Rocks and Catastrophic Events Vocabulary
advertisement
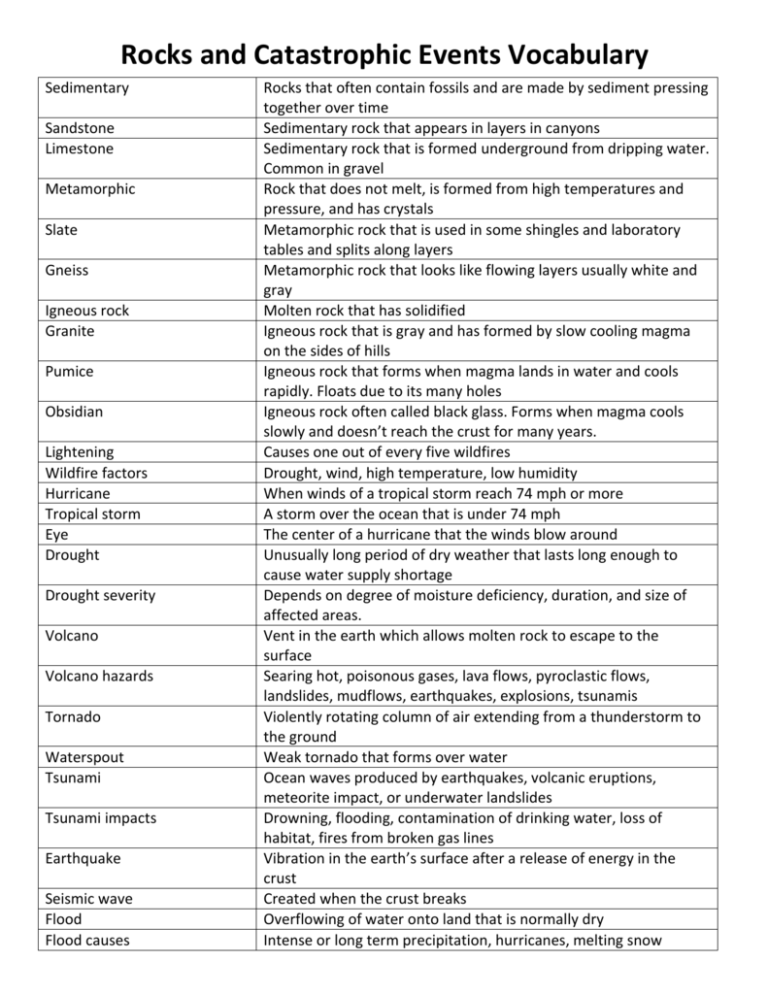
Rocks and Catastrophic Events Vocabulary Sedimentary Sandstone Limestone Metamorphic Slate Gneiss Igneous rock Granite Pumice Obsidian Lightening Wildfire factors Hurricane Tropical storm Eye Drought Drought severity Volcano Volcano hazards Tornado Waterspout Tsunami Tsunami impacts Earthquake Seismic wave Flood Flood causes Rocks that often contain fossils and are made by sediment pressing together over time Sedimentary rock that appears in layers in canyons Sedimentary rock that is formed underground from dripping water. Common in gravel Rock that does not melt, is formed from high temperatures and pressure, and has crystals Metamorphic rock that is used in some shingles and laboratory tables and splits along layers Metamorphic rock that looks like flowing layers usually white and gray Molten rock that has solidified Igneous rock that is gray and has formed by slow cooling magma on the sides of hills Igneous rock that forms when magma lands in water and cools rapidly. Floats due to its many holes Igneous rock often called black glass. Forms when magma cools slowly and doesn’t reach the crust for many years. Causes one out of every five wildfires Drought, wind, high temperature, low humidity When winds of a tropical storm reach 74 mph or more A storm over the ocean that is under 74 mph The center of a hurricane that the winds blow around Unusually long period of dry weather that lasts long enough to cause water supply shortage Depends on degree of moisture deficiency, duration, and size of affected areas. Vent in the earth which allows molten rock to escape to the surface Searing hot, poisonous gases, lava flows, pyroclastic flows, landslides, mudflows, earthquakes, explosions, tsunamis Violently rotating column of air extending from a thunderstorm to the ground Weak tornado that forms over water Ocean waves produced by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, meteorite impact, or underwater landslides Drowning, flooding, contamination of drinking water, loss of habitat, fires from broken gas lines Vibration in the earth’s surface after a release of energy in the crust Created when the crust breaks Overflowing of water onto land that is normally dry Intense or long term precipitation, hurricanes, melting snow







