Group Problem 16 - University of St. Thomas
advertisement

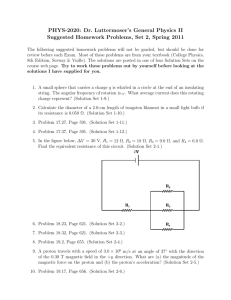
Group Problem #16 Physics 112-1 F12 Page 1 of 4 Group problem #16: Electromagnetic induction Two long straight wires carry parallel currents. The magnetic field B1 due to the current I1 is perpendicular to current I2. Calculate for the force on Current I2 due to B1. Calculate the force on current I1 due to magnetic field B2 generated by I2. What happens to the wires due to these magnetic fields? Group Problem #16 Physics 112-1 F12 Page 2 of 4 A solenoid that has length 30 cm, radius 1.2 cm and 300 turns carries a current of 2.6A. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field on the axis of the solenoid (a) at the center of the solenoid and (b) at one end of the solenoid. Group Problem #16 Physics 112-1 F12 Page 3 of 4 A uniform magnetic field makes an angle of 30.0° with the axis of a circular coil that has 300 turns and a radius equal to 4.00cm. The magnitude of the magnetic field increase s at the rate of 85.0 T/s while its direction remains fixed. Find the magnitude of the induced Emf in the coil. If the resistance is 200Ω, what is the induced current? If a current of 4.00A is induced in the above coil, what must the magnitude of the change of the magnetic field be to produce this current? Group Problem #16 Physics 112-1 F12 Page 4 of 4 A square look of side l = 5.0cm is in a uniform magnetic field B = 0.16T. What is the magnetic flux through the loop when: a) B is perpendicular to the face of the loop. b) When B is at an angle of 30° to the area of the loop What is the magnitude of the current in the loop if it has a resistance of 0.012Ω and is rotated from position (b) to position (a) in 0.14s?