Editable Lesson 2 Multi
advertisement

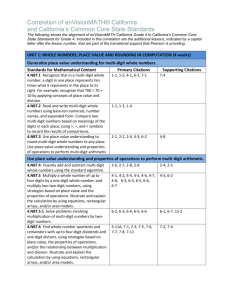
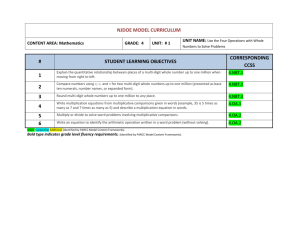
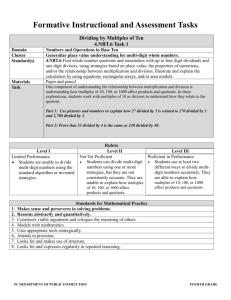
Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? Targeted Content Standard(s): Student Friendly Learning Targets 5.NBT.6 Find whole-number quotients of whole numbers with up to four-digit dividends and two-digit divisors, using strategies based on place value, the properties of operations, and/or the relationship between multiplication and division, illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models. I can… Divide multi-digit whole numbers. Explain how various models can be used to represent and solve problems involving division situations. Targeted Mathematical Practice(s): Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them Reason abstractly and quantitatively Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others Model with mathematics Use appropriate tools strategically Attend to precision Look for and make use of structure. Look for an express regularity in repeated reasoning Supporting Content Standard(s): (optional) 5.OA.1 Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols. Explanation of Rigor: (Fill in those that are appropriate.) Conceptual: Students will model division with multi-digit numbers using manipulatives, area models/arrays, and equations. Procedural: Students will use place value strategies and properties of operations to divide multi-digit whole numbers. Application: Students will apply their knowledge of the area model of division to solve real-life problems. Vocabulary: Divide Divisor Dividend Tens Hundreds Thousands Area model (length, width, area) Array Equation Parentheses Partial Quotient Quotient Evidence of Learning (Assessment): Pre-Assessment: Division-Subtraction Relationship, Division-Multiplication Relationship Formative Assessment(s): Dividing with Base 10 Blocks – Observation Checklist Array/Area Model for Division-Student Practice Sheet Partial Quotients Division Worksheet Column division vs. Partial quotients Formative Assessment Summative Assessment: 5.NBT.6 Base Ten Summative Assessment Multi-Digit Division Summative Assessment 1 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? Self-Assessment: 5.NBT.6 Multi-Digit Division Summative Self-Assessment Lesson Segments: 1. Assess student understanding of division/subtraction and division/multiplication relationships 2. Manipulative, area and array models for division 3. Solve real-world problems 4. Connecting area models and equations 5. Partial Quotients 6. Column Division 7. Assessment 2 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? Procedures: Segment 1 Approximate Time Frame: 20-30 minutes Focus: Assess students’ ability to connect area and multiplication. Lesson Format: Resources: Division-Subtraction Relationship Division-Multiplication Relationship Whole Group Small Group Independent Modeled Guided Collaborative Assessment Mathematical Practice Look Fors: MP4: Model with mathematics. Students should be making connections between the visual models and equations that they are using to represent multiplication of multi-digit numbers. MP7: Look for and make use of structure. Student’s visual models should represent the base 10 structure of numbers. Modalities Represented: Concrete/Manipulative Picture/Graph Table/Chart Symbolic Oral/Written Language Real-Life Situation Differentiation for Remediation: Have students model multiplication with either base 10 blocks or digi-blocks before making area models. Differentiation for English Language Learners: English language learners would benefit from being pretaught the vocabulary: “area model” and “array” before beginning this segment. Differentiation for Enrichment: Have students create real world situation word problems for each of the problems. Potential Pitfall(s): Students may have difficulty connecting visual models to justify procedures for multiplying multi-digit numbers. Independent Practice (Homework): Procedure: Teacher Notes/Reflections: Have students complete the Division-Subtraction and DivisionMultiplication Tasks independently. These documents are pre-assessments for this lesson. Students have used area models in the previous lesson for multiplication and in Grade 4 for division by 1-digit numbers. Students will build upon this experience to use area models and arrays for division of multi-digit numbers. 3 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? Segment 2 Approximate Time Frame: 90-100 min. Lesson Format: Whole Group Small Group Independent Modeled Guided Collaborative Assessment Focus: Students will create manipulative, area and array models for division. Math Practice Look For(s): MP4: Model with mathematics. Students will use base ten blocks to connect place value concepts to model the process of division. MP5: Use appropriately tools strategically. Look for students to strategically use the base 10 blocks to represent division. Students should know when to break up the 100 into 10 tens to represent the division situation. MP7: Look for and make use of structure. Students can see and understand how numbers are put together as parts and wholes. Resources: Base 10 Blocks Tape to make a Workmat (optional) Dividing with Base 10 Blocks Worksheet Dividing with Base 10 Blocks Observation Checklist Modalities Represented: Concrete/Manipulative Picture/Graph Table/Chart Symbolic Oral/Written Language Real-Life Situation Differentiation for Remediation: Students may benefit from being reminded how to write numbers in expanded notation to determine where to segment the diagram into sections. Differentiation for English Language Learners: Permit ELLs to work with partners who speak the same language and discuss their representations in their native language. Differentiation for Enrichment: Students who are using mental math or multiplication to solve problems should be asked to justify their calculations using visual models. They should also be asked to connect the written equations (using parentheses) to the visual models. Students can solve problems such as 403 ÷ 31, where it requires regrouping in the dividend. Students have to keep in mind that a rectangular array must be formed with the dividend. Example: 4 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? Potential Pitfall(s): Some students may not choose to use hundreds, but only work with tens and ones. Students may have difficulty representing the portions of the diagram with equations. They may not know where to divide the diagram into portions. Students may need to be reminded that the dividend should form a rectangular array. Independent Practice (Homework): 1) Write an equation for the following base ten blocks: Answer: 396 ÷ 33 = 21 2) Draw a representation for 231 ÷ 21 = 5 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? Procedure: Teacher Notes/Reflections: 1. Group students in partners or triads. Give each pair/triad 5 hundreds, 30 tens, 30 ones and a workmat. 2. Have the partners collaboratively build the number 320 out of base 10 blocks. 3. Next, tell them they will need to divide these into equal groups of 20. (If students can do this mentally, have them create the visual model to justify their calculation.) 4. Observe how students are arranging their groups. See if any students arrange their models in an array. Listen to students discussions as they collaborate with their partners to hear their strategies. (Observation Checklist) 5. If any students have arranged their manipulatives into an array, have them share their work. If not, model for students how you can arrange the base 10 blocks into an array using the workmat. (See diagram- The green represents the divisor 20 shown with 2 tens. The blue represents the dividend 320 shown as 2 hundreds and 12 tens. Start with the divisor and then lay the blocks for the dividend to line them up along the divisor blocks. Finally ask what block would be multiplied by 10 to equal 100? What block would be multiplied by 1 to equal 10? Lay the blocks down accordingly. quotient divisor dividend *Note: If the students have not used base ten blocks to model multiplication, they may need help understanding that the width of the divisor is the width of the dividend and the length of the quotient is the length of the dividend. *Students need to think about how to arrange the dividend into a rectangular array based upon the number of equal groups that must be created. 6. Once the students model the problem with base ten blocks, they can connect it to an area picture (not drawn to scale). Ask them how this picture connects back to the area model of multiplication. 10 + 20 200 6 120 6 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? 7. Have students repeat the process with their partners and then ask them to try to solve 440 ÷ 22 using the base ten blocks Teacher Notes/Reflections: *Note: The teacher may initially model how to place the divisor (green) on the workmat first and allow the students to explore how to place the dividend (blue). on the workmat. Once they have it placed they can determine the quotient (red). quotient divisor dividend 8. Once the students model the problem with base ten blocks, they can connect it to an area picture (not drawn to scale). 20 20 + 2 400 40 9. Again observe and listen using the observation checklist with the groups. Have students share out and then try to solve 132 ÷ 12 with the blocks. 7 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? Segment 3 Approximate Time Frame: 45-50 minutes Focus: Lesson Format: Resources: Whole Group Small Group Independent 5.NBT.6 Base Ten Assessment Modeled Guided Collaborative Assessment Modalities Represented: Concrete/Manipulative Picture/Graph Table/Chart Symbolic Oral/Written Language Real-Life Situation Students will apply their knowledge of base ten blocks and division to solve real world problems. Math Practice Look For(s): Differentiation for Remediation: MP1: Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. Students will be able to plan a solution that makes sense of the problem by connecting their prior knowledge of dividing with base ten blocks. Allow students to use base ten blocks to help solve the problem. MP3: Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. Students will cite evidence and develop a logical argument. Define length, width, and area to assist with the garden problem. Differentiation for English Language Learners: Differentiation for Enrichment: Have the students create another possible solution using 224 as the dividend. Then either use base ten blocks to model the solution or draw a diagram of the base ten blocks. Potential Pitfall(s): Independent Practice (Homework): In the garden problem, students need to find various unknowns within the dividend and quotient. They need to analyze the problem and determine a strategy to figure out the various problems which includes eliminating unnecessary information. Procedure: Teacher Notes/Reflections: 1. Either assign partners or small groups to work together to solve the assessment. 8 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? Segment 4 Approximate Time Frame: 135-150 minutes Lesson Format: Whole Group Small Group Independent Modeled Guided Collaborative Assessment Focus: Students will connect arrays to area models and use equations to represent the division situations. Resources: Array/Area Model for DivisionTeacher Notes Array/Area Model for DivisionStudent Practice Sheet Division Array/Area Model Formative Assessment Modalities Represented: Concrete/Manipulative Picture/Graph Table/Chart Symbolic Oral/Written Language Real-Life Situation Math Practice Look For(s): Differentiation for Remediation: MP2: Reason abstractly and quantitatively. Students need to reason to appropriate divisors to use when dividing using the array model. Students need to be able to use all of the operations to solve the problems. You may want to list the multiples of the divisor from 1-10 instead of just the multiples of 2, 5, and 10 in the help box. MP4: Model with mathematics. Students will use the area model to bridge the understanding of division with base ten blocks to partial quotients. For students that need a visual that is drawn to scale, they may begin with a smaller dividend and draw it to scale on centimeter grid paper. Differentiation for English Language Learners: MP7: Look for and make use of structure. Students can see and understand how the dividend can be broken into smaller parts. Differentiation for Enrichment: Potential Pitfall(s): Independent Practice (Homework): Some people prefer to draw a large rectangle first and divide it in sections as they solve the problem. Some prefer to build the sections, as they solve it. However, the rectangles do not need to be drawn to scale which may lead to some confusion. Encourage the students to create multiple solutions using the area model and then describe which one was the most efficient. A fish tank at the Shedd Aquarium holds 6,358 gallons of water. If every fish needs 13 gallons of water to survive, how many fish can be safely put into the tank? Use an array model to solve the problem. Or you can use the Division Array/Area Model Formative Assessment. 9 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? Procedure: 1. Review the Array/Area Model for Division-Teacher notes prior to the lesson. It clearly defines how to model the method and offers examples that can be used with the students in the Student Practice Sheet. 2. You may choose to watch the Teacher Tube video listed in the notes by yourself or as a class. 3. The benefits of this division method are that it is a visual representation that connects the multiplication area model and it allows the students to use different factors, which provides differentiation. 4. Prior to solving the problem, it may be beneficial to create a “help box” that offers multiples of the divisor. 2, 5, and 10 were chosen for the “help box” because they are basic factors that can later transfer to mental math. Work out the following problem on the board. Help Box Problem: 494 ÷ 13 13 x 2 = 26 13 x 5 = 65 Example 1: 13 x 10 = 130 Step 1: Draw a rectangle to represent the area model and record the divisor on the left. Eventually the area of the rectangle will be equal to the dividend. Step 2: Choose a multiple of 2, 5, or 10 so that 13 x that multiple = a number less than 494. Possible dialogue: “What would be the best number to choose to multiply by 13 to get an answer close to 494? 2, 5, or 10?” 10 494 - 130 13 130 364 10 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? Step 3: Choose a multiple of 13 that gets close to 364 without going over. Possible dialogue: “I chose 10 last time and it equaled 130, this time I am going to chose 20 so I can get closer to 364.” 10 20 260 130 13 494 Teacher Notes/Reflections: 364 -130 -260 364 104 Step 4: Continue to choose a multiple of 13 until you no longer have a remainder or that the remainder is less than the divisor. Answer: 10 13 20 260 130 494 364 104 39 5 2 1 65 26 13 13 -130 -260 - 65 -26 -13 364 104 39 13 0 Step 5: Then add 10 + 20 + 5 + 2 + 1 = 38. 11 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? Teacher Notes/Reflections: Therefore, 494 ÷ 13 = 38 5. Hand out the Array/Area Model for DivisionStudent Practice Sheet. Continue to solve practice problems either as a class, small groups, or partners until the students feel comfortable. Refer to the Array/Area Model for DivisionStudent Teacher Notes to promote dialogue. Remember that students can solve these problems multiple ways. Allow them to discuss and share their thoughts. For example, in the earlier problem, one could have solved it like this: 13 10 10 10 5 130 130 130 65 39 3 OR 13 30 8 104 104 12 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? Segment 5 Approximate Time Frame: 90-100 min. Focus: Lesson Format: Resources: Use any division worksheet used in the past, but have the students use partial quotients method to solve the problems. Whole Group Small Group Independent Modeled Guided Collaborative Assessment Modalities Represented: Concrete/Manipulative Picture/Graph Table/Chart Symbolic Oral/Written Language Real-Life Situation Students will use the partial quotients method to divide multi-digit whole numbers. Math Practice Look For(s): MP2: Reason abstractly and quantitatively. Students need to reason to appropriate divisors to use when dividing using the partial quotients method. Students need to be able to use all of the operations to solve the problems. MP6: Attend to precision. The students are using place value concepts to help them calculate accurately and efficiently. Differentiation for Remediation: Initially, provide students with a completed area model of the same product so they can see the direct connection to the partial product method. Differentiation for English Language Learners: Students will need clarification of divisor, dividend, and quotient. Differentiation for Enrichment: MP7: Look for and make use of structure. Students can see and understand how the dividend can be broken into smaller parts. Potential Pitfall(s): Independent Practice (Homework): Initially, students will use 2 or 10 as the only choice when dividing the dividend into smaller parts. Therefore, students need ample time to solve the problems in multiple ways so they can become more efficient in choosing factors. Have students create a word problem for 368 ÷ 23. Then write out the steps to solve it using number and words such as the bookshelf problem. Procedure: Teacher Notes/Reflections: The partial quotient method is an algorithm similar to the area model in the fact each step gets us closer to the quotient. Each step along the process allows the students to think of the values of the numbers. 13 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? NOTE: While students proceed throughout the lesson encourage them to discuss the connections to the area model. Also encourage them to solve the problem using various multiples of the divisor. As they discuss with each other, they will become more efficient in their problem solving. Teacher Notes/Reflections: 1. This example, 494 ÷ 13, is the same problem used in the previous Area Model lesson so you may want to post the diagram on your board and refer back to it so students can connect this process to it. Pose the following problems: A used bookstore has 494 books that need to be placed on 13 shelves. How many books are on a shelf? 1. Explain that 10 books are on each shelf, thus 130 books are dispersed all together. 2. There are still enough books left to put at least 20 more books on each shelf, 260 more books are put on the shelf. 3. Continue to put books on each shelf until all the books are put onto the shelves. Then determine how many books are on a shelf. 38 books/shelf. Encourage a discussion among the students, could they have put the books on the shelf differently? 14 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? Problem: Your family bought a new couch for $2469 and signed up for a payment plan through the store. The minimum amount to pay is $32 per month. How many months will it take to pay it off, if they only pay the minimum amount each month? While the students continue to complete sample problems, have them work in pairs. Use one paper and pencil and pass the paper back and forth to solve the problem. Each time they receive the paper, they try to divide by the largest number possible. Then pass it back to their partner to solve it. They continue to pass it back and forth until there is no remainder or the remainder is less than the divisor. During each step, the partner double- checks the work. 15 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? Segment 6 Approximate Time Frame: Lesson Format 90-100 min. Whole Group Small Group Independent Focus: Modeled Guided Collaborative Assessment Resources: Column division vs. Partial quotients Formative Assessment Modalities Represented: Concrete/Manipulative Picture/Graph Table/Chart Symbolic Oral/Written Language Real-Life Situation Students will learn the column division strategy to divide multi-digit whole numbers. Math Practice Look For(s): MP6: Attend to precision. The students are using place value concepts to help them calculate accurately and efficiently. Differentiation for Remediation: Allow students to use the area model or partial quotients method. Differentiation for English Language Learners: Differentiation for Enrichment: MP3: Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. Students will cite evidence and develop a logical argument. Potential Pitfall(s): Independent Practice (Homework): Students will rely on mnemonics instead of place value understanding to solve problems using the column division strategy. Procedure: Independent Practice (Homework): 1. Either assign partners or small groups to work together to solve the assessment. 2. Listen to the students’ discussion and address any misconceptions. Help students focus on place value while analyzing the work. 3. Once the students discover that “Katie’s way” of solving the problem is acceptable, teach more problems using the column method/aka traditional method. 4. Be sure to stress the place value when solving division. For example: When solving the problem, 855 ÷ 19, it is misleading to say, “There are 4 groups of 19 in 85?” Instead state, “There are 40 groups of 19 in 855.” 16 Grade 5 Lesson Title: Multi-Digit Division Unit 1: Whole Number Computation and Applications Time Frame: 7-12 days Essential Question: How do you choose different division strategies to divide multi-digit numbers? Segment 7 Approximate Time Frame: 40-50 minutes Focus: Lesson Format: Whole Group Small Group Independent Modeled Guided Collaborative Assessment Assess students conceptual and procedural understanding of division of multi-digit whole numbers. Resources: Multi-Digit Division Summative Assessment Self-Assessment Modalities Represented: Concrete/Manipulative Picture/Graph Table/Chart Symbolic Oral/Written Language Real-Life Situation Math Practice Look For(s): Differentiation for Remediation: MP5: Use appropriate tools strategically. Students can decide what is the best method for them to solve the multi-digit division problem. Differentiation for English Language Learners: Differentiation for Enrichment: MP7: Look for and make use of structure. Through the use of place value concepts and partial quotients, students can understand the structure behind dividing multi-digit whole numbers. MP8: Look for an express regularity in repeated reasoning. After students have fully developed conceptual understanding of multi-digit division, they can fluently use a standard algorithm to solve a problem. Potential Pitfall(s): Independent Practice (Homework): Procedure: Decide if you would like to assess the students individually or with partners. Afterwards, have the students self-assess themselves. 17