Beg of Early Humans Study Guide
advertisement

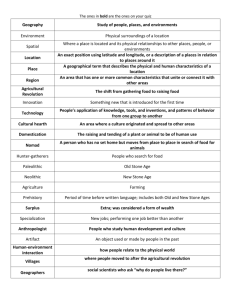
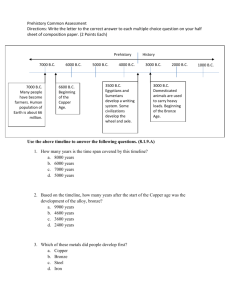
Chapter 1 and 3: The Beginning of Human Society Study Guide Vocabulary Artisan: A worker who is especially skilled in making items such as baskets and leather goods. Domesticate: To tame animals and raise them to be used by humans. History: The recorded events of people. Nomad: A person who has no single, settled home. Civilizations: A society with cities having government, jobs, and social classes. Irrigation: A system to water crops during the dry summer months. Oral Tradition: People who pass stories by word of mouth from generation to generation Archaeologist: a scientist who studies old objects, such as artifacts, bones, and fossils. Prehistory: The period of time before people began writing, known as the Old Stone Age and New Stone Age. Social Class: A group of people with similar backgrounds, wealth, and ways of living. Rich and powerful on top and poor and powerless on the bottom. Fertile: land where it would be easy to grow crops Surplus: More than is needed. Geography and History – Ch. 1 Old Stone Age is where almost all of human prehistory took place. Civilizations began on the banks of rivers – regular flooding resulted in rich soil for farming. Prehistory is before written records. “pre” means before. When scientist studies the Iceman’s life they learned about his clothing, tools, and body. Prehistory – Ch. 3 Lesson 1 and 2 - - Old Stone Age and New Stone Age People developed the ability to use fire during the prehistory period. The beginning of farming was the major difference between the Old Stone Age and the New Stone Age. During the Old Stone Age: o People got their food by hunting animals and gathering roots and berries. o Were Nomads o Used tools to hunt, to skin hides and cut meat o Hunted in groups o Used fire to keep warm, cook food, and moved to colder climates During the New Stone Age: o Grew their own food – farming began o Used better seeds for planting o Lived in warm climate – by the water o No longer nomads – settled in once place o Tamed animals The Beginnings of Civilization Lesson 3 – pages 68 to 69 Order of development: Farming ------- City ----- Civilizations Farming changed the way people lived by not having to move from place to place. Farming settlements developed into cities Having the surplus of food during the New Stone Age resulted in rapid population growth Having a dependable water source lead to cities and civilizations Trading – helped to spread new ideas and tools from one civilization to another. Farming villages: o More crops, and a surplus of food o Irrigation system o Families grew o Artisans – baskets, leather good, tools and pottery Cities: o Government developed – effective rulers o Temples and religious buildings were built o Variety of occupations – more artisans o Rich soil --- larger surplus of food Civilizations: o Even bigger crops o Trading – took goods by ship o Art, writing architecture o Artisans – jewelry, crafts, bronze o Social classes developed o Had cities – with official leaders o All Civilizations had the following: Geography – settled by rivers where there was fertile soil Religion – Belief system to explain nature and afterlife Achievements – time to make advancements and invent Politics – leader in charge with an army to maintain power Economics – a system to get what they needed (use nature, trade, money, jobs) Social Structure – putting the people into categories based on riches and power with the rich and powerful on top and the poor and powerless on the bottom.