Oceanography Exam II - Study Guide Geological Oceanography
advertisement

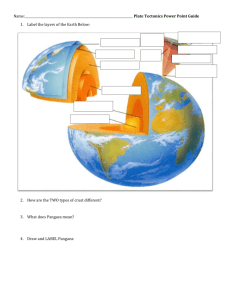
Oceanography Exam II - Study Guide Geological Oceanography Geography of the Ocean Know the zones of the ocean (review the triangle) by depth and characteristics Know the factors that differ between the zones and therefore define the zones Relate the zones with the geological features found within the earth’s ocean basins Origins of Earth (Ch. 3) Be able to define the following terms: nebular theory, protostar, big bang The Theory of Plate Tectonics (Ch. 13) Know how the layers of the earth are defined by their physical and chemical characteristics. Know the sources of heat within the core and mantle and how this heat causes plate movement Be able to define the following terms: lithosphere, asthenosphere, crust, mantle, core (inner/outer), Archimedes Principle, isostatic equilibrium, Panthalassa and Pangaea, subduction. convection cells. Know the difference between continental and oceanic crust and why it matters. Diagram the rock cycle and be able to describe and origin and formation of the three main types of rocks. Understand how continental drift and seafloor spreading relate to plate tectonics Know who Alfred Wegner was and what he did. Understand the evidences for Continental Drift as a theory and what was missing Know the connection between sea floor mapping technologies and the discovery of sea floor spreading Be able to label the geological features found within an ocean basin Be able to apply the theory of plate tectonics to describe the formation of ocean features Know how the distribution of earthquakes and volcanos relate to plate boundaries and formation of geological features. Know the three types of plate boundaries, examples of where they exist and features formed there. Marine Sediments (Ch. 14) Know the tools and techniques used to study sediments (5 methods) Know what data is collected from ocean sediments (“Ocean’s Memory” video) Understand how sediments are characterized by origin and size. Know the origins of the following sediment types: lithogeneous (aka terrigenious), biogenous, hydrogenous, cosmogeneous Know the order of the 7 classifications of sediments sizes in the wentworth scale. Be able to describe the economic value of ocean sediments and give examples Define these terms: stratigraphy, paleocenography, ooze, fecal pellets, nodules, diatomaceous earth, evaporates Differentiate between the origins of calcareous, siliceous oozes