4.3 Study Guide
advertisement

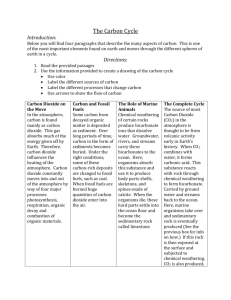
4.3 Study Guide Key facts 1. While energy enters and leaves ecosystems (flowing in one direction), nutrients are recycled or reused. 2. Common examples of this nutrient recycling include the carbon cycle, the water cycle, the nitrogen cycle and the carbon cycle. 3. The carbon cycle is a major factor in the greenhouse effect. 4. The carbon cycle represents the interaction of living organisms and the biosphere through the processes of photosynthesis, cell respiration, fossilization and combustion. 29. Photosynthesis allows the fixation of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Combustion results in the release of and accumulation of more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Respiration results in the release of carbon dioxide and accumulation in the atmosphere. 5. Decomposers, saprotrophs and detritivores, result in release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, and therefore, the recycling of carbon. 6. Autotrophs convert carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and other carbon compounds. 7. In aquatic habitats carbon dioxide is present as a dissolved gas and hydrogen carbonate ions. 8. Carbon dioxide diffuses from the atmosphere or water into autotrophs. 9. Carbon dioxide is produced by respiration and diffuses out of organisms into water or the atmosphere. 10. Methane is produced from organic matter in anaerobic conditions by methanogenic archaeans and some diffuses into the atmosphere. 11. Methane is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water in the atmosphere. 12. Peat forms when organic matter is not fully decomposed because of anaerobic conditions in waterlogged soils. 13. Partially decomposed organic matter from past geological eras was converted into oil and gas in porous rocks or into coal. 14. Carbon dioxide is produced by the combustion of biomass and fossilized organic matter. 15. Animals such as reef-building corals and molluscs have hard parts that are composed of calcium carbonate and can become fossilized in limestone. Additional skills and questions 17. Be able to analyze date from atmosphere monitoring stations showing annual fluctuations. 18. Draw and label a diagram of the carbon cycle to show the processes involved. Be certain to include photosynthesis, cell respiration, fossilization, combustion and decomposition. 19. List three sources of carbon dioxide in our atmosphere. 20. What major biological process allows a decrease in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels?_____________________ 21. The Gaia hypothesis views the biosphere on Earth as a single living organism because there appears to be a significant level of self-regulation. How does the carbon cycle contribute to this self-regulation? 22. Present some reasons for the increase in carbon dioxide levels in the Earth’s atmosphere since the 1800s. 23. Besides carbon dioxide, what are some other gases that may be contributing to the greenhouse effect? 24. Explain why carbon dioxide levels seem to increase in areas during the winter but decrease in those same areas during the summer.