Homework Revision Questions ch1 set 3
advertisement

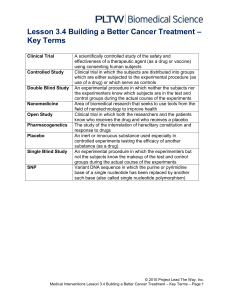
Homework Revision Questions Chapter One Set Three – Ways of minimising extraneous and confounding variables (pp 31- 50) Multiple Choice Short Answer 1/ Population is a term used in psychology to describe: a) groups with different characteristics; b) the people in the country the experiment is being done, c) the subgroup of the sample, d) the larger group from which the sample is drawn; 2/ Random sampling: a) is a procedure that ensures an equal chance of being selected, b) uses a haphazard method to pick subjects, c) is always done the same way, d) allows for some people to have a greater chance of selection 3/ When a participant doesn’t know whether they are in the experimental or control group, this is called: a) double blind; b) single blind; c) venetian blind; d) placebo blind; 4/ A repeated measures design: a) uses the same participants in the experimental and control group; b) eliminates confounding variables arising from subject differences; c) needs a smaller number of participants; d) all of the above; 8/ Will advertising for research participants and using a gift voucher or incentive payment result in ‘sample bias’? Explain your answer. TRUE OR FALSE 5/ A correlation coefficient is expressed as a decimal number. 7/ Convenience sampling is quick, easy and representative of the population being studied. 9/ What is the main difference between participant selection and participant allocation? 10/ explain how standardised instructions and procedures can be used to control or minimise the influence of demand characteristics and experimenter effects. Glossary words to review: Sampling Sample Random sampling Stratified sampling Experimental group Random allocation Single blind procedure Placebo Repeated measures design Matched participants design Population Convenience sampling Biased sample Stratified random sampling Control group Counterbalancing Double blind procedure Standardised instructions Standardised procedures Independent groups design