the same material having lengths in the ratio 1:2 and diameters in the ratio 2:3 are connected in series with an accumulator. Compute the ratio of p.d across the two wires. 15. If the current supplied to a variable resistor is constant, draw a graph between voltage and resistance. 16. A uniform wire of resistance “R” is shaped into a regular “n” sided polygon, where “n” is even. Find the equivalent resistance between 1) opposite corners of the polygon 2) adjacent corners of the polygon. 17. under what condition is the heat produced in an electric circuit 1) directly proportional 2) inversely proportional to the resistance of the circuit? 18. A student has two wires of iron and copper of equal length and diameter. He first joins the two wires in series and passes electric current through the combination which increases gradually. After that he joins the two wires in parallel and repeats the process of passing current. Which wire will glow first in each case and why? Unit-III: MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT 1. An electron and a proton are moving along the same direction with the same kinetic energy. When they pass through a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the THS, VK, Cl. XII Physics Topic: Summer HHW Session: 2013-14 Page 4 direction of their motion, they describe paths of the same radius. Is this statement true or false? 2. Uniform electric and magnetic fields are produced pointing in the same direction. An electron is projected in the direction of the fields. What will be the effect on the kinetic energy of the electron due to the two fields? 3. A particle of mass m and charge q moves at right angles to a uniform magnetic field. Plot a graph showing the variation of the radius of the circular path described by it with the increase in its (a) charge,(b) kinetic energy, where ,in each case other factors remain constant .Justify your answer. 4. A charged particle having a charge q ,is moving with a speed v along the x-axis. It enters a region of space where an electric field E along y-axis and a magnetic field B are both present. The particle, on emerging from this region, is observed to be moving along the x-axis only. Obtain an expression for the magnitude of B in terms of v and E. Also give the direction of B. 5. A long wire is first bent into a circular coil of one turn and then into a circular coil of smaller radius having n turns. If the same current passes in both the cases find the ratio of the magnetic field produced at the centers in the two cases. 6. Why is diamagnetism independent of temperature? 7. Identify the following curve and name it. Explain the following terms on the basis of the curve. (a) Soft magnetic material (b) Hard magnetic Material c) Give one example each for the material d) one application each for the material 8. Two wires of equal lengths are bent in the form of two loops. One of the loops is square shaped whereas the other loop is circular. These are suspended in uniform magnetic field and the same current is passing through them. Which loop will experience greater torque? 9. Does the torque on a planar current loop in a magnetic field change, when its shape is changed without changing its area? 10. Why are pole pieces of galvanometer made concave? 11. What type of materials is used for making permanent magnets transformer cores? Give two line reasons for each 12. Show that the far field of a solenoid resembles that of a bar magnet. Hence define the magnetic moment of a solenoid. 13. A long cylinder of radius Ro is carrying a current Io, which is uniformly distributed over its cross section. Derive an expression for the magnitude of magnetic field inside as well as outside the wire. Plot a curve to show the variation of magnetic field with radial distance. 14. using a labeled diagram explain the construction and working of a moving coil galvanometer. Define its current and voltage sensitivity and explain how they can be increased. THS, VK, Cl. XII Physics Topic: Summer HHW Session: 2013-14 Page 5 (b) A galvanometer with a coil resistance of 5 ohm can tolerate a maximum current of 10mA. Explain how this can be converted into an ammeter of range 1A. Investigatory Projects- Physics (2013-14) As per C.B.S.E. guidelines, all students have to prepare one Investigatory Project carrying 3 marks. All students are therefore, advised to prepare one Investigatory Project on any one of the following topics or any other topic of their choice based on concept of physics after consulting the teacher during the summer vacation. POINTERS FOR MAKING PROJECT REPORT The material should be placed and bound in the following order: 1. Top Sheet of transparent plastic –The top page of your report should carry the following information in printed form or handwritten in neat block letters: Title of Project: Name of Student: Roll Number: Date of submission: 2. Aim of Project 3. Apparatus required 4. Principle/theory 5. construction with labeled diagram, 6. Working 7. Observations 8. calculations, 9. Result/ Conclusions 10. Applications, 11. Graphs if any, 12. References/bibliography 13. Back cover of plastic: may be opaque or transparent List of Investigatory Projects 1. To study and construct Van de Graff generator 2. To study and construct A.C.Generator/ Motor 3. To study and construct Transformer 4. To study and show Diffraction of light 5. To investigate the dependence of the angle of deviation on the angle of incidence, using a hollow prism filled, one by one, with different transparent fluids. THS, VK, Cl. XII Physics Topic: Summer HHW Session: 2013-14 Page 6 6. Use of semiconductor devices (transistor) as amplifier, oscillator, fire alarm, rain alarm, etc. 7. To study and construct one way or two way intercom 8. To study Faraday law of EMI (self & mutual induction) 9. To study and construct Power/magnetic brake 10. To study and construct Thermo couple 11. To study various factors on which the internal resistance/emf of a cell depends. 12. To study the variations, in current flowing, in a circuit containing a LDR, because of a variation. (a) in the power of the incandescent lamp, used to 'illuminate' the LDR. (Keeping all the lamps at a fixed distance). (b) in the distance of a incandescent lamp (of fixed power) used to 'illuminate' the LDR. 13. To find the refractive indices of (a) water (b) oil (transparent) using a plane mirror, a equiconvex lens, (made from a glass of known refractive index) and an adjustable object needle. 14. To design an appropriate logic gate combination for a given truth table. 15. To investigate the relation between the ratio of (i) output and input voltage and (ii) number of turns in the secondary coil and primary coil of a self designed transformer. 16. To estimate the charge induced on each one of the two identical styro foam (or pith) balls suspended in a vertical plane by making use of Coulomb's law. 17. To set up a common base transistor circuit and to study its input and output characteristic 18. and to calculate its current gain. To study the factor on which the self inductance of a coil depends by observing the effect of this coil, when put in series with a resistor/(bulb) in a circuit fed up by an a.c. source of adjustable frequency. 19. To construct a switch using a transistor and to draw the graph between the input and output voltage and mark the cut-off, saturation and active regions. 20. To study the earth's magnetic field using a tangent galvanometer. Note: Complete the practical file, activity file and the investigatory project and submit the same within one week after re opening of school i.e.by 7th of July.2013. Name of Teacher: R.K. Sharma THS, VK, Cl. XII Physics Topic: Summer HHW Session: 2013-14 Page 7