Prelim 2013 - bankstowntafehsc
advertisement

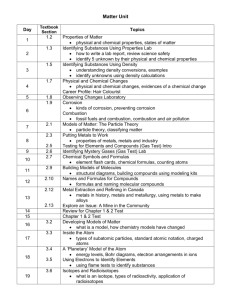
8.3 Metals 8.2 The Chemical Earth 1. The living and non living components of the Earth contain mixtures. 2. Although most elements are found in combinations on Earth, some elements are found uncombined. 3. Elements in the Earth material are present mostly as compounds because of interactions at atomic level. 4. Energy is required to extract elements from their naturally occurring sources. 5. The properties of elements and compounds are determined by their bonding and structure. Classify elements, compounds and mixtures, in terms of particle theory. Identify the spheres of the planet. Methods of separation and when to use. Systematic naming, formulae and equations. `Reactivity and occurrence Classify metal, non metals and semi metals. Uses related to metallic properties. Matter moving and interacting Energy levels and electron movement. Using periodic table Ionic formation. Molecules/Covalent formation. Lewis Dot diagrams. Physical and chemical changes, water as an example. Energy changes in reactions. Energy needed to break bonds. Physical and chemical properties. Metallic, molecular and network covalent bonds Empirical formula. Properties related to bonding. 1. Metals have extracted and used for many thousands of years o o o o Use of metals through history Alloys Extracting metals Metals known today 2. Metals differ in their reactivity with other chemicals and this influences their uses. o o o o o o o o o Reactions of metals Activity series Electron transfer Properties and uses Ionisation Energy 4. For efficient resource use, industrial chemical reactions must use measured amounts of each reactant. o o o o o Mole Conservation of mass Gay Lussac Law Avogardro’s number Empirical and molecular formula 5. The relative abundance and ease of extraction influences their value and breadth of use in the community o o o o Minerals and ores. Abundance extraction and price Separation of metals from ores Recycling 3. As metals and other elements were discovered, scientists recognised that patterns in their physical and chemical properties could be used to organise the elements into a periodic table Atomic structure Development of periodic table Trends in periodic table Must hand up all pracs for this topic. Must hand up all pracs for this topic. Prliminary Summary 2012 Bankstown General Science Version 1 Page 1 of 2 Last Updated: 5/2/2013 8.5 Energy 8.4 Water 1.Water is distributed on earth as a solid, liquid and gas. o o o Terms Importance Distribution 1. Living organisms make compounds which are important sources of energy. Role of photosynthesis Need of the sun Origins of fossil fuels. 2. The wide distribution and importance of water on the Earth is a consequence of its molecular structure and hydrogen bonding. o o o o o Lewis dot diagrams. Molecular structures Hydrogen bonding Polar molecules Intermolecular forces and properties. 2. There is a wide variety of carbon compounds. 3. Water is an important solvent. o o Solubility of different chemicals Solubility and polarity o o o o Solubiltiy and precipation Saturated solution Determine molarity. Concentration. Properties of carbon .Carbon bonds Large variety of compounds Describe fractional distillation Nomenclature. Properties alkanes and alkenes. Storage. Indicators of chemical reaction Combustion reactions are exothermic Changes in molecules and the energy associated Energy profiles Ignition temperature and activation energy Pollution associated. Combustion at different rates Collision Theory Temperature and kinetic energy Catalyst. 4. The concentration of salts in water will vary according to their solubility and precipitation can occur when the ions of insoluble salts are in solution together. 5. Water has a higher heat capacity than other liquids. o o o o 3. A variety of carbon compounds are extracted from organic sources. 4. Combustion provides another opportunity to examine the conditions under which chemical reactions occur. 5. The rate of energy release is affected by factors such as types of reactants. Specific heat capacity. Determine ΔH. Exothermic and endothermic. Importance in nature Must hand up all pracs for this topic. Must hand up all pracs for this topic. Prliminary Summary 2012 Bankstown General Science Version 1 Page 2 of 2 Last Updated: 5/2/2013