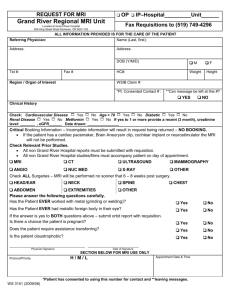
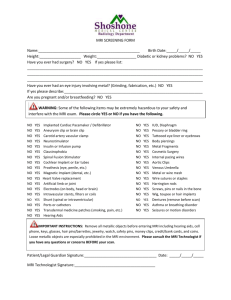
mri complications
advertisement

Indication Brain TIA/Stroke Study Comments If Code Stroke – CT Head w/o contrast to r/o hemorrhage Order CT if uncooperative or suspect bleed MRI DWI will detect acute infarct before CT Acute Bleed Severe Headache Subarachnoid hemorrhage F/u subarachnoid hemorrhage F/u subdural hemorrhage Brain tumor Suspected brain tumor METS Papilledema CNS Infection Abscess Meningitis AIDS Dementia Neurodegenerative disorder Multiple Sclerosis MRI Brain w/o contrast and MRA neck & head CT Head w/o contrast MRI Brain w/wo contrast CT more sensitive than MRI for SAH and acute bleed MRI may show source such as AVM or aneurysm MRI Brain w/wo contrast MRI superior to CT MRI Brain w/wo contrast MRI demonstrates abnormal meninges & other complications of infection MRI Brain w/wo contrast MRI Brain w/wo contrast Trauma CT preferred over MRI MRI Brain w/o contrast Cranial Nerve Deficit Cerebellar or Brainstem Lesion Diplopia Sensorineural Hearing Loss Tinnitus Acoustic Neuroma Bell’s Palsy Pituitary Tumor Sinus Thrombosis Known Aneurysm Arterial venous malformation Cavernous Angioma MRI Brain w/wo contrast MRI superior to CT MRI demonstrates white matter changes of aging and acute and chronic infarcts, Parkinson’s Disease, etc. Acute plaques may show enhancement with MRI. MRI superior to CT CT is indicated for acute trauma. Trauma MRI more sensitive for nonsurgical trauma, Post Concussion Syndrome. MRI superior to CT MRI Brain w/wo contrast CT not accurate. Recommend High resolution MR noncontrasted Limited MRI Brain w/wo contrast MRI Brain/MRV Head w/o contrast MRA w/o contrast MRI superior to CT Replaces conventional angiography. Does not replace angiography. Reasonable screening tool in patients With family Hx. Satisfactory to R/O aneurysms 5mm or larger. Muscloskeletal Meniscal Tear Ligamentous/Tendon/MuscleInjury Bone Contusion Fracture MRI w/o contrast MRI w/o contrast Avascular necrosis Cancer Metastasis Myeloma Osteomyelitis Cellulitis Infection/Abscess Soft Tissue Mass. Osteochondritis Dissecans Chondomalacia Bone Tumor MRI w/o contrast MRI w/wo contrast Loose Bodies MRI w/o contrast Spine Herniated Disc – Cervical or Thoracic Lumbar Herniated Disc MRI w/o contrast MRI w/o contrast Stenosis If post-surgery, then MRI w/wo contrast MRI w/o contrast Discitis Osteomyelitis Metastasis Epidural Tumor Compression Fracture Trauma Brachial plexus – mass or lesion Lower Extremity numbness/tingling/weakness Radiculopathy Transverse Myelitis MRI contrast w/wo contrast MRI if occult fracture CT if fracture seen on X-ray and position or alignment is to be addressed CT for avulsion or small cortical fractures Bone scan if MRI is contraindicated Bone Scan is good for whole body survey for metastasis 3 phase bone scan if MRI contraindicated Iridium WBC if abnormality on plain x-ray MRI w/o contrast MRI w/wo contrast MRI w/ contrast MRI w/wo contrast MRI w/o contrast MRI chest w/wo contrast MRI Lumbar spine w/o contrast MRI thoracic spine w/o contrast MRI thoracic spine w/wo contrast Evaluates extent/neurovascular involvement Contrast essential to distinguish between scar & disc post surgery. CT can be adequate in lumbar spine if MRI contraindicated MRI superior to CT Chest Pulmonary Embolus Aortic Dissection Lung Nodule, Mass, infiltrate Interstitial lung disease Liver – Mass, Hepatoma, Hemangioma, Cancer/Metastasis, Hepatitis, Cirrhosis, Fatty Liver, Abnormal LFTs Abdominal Pain Pancreas – Mass, epigastrsic pain Cancer/mets Pancreatitis Renal MRA Renal mass Hematuria Adrenal – Mass/Cysts Prostate Uterine Fibroids Pelvic Mass, pain, Ca/mets, infection/abscess Breast CA Orbit/Head & Neck Nasopharynx Tongue Floor of Mouth Neck Mass Soft Tissue Neck TMJ – pain/discomfort Orbit Proptosis Orbit or eye swelling (infection) Optic nerve visual field defect Carotid stenosis CTA Chest with IV contrast CT chest and/or abdomen with IV Contrast CT High resolution CT w/o contrast MRI Abdomen w/wo contrast CT is the most sensitive test If IV contrast is contraindicated or patient has poor venous access, V/Q Scan CT is the most sensitive test Peripheral nodules – can be imaged without contrast Hilar nodules – contrast helpful 1-2 mm slices at 5-10 mm increments MRI Abdomen w/wo contrast MRA kidneys with contrast MRI renals w/wo contrast Renal stenosis If mass involves vasculature then MRI abdomen w w/o and MRA with contrast MRI Abdomen w/o contrast MRI pelvis w/o contrast MRI pelvis w/wo contrast MRI pelvis w/wo contrast MRI Breast w/wo contrast CT Neck with contrast W/wo if stone suspected MRI only to r/o extension of mas into spinal canal, skull base or vocal cords MRI TMJ CT with IV contrast MRI with contrast MRA w/o contrast No contrast for Grave’s disease Orbit MRI Extremities Upper Extremity = upper any joint Shoulder, elbow or wrist Upper other than joint – humerus, forearm, hand Cancer Tumor Infection Osteomyelitis Abscess Masses Pain Muscle/Ligament tear Injury Swelling Tendonitis Lower Extremity Lower any joint – knee, hip, ankle Lower other than joint – femur, tib/fib, foot MRI Extremity w/wo contrast MRI extremity w/o contrast