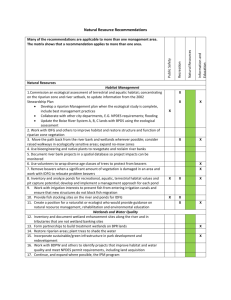
Flow Regime Components
advertisement

Time Allowance: 1.2.4. Flow Regime Components Definitions Hydrology-Based Environmental Flow Regime (HEFR) Analyses for Sabine-Neches Bay and Basin Expert Science Team (BBEST) • Subsistence flow – minimum streamflow needed during extreme drought conditions • Base flow – “normal” flow conditions found between storm events • High flow pulses – short-duration, high flows within the stream channel resulting from a storm event • Overbank flows –high-flow events that cause flow beyond the riverbanks TIFP Technical Overview Overbank the component of an instream flow regime that represents infrequent, high flow events that exceed the normal channel. These flows maintain riparian areas and provide lateral connectivity between the river channel and active floodplain. They may also provide life- cycle cues for various species. High Flow Pulse the component of an instream flow regime that represents short- duration, in-channel, high flow events following storm events. These flows maintain riparian areas and provide lateral connectivity between the river channel and active floodplain. They may also provide life- cycle cues for various species. Base the component of an instream flow regime that represents normal flow conditions (including variability) between precipitation events. Base flows provide a range of suitable habitat conditions that support the natural biological community of a specific river sub- basin. Subsistence the component of an instream flow regime that represents infrequent, naturally occurring low flow events that occur for a seasonal period of time. They maintain sufficient water quality and provide sufficient habitat to ensure organism populations capable of recolonizing the river system once normal, base flows return. Time Allowance: TSJ-BBEST Purpose Matrix Taken from SAC Guidance: Use of Hydrologic Data in the Development of Instream Flow Recommendations for the Environmental Flows Allocation Process and The Hydrology- Based Environmental Flow Regime (HEFR) (4/20/2009) Overbank Overbank flows are infrequent, high magnitude flow events that produce water levels that exceed channel banks and result in water entering the floodplain. A primary objective is to maintain riparian areas associated with riverine systems, eg, transport sediments and nutrients to riparian arease, recharge floodplain aquifers, and provide suitable conditions for seedlings. High Flow Pulse High flow pulses are short duration, high magnitude (but still within channel) flow events that occur during or immediately following rainfall events. They serve to maintain important physical habitat features and connectivity along a stream channel. Base Base flows represent the range of "average" or "normal" flow conditions in the absence of significant precipitation or runoff events. Base flows provide instream habitat conditions needed to maintain the diversity of biological communities in streams and rivers. Subsistence Subsistence flows are low flows that occur during times of drought or under very dry conditions. Time Allowance: Ecological Roles Taken from SAC Guidance: Use of Hydrologic Data in the Development of Instream Flow Recommendations for the Environmental Flows Allocation Process and The Hydrology- Based Environmental Flow Regime (HEFR) (4/20/2009) Overbank Provide migration and spawning cues for fish Provide lateral connection with oxbows, riparian habitats, and floodplain areas Shape physical habitats Drive lateral movement of the river channel Provide nursery areas for juvenile fish Recharge the floodplain water table Deliver sediments and nutrients to the floodplain and estuaries Create key habitat features such as snags Maintain diversity in floodplain forest High Flow Pulse Provide migration and spawning cues for fish Move fine sediments and expose cobbles and rocky substrate Fill backwater areas and provide some lateral connectivity Restore normal water quality conditions following prolonged dry periods. Prevent riparian vegetation from growing in the channel Scour macrophytes Base Provide habitat of sufficient depth and velocity, without excessive velocity which would require finding shelter Maintain water tables levels for riparian vegetation Enable fish to move longitudinally to feeding and spawning areas Keep fish and amphibian eggs wet and suspended Provide drinking water for terrestrial animals Subsistence Sustain a minimum level of interconnection between pools Provide sufficient flow to preclude lethal temperature and dissolved oxygen levels. Purge invasive species