HgCr2S4_SI_revised_Ywang
advertisement

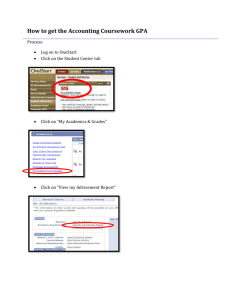
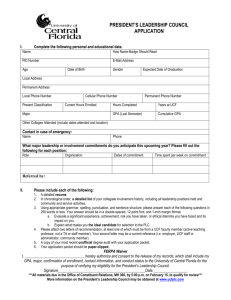
Multiple pressure-induced transitions in HgCr2S4 Ilias Efthimiopoulos1#, Alexander Yaresko2, Vladimir. Tsurkan3,4, Joachim Deisenhofer3, Alois Loidl3, Changyong Park5, and Yuejian Wang1* 1 Department of Physics, Oakland University, Rochester, MI, 48309, USA Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research, D-70569, Stuttgart, Germany 3 Experimental Physics 5, Center for Electronic Correlations and Magnetism, Institute of Physics, University of Augsburg, D-86159 Augsburg, Germany 4 Institute of Applied Physics, Academy of Sciences of Moldova, MD 2028 Chisinau, Republic of Moldova 5 High Pressure Collaborative Access Team, Geophysical Laboratory, Carnegie Institution of Washington, Argonne, IL 60439, USA 2 Supplementary Material FIG. S1: (a) XRD patterns of HgCr2S4 at selected pressures (T=300 K, λ=0.4246 Å). The various phases are indicated by different colors: black for Fd-3m, red for I41/amd, blue for orthorhombic, and dark green for HP3.. Asterisks mark the Bragg peaks of the Re gasket. Background has been subtracted for clarity. (b) Expanded view of the HgCr2S4 XRD patterns between 22 GPa and 49 GPa in the 6o-7.5o 2θ range. Notice the splitting of the (200) Bragg peak of the I41/amd phase at ~27 GPa, signaling the onset of the orthorhombic distortion. FIG. S2: Measured HgCr2S4 XRD pattern at 48.6 GPa (T=300 K, λ=0.4246 Å). The various colors of the Bragg peak positions (vertical ticks) represent different structures: blue for the HgCr 2S4 orthorhombic phase (estimated values), green for Re, and red for Ne. The more intense features in the diffractogram arise due to rhenium; the strongest Ne peak is located at ~13o1. TABLE S1: List of the lattice constants for the various phases of HgCr2S4 for all pressures. Phase P (GPa) a (Å) b (Å) c (Å) Fd-3m 1.00E-04 0.7 1.7 3.6 5.6 7.5 8.1 8.63 10.16 12.8 14.3 16.23 18.1 10.2414 10.2069 10.1835 10.1196 10.0767 10.0080 9.9947 9.9820 9.9440 9.8883 9.8619 9.8387 9.8085 10.2414 10.2069 10.1835 10.1196 10.0767 10.0080 9.9947 9.9820 9.9440 9.8883 9.8619 9.8387 9.8085 10.2414 10.2069 10.1835 10.1196 10.0767 10.0080 9.9947 9.9820 9.9440 9.8883 9.8619 9.8387 9.8085 19.96 22.2 25.2 7.2997 7.2948 7.2732 7.2997 7.2948 7.2732 8.3981 8.2391 8.1049 26.8 30.1 32.2 33.96 36.5 7.3013 7.2893 7.2586 7.2188 7.2069 7.2023 7.1714 7.1394 7.0894 7.0473 8.0453 7.9141 7.8865 7.8731 7.8509 I41/amd [Imma] TABLE S2: Refined crystallographic data for the ambient-pressure Fd-3m phase, and the high-pressure I41/amd and orthorhombic modifications of HgCr2S4. The SG Imma used for the refinement of the orthorhombic phase is tentative and was selected due to the following reasons: (1) it is a direct subgroup of SG I41/amd, and (2) it is a low-temperature modification of the related ZnCr2S4 spinel2, which undergoes a similar sequence of structural transitions upon lowering temperature. Space Group Fd-3m (227) I41/amd (141) [Imma (74)] Pressure (GPa) 5.6 22.2 32.2 a (Å) 10.0767(1) 7.2948(1) 7.2586(24) b (Å) 10.0767(1) 7.2948(1) 7.1394(10) c (Å) 10.0767(1) 8.239(2) 7.8865(35) c/a 1 1.13 1.087 c/b 1 1.13 1.105 V (Å ) 1023.2 438.4 408.7 Z 8 4 4 Rp, wRp 0.0084, 0.0126 0.0127, 0.0172 0.0103, 0.0155 Hg 8a (0.125, 0.125, 0.125) 4a (0, 0.75, 0.125) Cr 16d (0.5, 0.5, 0.5) 8d (0, 0, 0.5) S 32e (u, u, u) 16h (0, y, z) u=0.2621(5) y=0.4448(20) 3 Atomic parameters z=0.2335(10) Cr-S bond length (Å) 2.403(5) 2.316(3) x 4 /Cr-S(2) // ab-plane Hg-S bond length (Å) 2.393(8) 2.3996(20) Cr-S-Cr bond angle (degrees) 95.7(4) 103.91(3) (along ab-plane) 2.232(10) x 2 /Cr-S(1) // c-axis 93.05(5) (along c-axis) TABLE S3: Elastic parameters (volume VTr, the bulk modulus BTr, and the pressure derivative of bulk modulus B’Tr) for the various phases of HgCr2S4 under pressure, as obtained by the fitting of a Birch-Murnaghan EOS form3 to the measured P-V data. Each parameter is evaluated at the transition pressure point PTr. Phase PTr (GPa) -4 VTr/Z (Å3) BTr (GPa) B'Tr 133.7(4) 107(5) 4(fixed) Fd-3m 10 I41/amd 20 111.8(2) 112(3) 4(fixed) Orthorhombic 26.8 105.7(2) 142(10) 4(fixed) TABLE S4: Assignment4, frequencies, pressure coefficients, and the mode Gruneisen parameters γ of the Raman modes of HgCr2S4. The pressure depencence of the Raman-active modes is described by the relation: ω(P)=ωTr+αPTr, where frequeny ωTr is in cm-1 and pressure PTr in GPa. The Gruneisen parameters γ are determined from the relation: γ=(BTr/ωTr)x(∂ω/∂P), where BTr=107 GPa (Fd-3m) and BTr=85 GPa (I41/amd, extrapolated). Phase Assignment ωTr (cm-1) ∂ω/∂P (cm-1/GPa) γ Fd-3m Eg 257.9 2.7 1.1 PTr=1 bar F2g (2) 273 3.5 1.4 F2g (1) 404.9 3.8 1 I41/amd - 290.5 0.3 0.1 PTr=12.6 GPa - 296.4 0.8 0.2 FIG. S3: The ferromagnetic (FM) spin structure (left) and a non-collinear structure that gives zero moment (ZM) in each Cr tetrahedron (right). FIG. S4: Pressure dependence of the stabilization energies ΔE of the FM (blue) and ZM (red) spin configurations assumed for both Fd-3m and I41/amd phases of HgCr2S4. The stabilization energy is defined as ΔE=EM−E0, where EM and E0 are the total energies obtained from magnetic and nonspin-polarized calculations, respectively. FIG. S5: The AFM I41/amd structure FIG. S6: The pressure dependence of the difference E(q)-E(0), where E(0) is the energy of the FM solution, calculated for the Fd-3m structure with the wave vector q varying along (qq0) and (00q) lines. The values of qmin are 0.6 (0 GPa), 0.8 (5.6 GPa), 0.95 (10 GPa), and 1.05 (16.2 GPa) in 2π/a units. References 1 R.J. Hemley, C.S. Zha, A.P. Jephcoat, H.K. Mao, L.W. Finger, and D.E. Cox, Phys. Rev. B 39, 11820 (1989). 2 F. Yokaichiya, A. Krimmel, V. Tsurkan, I. Margiolaki, P. Thompson, H.N. Bordallo, A. Buchsteiner, N. Stuesser, D.N. Argyriou, and A. Loidl, Phys. Rev. B 79, 64423 (2009). 3 F. Birch, Phys. Rev. 71, 809 (1947). 4 A.K. Kushwaha, Commun. Theor. Phys. 50, 1422 (2008).