Algebra I 4th Quarter - South Henry School Corporation
advertisement
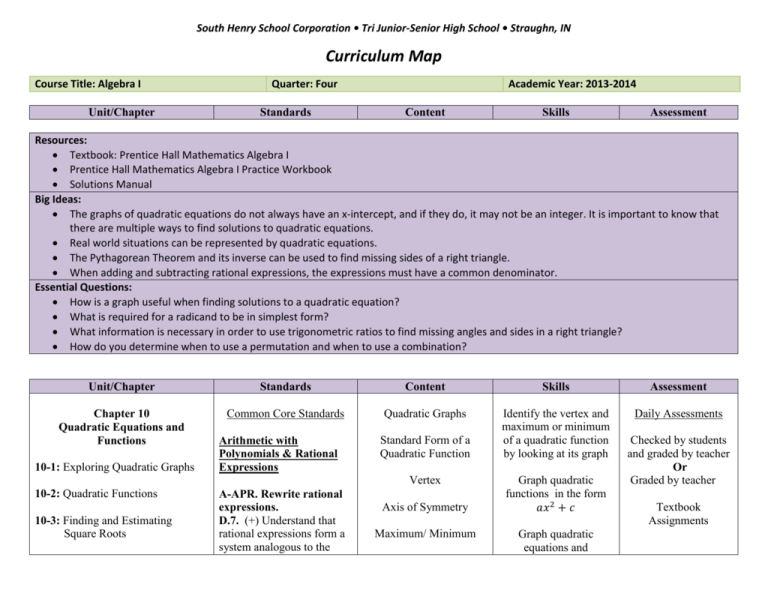
South Henry School Corporation • Tri Junior-Senior High School • Straughn, IN Curriculum Map Course Title: Algebra I Unit/Chapter Quarter: Four Standards Academic Year: 2013-2014 Content Skills Assessment Resources: Textbook: Prentice Hall Mathematics Algebra I Prentice Hall Mathematics Algebra I Practice Workbook Solutions Manual Big Ideas: The graphs of quadratic equations do not always have an x-intercept, and if they do, it may not be an integer. It is important to know that there are multiple ways to find solutions to quadratic equations. Real world situations can be represented by quadratic equations. The Pythagorean Theorem and its inverse can be used to find missing sides of a right triangle. When adding and subtracting rational expressions, the expressions must have a common denominator. Essential Questions: How is a graph useful when finding solutions to a quadratic equation? What is required for a radicand to be in simplest form? What information is necessary in order to use trigonometric ratios to find missing angles and sides in a right triangle? How do you determine when to use a permutation and when to use a combination? Unit/Chapter Standards Content Skills Assessment Chapter 10 Quadratic Equations and Functions Common Core Standards Quadratic Graphs Identify the vertex and maximum or minimum of a quadratic function by looking at its graph Daily Assessments 10-1: Exploring Quadratic Graphs Arithmetic with Polynomials & Rational Expressions Standard Form of a Quadratic Function Vertex 10-2: Quadratic Functions 10-3: Finding and Estimating Square Roots A-APR. Rewrite rational expressions. D.7. (+) Understand that rational expressions form a system analogous to the Axis of Symmetry Maximum/ Minimum Graph quadratic functions in the form 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑐 Graph quadratic equations and Checked by students and graded by teacher Or Graded by teacher Textbook Assignments South Henry School Corporation • Tri Junior-Senior High School • Straughn, IN Curriculum Map Course Title: Algebra I Unit/Chapter 10-4: Solving Quadratic Equations 10-5: Factoring to Solve Quadratic Equations 10-6: Completing the Square Quarter: Four Academic Year: 2013-2014 Standards Content Skills Assessment rational numbers, closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division by a nonzero rational expression; add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions. Quadratic Functions/Inequalities inequalities in the form 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 Worksheet Assignments Square Roots Simplify square root expressions and tell whether it is rational or irrational Observations In- Class Oral Responses Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities Quadratic Formula Discriminant Estimate Square roots Weekly/Bi-Weekly Modeling Solve quadratic equations by graphing to x-intercepts and by finding square roots. Notes Check A-REI. Understand solving equations as a process of reasoning and explain the reasoning A.2. Solve simple rational and radical equations in one variable, and give examples showing how extraneous solutions may arise. Solving Quadratic Equations 10-7: Using the Quadratic Formula 10-8: Using the Discriminant 10-9: Choosing a Linear, Quadratic, or Exponential Model A-REI. Solve equations and inequalities in one variable. B.4. Solve quadratic equations in one variable. B.4.a. Use the method of completing the square to transform any quadratic equation in x into an equation of the form (x – Quizzes Tests Solve quadratic equations by factoring and completing the square. Use the quadratic formula to solve quadratic equations Use the discriminant to determine the number of solutions of a specific equation Determine which type of graph is appropriate to South Henry School Corporation • Tri Junior-Senior High School • Straughn, IN Curriculum Map Course Title: Algebra I Unit/Chapter Chapter 11 Radical Expressions and Equations 11-1: Simplifying Radicals 11-2: The Pythagorean Theorem 11-3: The Distance and Midpoint Formulas 11-4: Operations with Radical Expressions 11-5: Solving Radical Equations 11-6: Graphing Square Root Functions 11-7: Trigonometric Ratios Quarter: Four Standards p)2 = q that has the same solutions. Derive the quadratic formula from this form. B.4.b. Solve quadratic equations by inspection (e.g., for x2 = 49), taking square roots, completing the square, the quadratic formula and factoring, as appropriate to the initial form of the equation. Recognize when the quadratic formula gives complex solutions and write them as a ± bi for real numbers a and b. F-IF Analyze functions using different representations C.7. Graph functions expressed symbolically and show key features of the graph, by hand in simple cases and using technology for more complicated cases. C.7.b. Graph square root, cube root, and piecewisedefined functions, including step functions and absolute Academic Year: 2013-2014 Content Skills represent a given situation or set of data (Linear, Quadratic, Exponential) Simplify Radical Expressions Simplest Radical Form Pythagorean Theorem and its converse Distance and Midpoint Formulas Operations with Radical Expressions Graph square root functions Trigonometric Ratios Application of Trigonometric Ratios to Find Angles of Elevation and Angles of Depression Apply multiplication and division properties of square roots in order to simplify the expression to its simplest radical form Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of a missing side of a triangle Determine whether three sides of a triangle construct a right triangle Use formulas to find the distance and midpoint between two given points Simplify radical expressions Solve radical Assessment South Henry School Corporation • Tri Junior-Senior High School • Straughn, IN Curriculum Map Course Title: Algebra I Quarter: Four Unit/Chapter Standards Chapter 12 Rational Expressions and Functions value functions. C.7.d. (+) Graph rational functions, identifying zeros and asymptotes when suitable factorizations are available, and showing end behavior. C.8. Write a function defined by an expression in different but equivalent forms to reveal and explain different properties of the function. C.8.a. Use the process of factoring and completing the square in a quadratic function to show zeros, extreme values, and symmetry of the graph, and interpret these in terms of a context. C.9. Compare properties of two functions each represented in a different way (algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables, or by verbal descriptions). For example, given a graph of one quadratic function and an algebraic expression for 12-1: Inverse Variation 12-2: Graphing Rational Functions 12-3: Simplifying Rational Expressions 12-4: Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 12-5: Dividing Polynomials 12-6: Adding and Subtracting Academic Year: 2013-2014 Content Skills expressions by isolating the radical Graphing square root functions with vertical and horizontal translations Use sine, cosine, and tangent ratios to find angles and missing side lengths in right triangles Inverse Variation Constant of Variation Graph Rational Functions Simplify Rational Expressions Operations with Rational Expressions Divide Polynomials Write an equation for an inverse variation when given a point Determine whether data represents direct or indirect variation Graph rational functions and find the vertical and horizontal asymptotes Simplify rational expressions Solve Rational Equations Counting Methods Add, subtract, multiply and divide rational Assessment South Henry School Corporation • Tri Junior-Senior High School • Straughn, IN Curriculum Map Course Title: Algebra I Unit/Chapter Rational Expressions Quarter: Four Standards another, say which has the larger maximum. Academic Year: 2013-2014 Content expressions Permutations 12-7: Solving Rational Equations 12-8: Counting Methods and Permutations 12-9: Combinations ECA Review and Exam Standards for Mathematical Practice MP1: Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. MP2: Reason abstractly and quantitatively. MP3: Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. MP4: Model with mathematics. MP5: Use appropriate tools strategically. MP6: Attend to precision. MP7: Look for and make use of structure. MP8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Skills Combinations Probability with Permutations and Combinations Divide polynomials by a monomial or binomial Solve rational equations by factoring Use permutation notation and combination notation to simplify expressions Use permutations and combinations to find probabilities Assessment South Henry School Corporation • Tri Junior-Senior High School • Straughn, IN Curriculum Map Course Title: Algebra I Unit/Chapter Quarter: Four Standards Academic Year: 2013-2014 Content Skills Assessment