Honors Physics Syllabus
advertisement

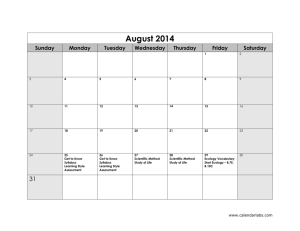
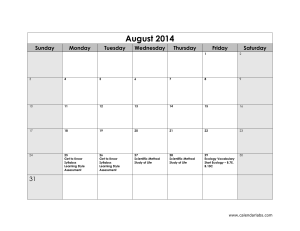
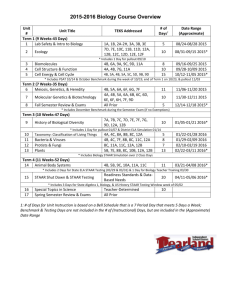
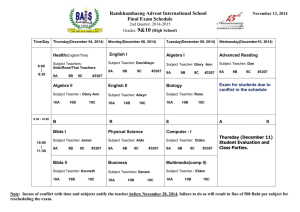
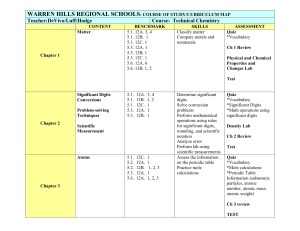
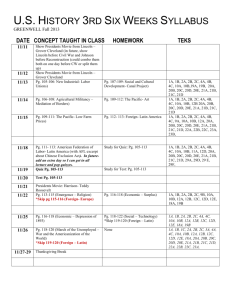
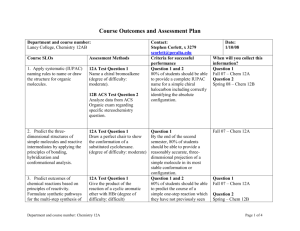
Honors Physics Syllabus Honors Physics is a standards based course that covers topics in Mechanics [Newtonian Physics] , Earth and Space Science, and Nuclear [Modern] Physics. Physics students “learn while doing”, engaging in discussions, mathematical modeling and analysis, collaborating on projects and conducting laboratory activities. In doing so, they practice the skills that will be needed for lifelong success in the real worldteamwork, perseverance, goal conflict resolution, judgment, persuasion, management, and communication. Students will be able to … 5.1 Science Practices 5.1.12A Understand Scientific Explanations 5.1.12A.1 Use mathematical ,physical and computational skills to explain concepts 5.1.12A.2 Interpret and manipulate evidence based models 5.1.12A.3 Revise of predictions and explanations based on systematic observation, measurements, and data 5.1.12B Generate scientific Evidence through active Investigations 5.1.12B.1 Logically design investigations to generate evidence to build/refine models 5.1.12B.2 Use math tools and technology to gather, analyze, communicate results 5.1.12B.3 Use empirical evidence to construct/defend arguments 5.1.12B.4 Use Scientific reasoning to evaluate and interpret data patterns and scientific conclusions. 5.1.12C Reflect on Scientific Knowledge 5.1.12C.1 Refine models/explanations as new evidence incorporated 5.1.12C.2 Use data and refined models to revise predictions and explanations 5.1.12.C.3 Understand science is established body of knowledge that is continually revised/refined due to new evidence 5.1.12D Participate Productively in Science 5.1.12D.1 Engage in productive social interactions with peers: partner talk, whole and small group discussions 5.1.12D.2 Use oral and written language for presenting thoughts 5.1.12D.3 Demonstrate proper care for instruments 5.2 Physical Science 5.2.12A Properties of Matter 5.2.12A.1 Explain atoms contain protons, neutrons, electrons.; Nucleus contains protons and neutrons.; Strong force holds nucleus together; electrostatic force holds protons and electrons together 5.2.12A.4 Explain number of protons equals number of electrons in a neutral atom 5.2.12B Changes in Matter 5.2.12B.3 Apply conservation of matter(matter is neither created nor destroyed) 5.2.12C Forms of Energy 5.2.12C.1 Describe kinetic molecular theory ; describe gas laws in terms of KMT; entropy 5.2.12C.2 Explain temperature directly related to energy ; particles of all matter always in motion 5.2.12D Energy Transfer and Conservation 5.2.12D.1 Demonstrate gravitational PE related to height 5.2.12D.2 Distinguish between exothermic and endothermic reactions; understand nergy/entropy drives reactions 5.2.12D.3 Compare fission and fusion reactions; calculate E = mc2 5.2.12D.4 Explain energy transferred during collision; energy conserved 5.2.12E Forces and Motion 5.2.12E.1 Explain motion is described by position and velocity wrt time; define average speed and average acceleration 5.2.12E.2 Describe motion as : translation, rotation, vibration 5.2.12E.3 Show force required to change state of motion 5.2.12E.4 Apply and calculate a = Fnet / m 5.4 Earth Systems Science 5.4.12A Objects in the Universe 5.4.12A.1 Compare geocentric model to heliocentric 5.4.12A.2 Describe Earth and Solar System formed from nebular cloud of gas and dust 4.6 bya 5.4.12A.3 Illustrate life cycle of stars using H-R diagram 5.4.12A.4 Estimate Milky Way galaxy contains 200 billion stars,, 100 billion other galaxies in Universe 5.4.12A.5 Explain Big Bang theory : Universe began 13.7 bya; H and He coalesce into stars 5.4.12A.6 Describe Big Bang theory claims Universe is expanding, galaxies moving apart. 5.4.12B History of Earth 5.4.12B.1 Explain how evolution of life affected Earth's atomosphere [originally no O2 in atmosphere] 5.4.12B.2 Apply relative dating: use fossil index and strata sequences to determine geologic events 5.4.12B.3 Apply absolute dating: use radioactive isotopes in rocks 5.4.12C Properties of Earth Materials 5.4.12C.1 Compare soils at interface of biosphere, geosphere, atmosphere and hydrosphere 5.4.12C.2 Explain chemical and physical properties of vertical structure of atmosphere support life 5.4.12D Tectonics 5.4.12D.1 Describe motion of plates: due to convection currents in upper mantle; subduction and spreading zones 5.4.12D.2 Describe reversals of Earth's magnetic poles: evidence in ocean bottom lava flows 5.4.12E Energy in Earth Systems 5.4.12E.1 Describe energy transfer,circulation of energy via convection currents 5.4.12E.2 Explain how Sun's energy transformed/transferred in global wind circulation, ocean circulation and water cycle. 5.4.12.F Climate and Weather 5.4.12.F.1 Explain global climate results from uneven heating of Earth's surface from Sun; seasons due to tilt of Earth 5.4.12F.2 Describe climate determined by energy transfer from the Sun at and near surface of Earth; cloud cover, oceans, burning fossil fuels may affect global climate 5.4.12F.3 Explain how Earth's radiation budget is balanced globally, but varied locally; hydrologic cycle varies globally, regionally, locally 5.4.12G Biogeochemical Cycles 5.4.12G.1 Explain how natural and manufactured chemicals circulate in water cycle 5.4.12G.2 Describe how array of vital functions provided by natural ecosystems affect humans: soil generation, water cycle, recycling nutrients; quality of atmosphere 5.4.12G.3 Understand movement of matter through Earth's system driven by Earth's internal and external energy sources and changes in physical and chemical properties of matter 5.4.12G.4 Determine how natural and human activities impact cycling of matter and flow of energy in ecosystems 5.4.12G.5 Describe how human activities have changed Earth's land, oceans, atmosphere, plant populations and animal species 5.4.12G.6 Use scientific, economic, and other data to assist in assessing environmental risks/benefits associated with societal acivity 5.4.12G.7 Apply conservation of mass: Earth is system with fixed amounts of chemical elements that move through solid Earth, oceans, atmosphere and living things in geochemical cycles