cea12645-sup-0001-Supinfo
advertisement

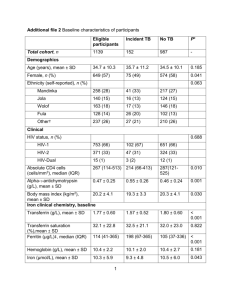
Associations of maternal and fetal 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with childhood lung function and asthma. The Generation R Study. Supplementary material Table E-1 Observed and imputed characteristics of mothers and their children Table E-2 Characteristics of subjects included and lost to follow-up Table E-3 Associations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with Rint and FeNO in children at age 6 years: unadjusted model Table E-4 Associations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with wheezing patterns and asthma of children until age 6 years: unadjusted model Table E-5 Associations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with Rint and FeNO, additionally adjusted for child’s 25-hydroxyvitamin D level Table E-6 Associations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with wheezing patterns and asthma, additionally adjusted for child’s 25-hydroxyvitamin D level Table E-7 Associations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with Rint and FeNO in children at age 6 years according to clinical cut-offs of 25-hydroxyvitamin D Table E-8 Associations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with wheezing patterns and asthma of children until age 6 years according to clinical cut-offs of 25hydroxyvitamin D Figure E-1 Flowchart of participants Table E-1. Observed and imputed characteristics of mothers and their children Maternal characteristics Age, years Missing Body mass index at enrolment Missing Educational level (%) Primary, or secondary Higher Missing History of asthma or atopy (%) No Yes Missing Psychological distress Missing Parity (%) 0 ≥1 Missing Smoking during pregnancy (%) No Yes Missing Pet keeping (%) No Yes Missing Folate level in 1st trimester, nmol/L Missing Mid-gestational blood sampling season (%) Spring Summer Autumn Winter Missing Child characteristics Female sex (%) Missing Gestational age at birth (weeks) Missing Birth weight (grams) Missing Ever breastfeeding (%) No Yes Missing Observed Imputed 31.6 (4.2) 0 24.2 (4.0) 0.5 (16) Not imputed 38.5 (1,159) 61.5 (1,924) 1.5 (47) 37.8 (1,184) 62.2 (1,946) 62.3 (1,762) 37.7 (1,066) 9.6 (302) 0.2 (0.2) 11.3 (353) 63.5 (1,987) 36.5 (1,143) 60.7 (1,901) 39.3 (1,229) 0 Not imputed 88.0 (2,183) 22.0 (688) 8.3 (259) 86.0 (2,380) 24.0 (750) 61.9 (1,612) 38.1 (1,192) 10.4 (326) 20.2 (8.7) 22.2 (694) 57.8 (1,809) 42.2 (1,321) 28.5 (817) 23.2 (665) 24.0 (688) 24.2 (693) 8.5 (267) 28.9 (906) 23.1 (724) 23.8 (744) 24.1 (755) 50.3 (1,573) 0 40.0 (26.7-43.4) 0 3,503 (547) 0.1 (4) Not imputed 8.5 (249) 91.5 (2,112) 24.6 (769) 9.1 (315) 89.9 (2,815) 24.2 0.2 20.2 Not imputed 3,503 Lower respiratory infections (%) No 95.9 (2,769) 95.9 (2,999) Yes 4.1 (119) 4.1 (131) Missing 7.7 (242) Inhalant allergies (%) No 91.2 (2,598) 91.2 (2,853) Yes 8.8 (250) 8.8 (277) Missing 9.0 (282) Eczema (%) No 84.0 (2,164) 83.6 (2,617) Yes 16.0 (413) 16.4 (513) Missing 17.7 (533) At birth blood sampling season (%) Spring 25.0 (715) Not imputed Summer 25.9 (741) Autumn 28.4 (811) Winter 20.7 (591) Missing 0 Values are means (SD), medians (total range) or percentages (absolute numbers) Table E-2. Characteristics of subjects included and lost to follow-up Maternal characteristics Age, years Body mass index at enrolment Educational level (%) Primary, or secondary Higher History of asthma or atopy, yes (%) No Yes Psychological distress Parity (%) 0 ≥1 Smoking during pregnancy (%) No Yes Pet keeping (%) No Yes Folate level in 1st trimester, nmol/L Mid-gestational blood sampling season (%) Spring Summer Autumn Winter Child characteristics Female sex (%) Gestational age at birth (weeks) Birth weight (grams) Ever breastfeeding (%) No Yes Lower respiratory infections (%) No Yes Inhalant allergies (%) No Yes Eczema (%) No Yes At birth blood sampling season (%) Spring Included N= 3,130 Lost to follow-up n = 297 p-value for difference 31.6 (4.2) 24.2 (4.0) 29.4 (5.4) 25.2 (4.8) 0.001 0.009 61.5 (1,924) 38.5 (1,159) 87.0 (254) 13.0 (38) 0.001 62.3 (1,762) 37.7 (1,066) 0.2 (0.2) 66.3 (185) 33.7 (94) 0.2 (0.3) 0.195 60.7 (1,901) 39.3 (1,229) 52.5 (156) 42.8 (127) 88.0 (2,183) 22.0 (688) 55.1 (156) 44.9 (127) 0.001 61.9 (1,612) 38.1 (1,192) 20.2 (8.7) 35.4 (105) 57.2 (170) 17.1 (8.9) 0.001 28.5 (817) 23.2 (665) 24.0 (688) 24.2 (693) 27.9 (83) 24.2 (72) 16.5 (49) 18.2 (54) 0.076 50.3 (1,573)) 40.0 (26.7, 43.4) 3,503 (547) 43.4 (129) 39.6 (26.7-42.8) 3,383 (585) 0.025 0.002 0.001 8.5 (249) 91.5 (2,112) 24.3 (37) 75.7 (115) 0.001 95.9 (2,769) 4.1 (119) 94.3 (66) 5.7 (4) 0.535 91.2 (2,598) 8.8 (250) 91.7 (66) 8.3 (6) 0.554 84.0 (2,164) 16.0 (413) 83.3 (5) 16.7 (1) 1.000 25.0 (715) 24.3 (157) 0.441 0.028 0.006 0.001 Summer 25.9 (741) 27.7 (179) Autumn 28.4 (811) 22.9 (148) Winter 20.7 (591) 25.2 (163) Values are means (± SD), medians (total ranges) or percentages (absolute numbers) based on original data. P-value for difference was calculated using Student’s t-test for continuous normally distributed variables, Mann-Whitney U test for continuous not normally distributed variables, and chi-square test for categorical variables. Table E-3. Associations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with Rint and FeNO in children at age 6 years: unadjusted model (n= 3,130) Rint FeNO Z-score Symmpercent (95% CI) (95% CI) n = 1,929 n = 1,857 0.18 (-0.13, 0.49) -3.7 (-9.9, 2.5) 597/1,752 612/1,706 2nd tertile, n = 1,081 -0.13 (-0.44, 0.18) 0.3 (-6.1, 6.7) 52.5 – 80.7 nmol/L 584/1,752 549/1,706 3rd tertile, n = 1,079 Reference Reference 80.9 – 193.2 nmol/L 571/1,752 551/1,706 0.89 0.40 1st tertile, n = 813 -0.33 (-0.66, 0.01) -0.2 (-7.4, 7.0) 0.1 – 30.5 nmol/L 449/1,326 439/1,238 2nd tertile, n = 793 0.16 (-0.18, 0.50) 1.7 (-5.7, 9.1) 30.6 – 49.0 nmol/L 415/1,326 389/1,238 3rd tertile, n = 801 Reference Reference 49.2- 144.9 nmol/L 462/1,326 410/1,238 0.05 0.56 25-hydroxy vitamin D in mid-gestation 1st tertile, n = 1,083 2.3 – 52.4 nmol/L p-value for trend 25-hydroxy vitamin D at birth p-value for trend Values are changes in Z-score or sympercent (95% confidence interval) from linear regression models. “n =” represents number of cases per total group. Table E-4. Associations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with wheezing patterns and asthma of children until age 6 years: unadjusted model (n=3,130) Early Wheezing Late Wheezing Persistent Wheezing Asthma Odds Ratio Odds Ratio Odds Ratio Odds Ratio (95% CI) (95% CI) (95% CI) (95% CI) n = 604 n = 77 n = 255 n = 158 1.33 (1.03, 1.31)* 1.13 (0.63, 2.02) 0.98 (0.69, 1.38) 1.03 (0.69, 1.53) 192/657 24/657 72/657 51/782 2nd tertile, n = 1,081 1.45 (1.13, 1.86)* 1.09 (0.61, 1.97) 1.13 (0.81, 1.58) 0.88 (0.58, 1.32) 52.5 – 80.7 nmol/L 207/676 23/676 82/676 45/800 3rd tertile, n = 1,079 Reference Reference Reference Reference 80.9 – 193.2 nmol/L 163/686 24/686 83/686 51/801 0.01 0.43 0.91 0.90 1st tertile, n = 813 1.05 (0.78, 1.40) 1.08 (0.58, 2.02) 0.96 (0.65, 1.42) 0.91 (0.57, 1.44) 0.1 – 30.5 nmol/L 130/492 21/492 59/492 37/591 2nd tertile, n = 793 1.11 (0.84, 1.48) 0.59 (0.29, 1.22) 0.88 (0.59, 1.30) 0.87 (0.55, 1.39) 30.6 – 49.0 nmol/L 144/506 12/506 56/506 36/597 Reference Reference Reference Reference 134/525 21/525 66/525 41/599 25-hydroxy vitamin D in mid-gestation 1st tertile, n = 1,083 2.3 – 52.4 nmol/L p-value for trend 25-hydroxy vitamin D at birth 3rd tertile, n = 801 49.2- 144.9 nmol/L p-value for trend 0.70 0.44 0.84 0.88 *P<0.05; Values are odds ratios (95% confidence interval) from polynomial regression and logistic regression models. “n =” represents number of cases per total group. Table E-5. Associations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with Rint and FeNO in children at age 6 years additionally adjusted for child’s 25-hydroxyvitamin D level (n = 1,783) Rint FeNO Z-score Symmpercent (95% CI) (95% CI) n = 1,248 n = 1,227 1st tertile, n = 576 0.47 (-0.04, 0.97) -0.9 (-10.7, 8.8) 2.3 – 52.4 nmol/L 401/1,142 413/1,129 2nd tertile, n = 549 -0.05 (-0.54, 0.43) -2.6 (-12.0, 6.8) 52.5 – 80.7 nmol/L 375/1,142 361/1,129 3rd tertile, n = 520 Reference Reference 80.9 – 193.2 nmol/L 366/1,142 355/1,129 0.20 0.55 1st tertile, n = 416 -0.55 (-1.08, 0.01) -3.7 (-14.0, 6.6) 0.1 – 30.5 nmol/L 282/849 281/824 2nd tertile, n = 395 0.21 (-0.28, 0.70) 7.0 (-2.4, 16.4) 30.6 – 49.0 nmol/L 277/849 263/824 Reference Reference 290/849 280/824 0.32 0.93 25-hydroxy vitamin D in mid-gestation p-value for trend 25-hydroxy vitamin D at birth 3rd tertile, n = 402 49.2- 144.9 nmol/L p-value for trend Values are changes in Z-score or sympercent (95% confidence interval) from linear regression models. “n =” represents number of cases per total group. Models were adjusted for maternal age, body mass index at enrolment, educational level, history of asthma/allergy, maternal distress, parity, smoking during pregnancy, pet keeping, folate level, mid-gestational season of blood sampling, child’s sex, gestational age at birth, birth weight, breastfeeding, child’s lower respiratory tract infections, inhalant allergies, eczema, at birth season of blood sampling, mutually for mid-gestational and cord blood 25-hydroxyvitamin D and child’s current 25-hydroxy vitamin D. Table E-6. Associations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with wheezing patterns and asthma of children until age 6 years additionally adjusted for child’s 25-hydroxyvitamin D level (n = 1,783) Early Wheezing Late Wheezing Persistent Wheezing Asthma Odds Ratio Odds Ratio Odds Ratio Odds Ratio (95% CI) (95% CI) (95% CI) (95% CI) n = 346 n = 49 n = 135 n = 86 1st tertile, n = 576 1.15 (0.70, 1.90) 0.78 (0.24, 2.49) 0.78 (0.35, 1.73) 1.11 (0.45, 2.76) 2.3 – 52.4 nmol/L 117/403 19/403 38/403 24/468 2 tertile, n = 549 1.28 (0.81, 2.00) 0.91 (0.31, 2.66) 1.55 (0.79, 3.06) 1.64 (0.73, 3.70) 52.5 – 80.7 nmol/L 125/396 13/396 50/396 30/478 Reference Reference Reference Reference 88/367 15/367 40/367 26/438 0.51 0.82 0.57 0.65 1st tertile, n = 416 0.80 (0.46, 1.40) 1.61 (0.47, 5.53) 1.33 (0.57, 3.11) 1.45 (0.60, 3.50) 0.1 – 30.5 nmol/L 68/278 13/278 33/278 22/339 2 tertile, n = 395 1.01 (0.64, 1.59) 1.18 (0.39, 3.56) 1.05 (0.51, 2.18) 1.18 (0.52, 2.69) 30.6 – 49.0 nmol/L 80/279 9/279 25/279 17/337 Reference Reference Reference Reference 80/298 15/298 32/298 20/338 0.58 0.14 0.77 0.35 25-hydroxy vitamin D in mid-gestation nd 3rd tertile, n = 520 80.9 – 193.2 nmol/L p-value for trend 25-hydroxy vitamin D at birth nd 3rd tertile, n = 402 49.2- 144.9 nmol/L p-value for trend Values are odds ratios (95% confidence interval) from multivariate polynomial regression and logistic regression models. “n =” represents number of cases per total group. Models were adjusted for maternal age, body mass index at enrolment, educational level, history of asthma/allergy, maternal distress, parity, smoking during pregnancy, pet keeping, folate level, mid-gestational season of blood sampling, child’s sex, gestational age at birth, birth weight, breastfeeding, child’s lower respiratory tract infections, inhalant allergies, eczema, at birth season of blood sampling, mutually for mid-gestational and cord blood 25-hydroxyvitamin D and child’s current 25-hydroxy vitamin D. Table E-7. Associations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with Rint and FeNO in children at age 6 years according to clinical cut-offs of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (n = 3,130) Rint FeNO Z-score Symmpercent (95% CI) (95% CI) n = 1,929 n = 1,857 0.20 (-0.15, 0.54) -2.2 (-9.1, 4.6) 528/1,754 541/1,707 -0.15 (-0.49, 0.18) -2.0 (-8.8, 4.7) 50-74.9 nmol/L 547/1,754 509/1,707 Optimal n = 1,138 Reference Reference ≥75.0 nmol/L 679/1,754 657/1,707 0.75 0.27 -0.27 (-0.63, 0.08) -0.4 (-8.1, 7.3) 893/1,332 846/1,241 0.17 (-0.21, 0.55) 3.9 (-4.3, 12.1) 50-74.9 nmol/L 354/1,332 319/1,241 Optimal n = 150 Reference Reference 94/1,332 76/1,241 0.03 0.77 25-hydroxy vitamin D in mid-gestation Deficient, n = 856 <50.0 nmol/L Sufficient n = 867 p-value for trend 25-hydroxy vitamin D at birth Deficient, n = 1,459 <50.0 nmol/L Sufficient n = 532 ≥75.0 nmol/L p-value for trend Values are changes in Z-score or sympercent (95% confidence interval) from linear regression models. “n =” represents number of cases per total group. Models were adjusted for maternal age, body mass index at enrolment, educational level, history of asthma/allergy, maternal distress, parity, smoking during pregnancy, pet keeping, folate level, midgestational season of blood sampling, child’s sex, gestational age at birth, birth weight, breastfeeding, child’s lower respiratory tract infections, inhalant allergies, eczema, at birth season of blood sampling, mutually for mid-gestational and cord blood 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Table E-8. Associations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with wheezing patterns and asthma of children until age 6 years according to clinical cut-offs of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (n = 3,130) Early Wheezing Late Wheezing Persistent Wheezing Asthma Odds Ratio Odds Ratio Odds Ratio Odds Ratio (95% CI) (95% CI) (95% CI) (95% CI) n = 604 n = 77 n = 255 n = 158 1.21 (0.92, 1.61) 1.20 (0.60, 2.41) 1.23 (0.81, 1.87) 1.20 (0.75, 1.94) 171/591 22/591 69/591 47/698 1.20 (0.92, 1.56) 1.07 (0.55, 2.07) 1.16 (0.78, 1.71) 1.09 (0.69, 1.72) 181/614 21/614 69/614 43/733 Reference Reference Reference Reference 211/817 28/817 99/817 57/954 0.01 0.50 0.54 0.86 1.02 (0.62, 1.67) n/a 0.75 (0.36, 1.54) 0.70 (0.32, 1.52) 286/1,029 35/1,029 119/1,029 75/1,219 0.89 (0.53, 1.49) n/a 0.79 (0.38, 1.66) 0.74 (0.32, 1.72) 50-75.0 nmol/L 94/386 18/386 48/386 29/440 Optimal n = 150 Reference Reference Reference Reference 30/112 1/112 15/112 10/131 0.61 0.05 0.47 0.21 25-hydroxy vitamin D in mid-gestation Deficient, n = 856 <50.0 nmol/L Sufficient n = 867 50-75.0 nmol/L Optimal n = 1,138 >75.0 nmol/L p-value for trend 25-hydroxy vitamin D at birth Deficient, n = 1,459 <50.0 nmol/L Sufficient n = 532 >75.0 nmol/L p-value for trend n/a – not applicable; Values are odds ratios (95% confidence interval) from multivariate polynomial regression and logistic regression models. “n =” represents number of cases per total group. Models were adjusted for maternal age, body mass index at enrolment, 12 educational level, history of asthma/allergy, maternal distress, parity, smoking during pregnancy, pet keeping, folate level, midgestational season of blood sampling, child’s sex, gestational age at birth, birth weight, breastfeeding, child’s lower respiratory tract infections, inhalant allergies, eczema, at birth season of blood sampling, mutually for mid-gestational and cord blood 25hydroxyvitamin D. 13 Figure E-1. Flowchart of participants n = 4,236 Cohort with consent for follow-up of Dutch subjects until age 6 years n = 809 Data on twins (n = 135) and missing data on 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels in mid-gestation and at birth (n = 674) excluded n = 3,427 Data on any 25-hydroxyvitamin D level in mid-gestation or at birth available n = 297 Missing data on all Rint, FeNO, wheezing patterns and asthma excluded n =3,130 Data on Rint, FeNO, wheezing pattern or asthma available Rint FeNO Wheezing patterns Asthma n = 1,929 n = 1,857 n = 2,181 n = 2,591 14 15

![Michaelis Menten Plot Lineweaver-Burke Eadie Hofstee [S] (mM](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006783200_1-6f852f20ab04d5dae16be5528b1f30cf-300x300.png)