Mechanical vs. Chemical Weathering LAB
advertisement

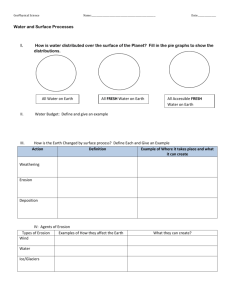
Name: __________________________ Date: ___________________ Pd. ________ Mechanical vs. Chemical Weathering Objectives: Students will… identify types and causes of weathering and differentiate between them. Introduction: The earth is in a constant state of motion, both as a planet in the solar system and as a body of interactive systems. Many of these systems create forces that change the face of the planet. The term weathering refers to any force that breaks down rocks and other objects in nature into smaller pieces. Erosion refers to the movement of the parts that were broken off through the weathering process. Mechanical weathering is when physical forces are applied to break rocks down into smaller particles. Chemical weathering is when chemical reactions take place such as oxidation (rust). There are differences between mechanical and chemical weathering but both serve the same purpose. Materials: Weathering Vocabulary Types of Weathering Stopwatch 1 piece of hard candy (per student) water 2 beakers (per group) vinegar or lemon juice 2 alka seltzer tablets (per group) Pre-Lab (10 Points) Read the introduction and procedure and answer the essential lab questions: What am I trying to find out? How am I trying to find this out? Procedure: PART A: Weathering Vocabulary and picture association You will be moving around the room to locate different weathering terms. There are two posters for each term. You will be recording the definition for each term and drawing a picture or writing the example in the box on the back. Posters around the room PART B: Mechanical and Chemical weathering matching. Mechanical vs. Chemical Weathering Separate the vocabulary terms, THAT ARE BELOW, into the correct mechanical and chemical weathering columns. MECHANICAL WEATHERING CHEMICAL WEATHERING 1. ______________________________ _____ 1. _____________________________ _____ 2. ______________________________ _____ 2. _____________________________ _____ 3. ______________________________ _____ 3. _____________________________ _____ 4. ______________________________ _____ 4. _____________________________ _____ 5. ______________________________ _____ 5. _____________________________ _____ 6. ______________________________ _____ Match weathering terms to weathering examples. Frost Action _____ A. Feldspar turns into clay Plant Acids _____ B. Blurred inscriptions of grave markers Hydrolysis _____ C. Carbonic acid dissolves rocks Abrasion _____ D. Large sheets of loosed rock break away from outcropping Gravity _____ E. Red soil or rocks Sulfuric Acid _____ F. Formation of potholes in winter Oxidation _____ G. Rocks falling from high places Organic Activity _____ H. Lichens growing on rocks Wetting and Drying _____ I. Drought causes soil to crack Carbonation _____ J. Rounded pebbles in a stream bed Joint Sheeting _____ K. Lifted sections of sidewalk along tree-lined streets PART C: Candy Crush 1. After looking at the pictures, discuss the similarities and differences between the pictures and the way they’re related with the people at your table. ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Describe the process and where you have seen “weathering” evidence in your daily life. ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Take the piece of candy that Ms. Glover has handed to you and unwrap it. DO NOT PUT IT IN YOUR MOUTH YET! (assign half of the class to briefly chew their candy before dissolving it in their mouths and the other half to NOT chew their candy) 4. Once Ms. Glover has told you to put it in your mouth, raise your hand when you are finished eating it. (document the time taken to dissolve each candy completely) 5. Explain to me how eating the candy has represented weathering. ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ (chewed candies were MECHANICALLY weathered (increasing the surface area of the candy) before the CHEMICAL weathering (saliva dissolving the candy) increased surface area speeds up weathering) 6. Complete the following concept map comparing the types of weathering and their causes. Also, describe the differences between the types of causes and provide examples. WEATHERING Mechanical Chemical Definition Definition Definition PART D 7. In each group, you have two beakers filled with water. One is marked “A” and has water in it. The other is marked “B” and has vinegar in it. a. PREDICT: which group is chemical weathering going to occur? Explain. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 8. Separate and unwrap the tablets. Two people will need to be time keepers and two people will be in charge of dropping the tablet in and saying stop. 9. Place one alka seltzer tablet into each beaker and watch to see which one dissolves quicker. Record the time in seconds. Beaker A____________________ Seconds Beaker B_____________________seconds 10. Which liquid (Beaker “A” or Beaker “B”) contained a substance that would chemically weather the tablets? How would mechanically weathering (crushing) the tablets beforehand dropping them into the beaker speed up the results? Explain how you came up with this conclusion. Was your “prediction” correct? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ Essential Lab Questions: 1. What types of weathering are prevalent in Edgewood compared to other parts of the country? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Thinking about the Grand Canyon, explain what type(s) of weathering that has occurred. How do you know? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________