Key Terms
advertisement

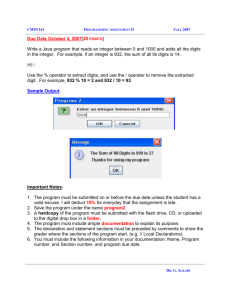
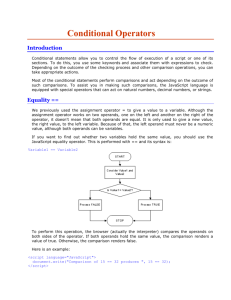
A First Book of C++ 4th Edition 2-1 Key Terms Assignment statement: Tells the computer to assign (store) a value in a variable. Associativity: The order in which operators of the same precedence are evaluated. Atomic data type: Data type that only supports atomic data values. Atomic data value: A value that is considered a complete entity by itself and cannot be decomposed into a smaller data type. Binary operator: An operator that requires two operands to produce a result. bool data type: Used to represent Boolean (logical) data, so it’s restricted to one of two values: true or false. Built-in data type: Provided as an integral part of the programming language. char data type: Used to store single characters, including the letters of the alphabet (uppercase and lowercase), the digits 0 through 9, and special symbols, such as + $ . , and !. Constant: See literal value. Data type: Set of values and a set of operations that can be applied to these values. Declaration statement: Used to name a variable and specify the data type that can be stored in it. Definition statements: Declaration statements used to force the compiler to reserve enough physical memory storage for each variable. Escape character: When placed directly in front of a select group of characters, it tells the compiler to escape from the way these characters would normally be interpreted. Exponential notation: Similar to scientific notation and is commonly used to express both very large and very small values in compact form. Floating-point expression: An expression containing only floating-point values (singleprecision and double-precision) as operands. Floating-point number: The number zero or any positive or negative number that contains a decimal point. int Data Type: The values supported by the int data type are whole numbers, which are mathematically known as integers. Initialization: Using a declaration statement to store a value in a variable. Integer expression: An expression containing only integer values as operands. Integer value: Consists of digits only and can optionally be preceded by a plus (+) or minus (-) sign. Literal: See literal value. Literal value: A self-identified value. Manipulator: An item used to manipulate how the output stream of characters is displayed. Mixed-mode expression: An expression containing integer and floating-point values. Modulus operator: Also referred to as the “remainder operator”, which has the symbol %. This operator captures the remainder when an integer is divided by an integer. Operand: Can be a literal value or an identifier with an associated value. Overloaded operator: A symbol that represents more than one operation and whose execution depends on the type of operands encountered. Precision: In computer programming, “precision” can refer to a number’s accuracy or the number of significant digits A First Book of C++ 4th Edition 2-2 Primitive types: See built-in data type. Signed data type: A data type that permits storing negative values in addition to zero and positive values. Significant digits: Defined as the number of clearly correct digits plus 1. Simple binary arithmetic expression: Consists of a binary operator connecting two literal values in this form: literalValue operator literalValue. Unary operators: Operate on a single operand. Unsigned data type: Provides for only non-negative values (that is, 0 and positive values). Variable: A name the programmer uses to refer to computer storage locations.