Nuclear Reactions Notes Key with HW key
advertisement
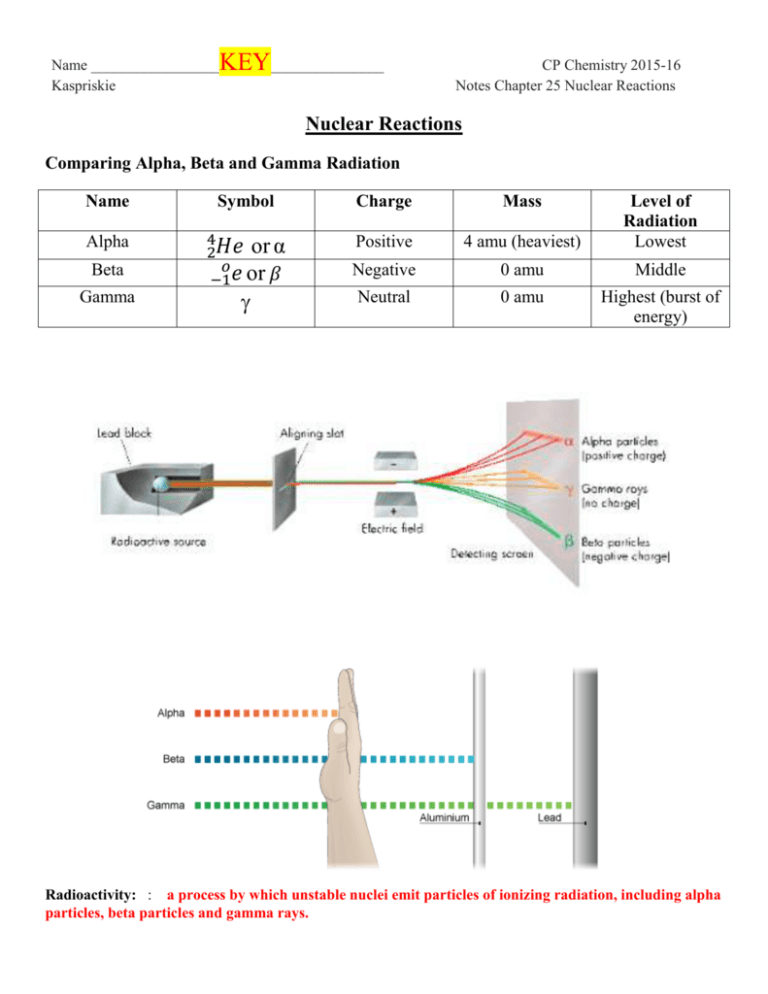
Name _________________ Kaspriskie KEY_______________ CP Chemistry 2015-16 Notes Chapter 25 Nuclear Reactions Nuclear Reactions Comparing Alpha, Beta and Gamma Radiation Name Symbol Charge Mass Alpha 4 2𝐻𝑒 or α 𝑜 −1𝑒 or 𝛽 Positive 4 amu (heaviest) Level of Radiation Lowest Negative 0 amu Middle Neutral 0 amu Highest (burst of energy) Beta Gamma Radioactivity: : a process by which unstable nuclei emit particles of ionizing radiation, including alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays. Fission Reaction: a reaction in which the nucleus splits, or emits particles of radiation Types of Natural Radioactivity: 1. alpha particle: α 4 or 2𝐻𝑒 2 protons, 2 neutrons - positively charged, heaviest DECAY = particle is emitted (is a product of the reaction) EXAMPLES: 238 92𝑈 234 90𝑇ℎ 2. 𝟐𝟑𝟖 𝟒 𝟗𝟐𝑼 𝟐𝑯𝒆 (alpha decay) + 𝟐𝟑𝟒 𝟗𝟎𝑻𝒉 𝟒 𝟐𝟑𝟎 (alpha decay with gamma radiation) 234 90𝑇ℎ 𝟐𝑯𝒆 + 𝟖𝟖𝑹𝒂 𝑜 Beta Particle: −1𝑒 or + 𝑜 −1𝛽 DECAY = particle is emitted (is a product of the reaction) CAPTURE = particle is aborbed (is a reactant of the reaction) EXAMPLES: 14 6𝐶 24 10𝑁𝑒 204 84𝑃𝑜 (beta decay with gamma radiation ) (beta decay with gamma radiation) (beta capture with x rays ) 𝟏𝟒 𝟔𝑪 𝟐𝟒 𝟏𝟎𝑵𝒆 𝟐𝟎𝟒 𝟖𝟒𝑷𝒐 𝟎 𝟏𝟒 𝟕𝑵 + −𝟏𝒆 + 𝟎 𝟐𝟒 𝟏𝟏𝑵𝒂 + −𝟏𝒆 + 𝒐 + −𝟏𝒆 𝟐𝟎𝟒 𝟖𝟑𝑩𝒊 + x-rays 3. What is gamma radiation? Why is it so harmful? Gamma radiation is a form of energy given off during a nuclear reaction. It is harmful because it is capable of penetrating the skin. PRACTICE: Write equations for the following nuclear reactions: 1. alpha decay with gamma radiation 𝟒𝟐𝑯𝒆 + 60 27𝐶𝑜 2. beta decay 131 53𝐼 3. 𝟏𝟑𝟏 𝟓𝟒𝑿𝒆 𝟒𝟐𝑯𝒆 + 𝟎 −𝟏𝒆 𝟏𝟎𝟓 𝟒𝟒𝑹𝒖 beta decay with gamma radiation 𝟐𝟔𝟗 269 110𝐷𝑠 𝟏𝟏𝟏𝑹𝒈 5. + alpha decay 109 46𝑃𝑑 4. + 𝟓𝟔 𝟐𝟓𝑴𝒏 + 𝟎 −𝟏𝒆 + beta capture with x rays + −𝟏𝒐𝒆 188 76𝑂𝑠 6. 19𝐾 −1𝑒 42 0 𝟒𝟐 𝟐𝟎𝑪𝒂 + 7. 239 4 94𝑃𝑢 2𝐻𝑒 8. 𝟒 235 92𝑈 𝟐𝑯𝒆 + 𝟐𝟑𝟓 𝟗𝟐𝑼 + 231 90𝑇ℎ 𝟏𝟖𝟖 𝟕𝟓𝑹𝒆 + x-rays 9. 𝟒𝟎 40 𝟏𝟗𝑲 20𝐶𝑎 14 10. 7𝑁 11. 0 −1𝛽 + 10𝑛 𝟏𝟒𝟔𝑪 + 11𝐻 𝟐𝟑𝟖 𝟗𝟐𝑼 0 + 10𝑛 239 93𝑁𝑝 + −1𝛽 113 + 10𝑛 𝟏𝟏𝟒 𝟒𝟖𝑪𝒅 + 12. 48𝐶𝑑 2 13. 1𝐻 + 𝟑𝟏𝑯 42𝐻𝑒 + 10𝑛 239 14. 92𝑈 1 15. 1𝐻 16. + + 31𝐻 𝟒𝟐𝑯𝒆 9 4𝐵𝑒 6 1 + 42𝐻𝑒 𝟐𝟒𝟐 𝟗𝟒𝑷𝒖 + 0𝑛 17. 3𝐿𝑖 + 11𝐻 𝟔𝟑𝑳𝒊 + 42𝛼 + 10𝑛 42𝐻𝑒 + 𝟑𝟏𝑯 18. 56 26𝐹𝑒 19. 209 83𝐵𝑖 + 21𝐻 𝟒𝟐𝑯𝒆 + 54 25𝑀𝑛 + 54 1 24𝐶𝑟 0𝑛 + 𝟐𝟔𝟐 𝟏𝟎𝟕𝑩𝒉