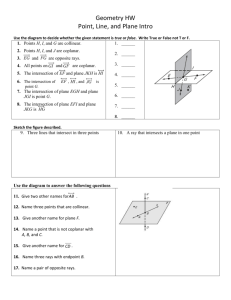
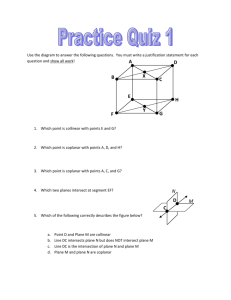
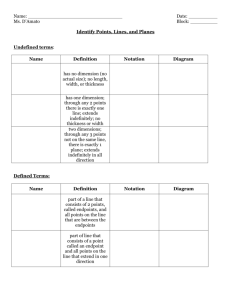
Example 1: Determine the line of intersection of two planes.
advertisement

Orthographic Projection Intersection of two planes: is a line shared by the two planes! Example: Orthographically determine the intersection of Plane 1 (340, 36NE) and Plane 2 (042, 20W). Procedure: 1. Draw the trace of the two planes on a graph paper (map view) using their strikes, through point ‘O’, preferably located at the center of your graph paper. Use the grid system of your graph paper to represent N and E. Make sure to put tick marks to represent the dip for the two planes across their traces. 2. Arbitrarily, mark point A on the trace of plane 1. At this point, draw a folding line (FL1) perpendicular to the trace of Plane 1. The length of this line may be 4 or 5 cm. 3. Put a protractor at point A and draw a second line, at an angle equal to the dip amount (i.e., =36o) from FL1. Let’s call this line: the ‘oblique line’. 4. Put a straight edge ruler across FL1, and select a convenient depth, d at point A’ along FL1. The length of d is conveniently chosen to be a whole number, e.g., 2 cm or 3 cm. Mark the intersection of the ‘d’ line with the oblique line as ‘Ad’, i.e., ‘A’ at depth d. 5. Repeat steps 2 through 4 for plane 1, using the same d depth for you construction. Make sure to use FL2, B, and Bd instead of FL1, A, and Ad for plane 2. 6. Notice that points Bd and Bd are at the same depth below the map surface! 7. Draw a line through Ad and A, and extend it parallel to the strike of Plane 1. 8. Draw a line through Bd and B, and extend it parallel to the strike of Plane 2. 9. The two lines intersect at point C. 10. Connect O to C. This is the line of intersection of the two planes. 11. Now you need to determine the plunge of this line of intersection OC. 12. At point C, draw the folding line FL3 across OC, with length d, extended to point C’ 13. Connect C’ to O. 14. Read the angle of plunge, , between OC and OC’. SEE NEXT PAGE FOR SOLUTION! Plane 1 (340, 36NE) Plane 2 (042, 20W) is dip amount A’ A d line of intersection C FL2 FL3 N C’ O Plane 2 Solution: Trend & plunge of line of intersection = 14o, 000