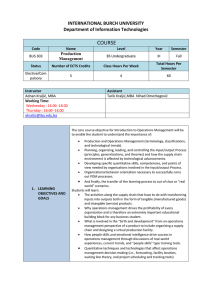
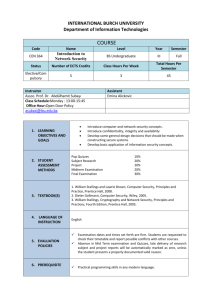
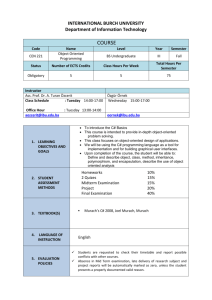
Assignment no.1 15% - Department of Architecture
advertisement
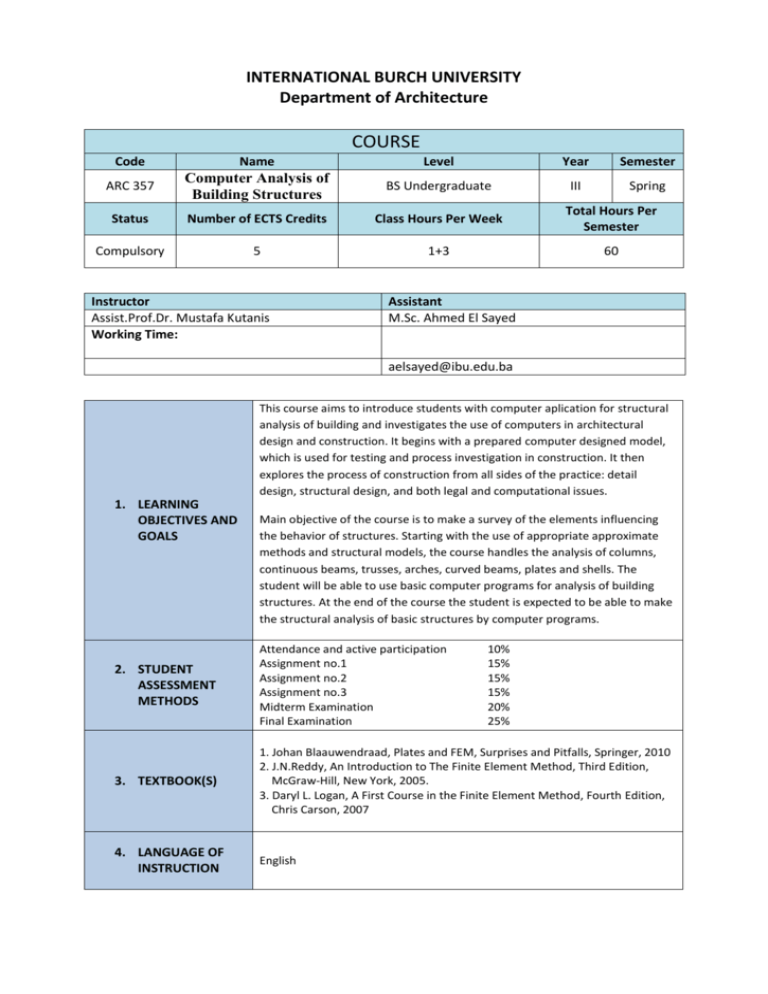
INTERNATIONAL BURCH UNIVERSITY Department of Architecture COURSE Code Name Level Year Semester ARC 357 Computer Analysis of Building Structures BS Undergraduate III Spring Status Number of ECTS Credits Class Hours Per Week Total Hours Per Semester Compulsory 5 1+3 60 Instructor Assist.Prof.Dr. Mustafa Kutanis Working Time: Assistant M.Sc. Ahmed El Sayed aelsayed@ibu.edu.ba This course aims to introduce students with computer aplication for structural analysis of building and investigates the use of computers in architectural design and construction. It begins with a prepared computer designed model, which is used for testing and process investigation in construction. It then explores the process of construction from all sides of the practice: detail design, structural design, and both legal and computational issues. 1. LEARNING OBJECTIVES AND GOALS Main objective of the course is to make a survey of the elements influencing the behavior of structures. Starting with the use of appropriate approximate methods and structural models, the course handles the analysis of columns, continuous beams, trusses, arches, curved beams, plates and shells. The student will be able to use basic computer programs for analysis of building structures. At the end of the course the student is expected to be able to make the structural analysis of basic structures by computer programs. 2. STUDENT ASSESSMENT METHODS Attendance and active participation Assignment no.1 Assignment no.2 Assignment no.3 Midterm Examination Final Examination 10% 15% 15% 15% 20% 25% 3. TEXTBOOK(S) 1. Johan Blaauwendraad, Plates and FEM, Surprises and Pitfalls, Springer, 2010 2. J.N.Reddy, An Introduction to The Finite Element Method, Third Edition, McGraw-Hill, New York, 2005. 3. Daryl L. Logan, A First Course in the Finite Element Method, Fourth Edition, Chris Carson, 2007 4. LANGUAGE OF INSTRUCTION English 5. EVALUATION POLICIES 6. PREREQUISITE Examination dates and times set forth are firm. Students are requested to check their timetable and report possible conflicts with other courses. Absence in Mid Term examination, late delivery of research subject and project reports will be automatically marked as zero, unless the student presents a properly documented valid reason. Advanced knowledge of elementary Mathematics, Statics and Strength of Materials, as well as Theory of Structures. 7. SCHEDULE OF LECTURES AND READINGS Topic Week 1 1+3 Introduction to Computer Analysis Week 2 1+3 Basic Concepts of Numerical Analysis Week 3 1+3 Fundamental Laws of Continuum Mechanics and Constitutive Relationships Week 4 1+3 Finite Element Method and its Application Week 5 1+3 Finite Elements formulation for OneDimensional Problems; Single Bar and Beam Elements Week 6 1+3 Finite Elements Formulation for TwoDimensional Problems Week 7 Teaching Methods Lectures, Recitation, Practical Sessions Lectures, Recitation, Practical Sessions Lectures, Recitation, Practical Sessions Lectures, Recitation, Practical Sessions Lectures, Recitation, Practical Sessions Lectures, Recitation, Practical Sessions Mid-term Week 8 1+3 2D Analysis of Structural Elements, SAP 2000 Week 9 1+3 2D Analysis of Structural Elements, SAP 2000 Week 10 1+3 2D Analysis of Structural Elements, SAP 2000 Week 11 1+3 Finite Elements Formulation for Multidimensional Problems; Plate and Shell Elements Week 12 1+3 3D Analysis of Buildings, SAP 2000 Lectures, Recitation, Practical Sessions Lectures, Recitation, Practical Sessions Lectures, Recitation, Practical Sessions Lectures, Recitation, Practical Sessions Lectures, Recitation, Practical Sessions Reading Singiresu S. Rao, The Finite Element Method in Engineering, fifth edition. Elsevier, 2011. Aslam Kassimali, Matrix Analysis of Structures, second edition. Global Engineering: Christopher M. Shortt, 2012. Class Hours Date Week 13 1+3 3D Analysis of Buildings, ETABS Week 14 1+3 3D Analysis of Buildings, ETABS Week 15 1+3 3D Analysis of Buildings, ETABS Lectures, Recitation, Practical Sessions Lectures, Recitation, Practical Sessions Lectures, Recitation, Practical Sessions Plagiarism Notice: Plagiarism is a serious academic offense. Plagiarism is a form of cheating in which a student tries to pass off someone else's work or part of it as his or her own. It usually takes the form of presenting thoughts, terms, phrases, passages from the work of others as one's own. When it occurs it is usually found in essays, research papers or term papers. Typically, passages or ideas are 'lifted' from a source without proper credit being given to the source and its author. To avoid suspicion of plagiarism you should use appropriate references and footnotes. If you have any doubt as to what constitutes plagiarism you should consult your instructor. You should be aware that there are now internet tools that allow each submitted paper to be checked for plagiarism. Remember plagiarism is serious and may result in a reduced or failing grade or other disciplinary actions. Cheating: Cheating in any form whatsoever is unacceptable and will subject you to IBU disciplinary procedures. Cheating includes signing in others for attendance, exams or anything else; using prohibited electronic and paper aides; having others do your work; having others do your work, copying from others or allowing others to copy from you etc. Please do not cheat in any way! Please consult me if you have any questions. Assignments: 1. Structural Analysis – 1D problems 2. Structural Analysis – 2D problems 3. Structural Analysis – 3D problems