Key Concept Builder
advertisement
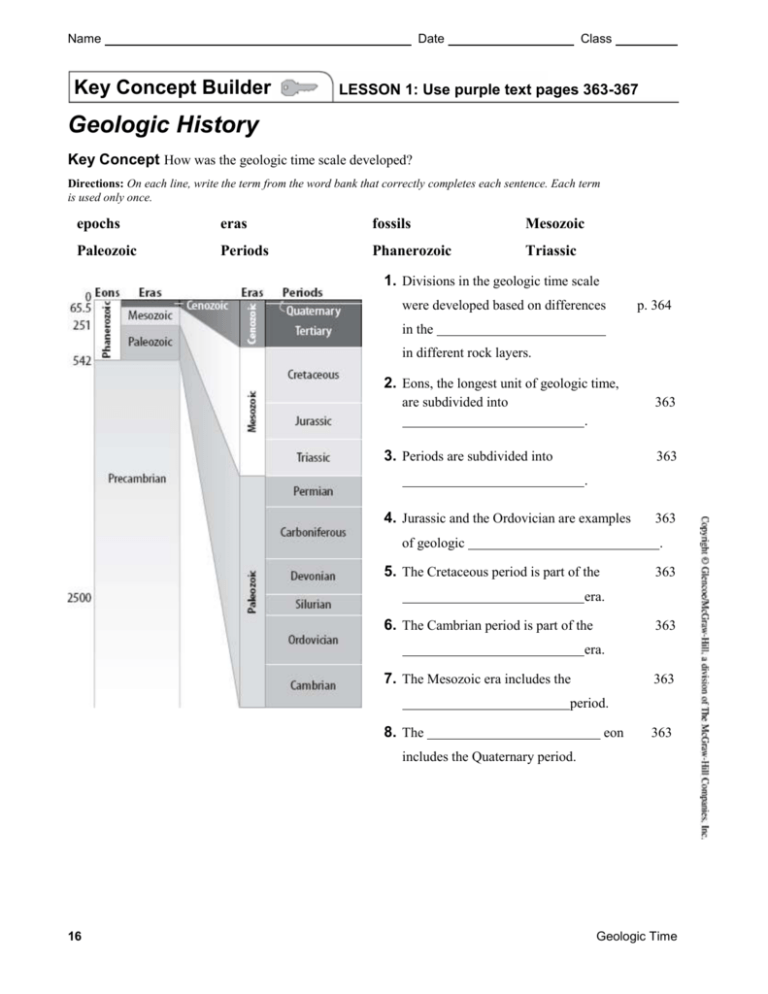
Name Date Key Concept Builder Class LESSON 1: Use purple text pages 363-367 Geologic History Key Concept How was the geologic time scale developed? Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly completes each sentence. Each term is used only once. epochs eras fossils Mesozoic Paleozoic Periods Phanerozoic Triassic 1. Divisions in the geologic time scale were developed based on differences p. 364 in the in different rock layers. 2. Eons, the longest unit of geologic time, are subdivided into 363 . 3. Periods are subdivided into 363 . 4. Jurassic and the Ordovician are examples of geologic 363 . 5. The Cretaceous period is part of the 363 era. 6. The Cambrian period is part of the 363 era. 7. The Mesozoic era includes the 363 period. 8. The eon 363 includes the Quaternary period. 16 Geologic Time Name Date Key Concept Builder Class LESSON 2: Use purple text pgs 371-375 The Paleozoic Era Key Concept What major geologic events occurred during the Paleozoic era? Directions: Answer each question on the lines provided Early Paleozoic 1. Which age is this time known as? p.371 2. What was the climate like? 372 3. What happened to the seas during this time? 372 4. What two things resulted from this change in sea level? 372 5. Where was North America located? p.372 6. Where did animal life exist? 372 7. Which type of animals existed? 371 Middle Paleozoic 8. Which age is this time known as? p.373 9. What happened between moving continents? 373 10. What was created from this movement? 373 11. Which type of animals further evolved in the seas? 373 12. Which type of animals evolved on land? 373 Late Paleozoic 13. Which age is this time known as? p.374 14. What was the climate like near the end of this time? 375 15. What landmass formed during this time? 375 16. Which type of animals evolved on land toward the end of this time? 374 17. What happened to 70 percent of all life-forms on land at the end of this time? 375 34 Geologic Time Name Date Content Practice A Class LESSON 3: Use purple text pages 379-383 The Mesozoic Era 251 mya • Mesozoic era begins. • Pangaea begins to break apart. • Ocean water flows onto continents. • Inland seas • Flowering plants appear. • Dinosaurs become the dominant reptile. form. • Two continents form—Late Triassic. • Mammals evolve. 65.5 mya • A meteorite hits Earth. • Volcanoes erupt. • A mass extinction occurs. Directions: Use the diagram to answer each question. 1. How long ago did the Mesozoic era begin? p. 379 2. What happened to Pangaea? 379 3. What happened as the ocean waters rose higher? 380 4. Which life-forms evolved during the Mesozoic era? 382 5. Which reptile was dominant during the Mesozoic era? 382 6. Which event marks the end of the Mesozoic era? 383 7. What do scientists hypothesize led to the mass extinction? 383 Geologic Time 4 Name Date Key Concept Builder Class LESSON 4: Use purple book pp. 386-393 The Cenozoic Era Key Concept What major geologic events occurred during the Cenozoic era? Eon Era Period Epoch Start Date (mya) Neogene Tertiary Cenozoic Phanerozoic Quaternary Paleogene Holocene 0.01 Pleistocene 1.64 Pliocene 5.2 Miocene 23.3 Oligocene 35.4 Eocene 56.5 Paleocene 65.5 Directions: Put a check mark in the space that correctly identifies when each geologic event occurred. Note: You may have to refer back to Fig. 21 on pp. 388-389 to confirm a few answers. 1. India crashes into Asia. Tertiary Period p. 388 2. The climate begins to cool. 389 3. Glaciers cover 30 percent of Earth’s land surface. 389 4. The Alps form. 388 5. Glaciers advance and retreat several times. 389 6. Antarctica links Australia to South America. Fig. 21 & 391 7. The Himalayas form. 388 8. The Sierra Nevadas form. 388 9. Forests replace grasses. Fig. 21 & 392 10. The climate is warm and drier. 392 11. Ice covers poles during the Pliocene epoch. 389 12. Inland seas that had covered the land drain away. 389 13. Australia is located near India. 14. Africa pushes into Europe. 72 Quaternary Period Fig. 21 & 391 388 Geologic Time









