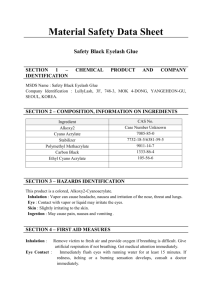
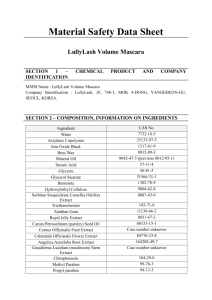
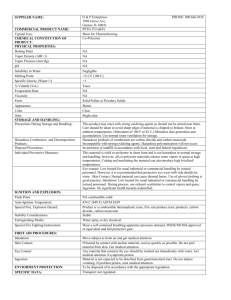
shoes before reuse. Get medical attention immediately.
advertisement

INDERJIT C62016 UNIT Code: UEENEEE024B TV CORD RISK Power cords can become frayed or damaged from heavy use and age and should be inspected regularly. Frequently, mishandling (such as pulling a plug from a socket by jerking the cord rather than removing the plug carefully by hand) causes the most significant damage to a cord over time, tearing the external protective sheathing or detaching it from the plug head and exposing energized wires. Less obvious than damaged and frayed cords is the threat posed by missing ground prongs, the rounded third prong on electrical plugs. These ground prongs often break off from mishandling or are removed intentionally to fit a plug into two-prong outlets. Ungrounded plugs – especially on kitchen appliances like refrigerators and dishwashers – can pose a significant electrocution risk. Fast Facts About Damaged Power Cords Statistics on Injuries and Losses Related to Electric Parts in 2002 * 13.4 injuries per 10,000 employees # 122 fatal injuries # 32% of employees unable to work because of injuries from electric parts were away for thirty-one days or More. Common Hazards to Avoid with Power Cords Power cords with frayed or damaged external sheathing, sheathing torn away from the plug head, or ground prongs removed Pulling a plug from a socket by jerking the cord rather than removing the plug carefully by hand Regulations Related to Damaged and Ungrounded Power Cords The Code of Federal Regulations (CFR 1910.303) states that electrical insulation shall be free from recognized hazards that cause death or serious physical harm to employees The Code of Federal Regulations (CFR 1910.334(a)(2)(ii)) requires damaged or defective power equipment to be rem oved from service until repairs are made and tests show the equipment is safe Missing ground prongs are a violation of Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations and the National Electric Code. As required by CFR 1910.334(a)(3)(ii), attachment plugs and receptacles may not be connected or altered in a manner which would prevent proper continuity of the grounding conductor Examples of Frayed and Damaged Power Cords At right is a power cord for a shop appliancefound on an inspection of a Congressionalfacility. The cord has been sliced open, exposingthe energized wires. The appliance was stillplugged in and still in use. To the left is a power cord in use in a Congressional facility. The cord has had its protective sheathing torn away from the plug head, exposing energized wires. PCB Etching Area Here we showing that there are some chemicals substance may be hazardous. They can affect your health. They can enter your body by injection, inhalation or skin absorption. They may be in the form of solids, liquids, gases, fumes or vapors. Ferric chloride Potential Acute Health Effects: Very hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of eye contact (irritant), of ingestion, . Hazardous in case of skin contact (corrosive, permeator), of eye contact (corrosive). Slightly hazardous in case of inhalation (lung sensitizer). Non-corrosive for lungs. Liquid or spray mist may produce tissue damage particularly on mucous membranes of eyes, mouth and respiratory tract. Skin contact may produce burns. Inhalation of the spray mist may produce severe irritation of respiratory tract, characterized by coughing, choking, or shortness of breath. Severe over-exposure can result in death. Inflammation of the eye is characterized by redness, watering, and itching. Skin inflammation is characterized by itching, scaling, reddening, or, occasionally, blistering. First Aid Measures Eye Contact: Check for and remove any contact lenses. In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes. Cold water may be used. Get medical attention immediately. Skin Contact: In case of contact, immediately flush skin with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes while removing contaminated clothing and shoes. Cover the irritated skin with an emollient. Cold water may be used.Wash clothing before reuse. Thoroughly clean shoes before reuse. Get medical attention immediately. Serious Skin Contact: Wash with a disinfectant soap and cover the contaminated skin with an anti-bacterial cream. Seek immediate medical attention. Inhalation: If inhaled, remove to fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. Get medical attention immediately. Serious Inhalation: Evacuate the victim to a safe area as soon as possible. Loosen tight clothing such as a collar, tie, belt or waistband. If breathing is difficult, administer oxygen. If the victim is not breathing, perform mouth-tomouth resuscitation. Seek medical attention. Ingestion: If swallowed, do not induce vomiting unless directed to do so by medical personnel. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Loosen tight clothing such as a collar, tie, belt or waistband. Get medical attention immediately. Hydrochloric Acid Hazards Identification Potential Acute Health Effects: Hazardous in case of eye contact (irritant). Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant, permeator), of eye contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation. Potential Chronic Health Effects: CARCINOGENIC EFFECTS: Classified 3 (Not classifiable for human.) by IARC [Hydrogen chloride]. MUTAGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. TERATOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY: Not available. The substance may be toxic to kidneys, liver, mucous membranes, upper respiratory tract, skin, eyes, , teeth. Repeated or prolonged exposure to the substance can produce target organs damage. First Aid Measures Eye Contact: Check for and remove any contact lenses. In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes. Cold water may be used. Get medical attention immediately. Skin Contact: In case of contact, immediately flush skin with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes while removing contaminated clothing and shoes. Cover the irritated skin with an emollient. Cold water may be used.Wash clothing before reuse. Thoroughly clean shoes before reuse. Get medical attention immediately. Serious Skin Contact: Wash with a disinfectant soap and cover the contaminated skin with an anti-bacterial cream. Seek medical attention. Inhalation: If inhaled, remove to fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. Get medical attention immediately. Ingestion: Do NOT induce vomiting unless directed to do so by medical personnel. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. If large quantities of this material are swallowed, call a physician immediately. Loosen tight clothing such as a collar, tie, belt or waistband. Sulphuric Acid Hazards Identification Potential Acute Health Effects: Very hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of eye contact (irritant), of ingestion, . Hazardous in case of skin contact (corrosive, permeator), of eye contact (corrosive). Slightly hazardous in case of inhalation (lung sensitizer). Liquid or spray mist may produce tissue damage particularly on mucous membranes of eyes, mouth and respiratory tract. Skin contact may produce burns. Inhalation of the spray mist may produce severe irritation of respiratory tract, characterized by coughing, choking, or shortness of breath. Inflammation of the eye is characterized by redness, watering, and itching. Skin inflammation is characterized by itching, scaling, reddening, or, occasionally, blistering. Potential Chronic Health Effects: CARCINOGENIC EFFECTS: Classified 1 (Proven for human.) by IARC, + (Proven.) by OSHA [Sulfuric acid]. Classified A2 (Suspected for human.) by ACGIH [Sulfuric acid]. MUTAGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. TERATOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY: Not available. The substance is toxic to lungs. Repeated or prolonged exposure to the substance can produce target organs damage. Repeated or prolonged contact with spray mist may produce chronic eye irritation and severe skin irritation. Repeated or prolonged exposure to spray mist may produce respiratory tract irritation leading to frequent attacks of bronchial infection. First Aid Measures Eye Contact: Check for and remove any contact lenses. In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes. Cold water may be used. Get medical attention immediately. Skin Contact: In case of contact, immediately flush skin with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes while removing contaminated clothing and shoes. Cover the irritated skin with an emollient. Cold water may be used.Wash clothing before reuse. Thoroughly clean shoes before reuse. Get medical attention immediately. Serious Skin Contact: Wash with a disinfectant soap and cover the contaminated skin with an anti-bacterial cream. Seek immediate medical attention. Inhalation: If inhaled, remove to fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. Get medical attention immediately. Serious Inhalation: Evacuate the victim to a safe area as soon as possible. Loosen tight clothing such as a collar, tie, belt or waistband. If breathing is difficult, administer oxygen. If the victim is not breathing, perform mouth-tomouth resuscitation. WARNING: It may be hazardous to the person providing aid to give mouth-to-mouth resuscitation when the inhaled material is toxic, infectious or corrosive. Seek medical attention. Ingestion: Do NOT induce vomiting unless directed to do so by medical personnel. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Loosen tight clothing such as a collar, tie, belt or waistband. Get medical attention if symptoms appear.