Sodium-24: Uses, Advantages, and Disadvantages
advertisement

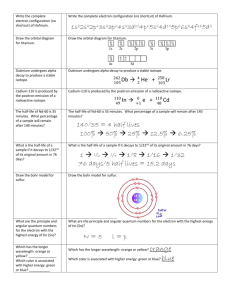
Sodium-24 (from http://nsb.wikidot.com/c-9-2-5-6) 23 11𝑁𝑎 24 11𝑁𝑎 + 10𝑛 → → 24 12𝑀𝑔 24 11𝑁𝑎 +𝛾 + −10𝑒 + 2𝛾 Sodium-24 is a widely used radioisotope in industry for the detection of leaks in pipes. It is created through neutron bombardment of Sodium-23. Advantages of using Sodium-24 Sodium and magnesium are both non-toxic to humans and animals. Magnesium-24 is a stable isotope so emits no radiation. Although sodium-24 may form organic compounds when absorbed into the blood stream, this will not unduly affect the health of humans or animals absorbing it due to a variety of other factors such as its short half-life and low intensity emission of gamma radiation. Sodium-24 is a beta and low intensity gamma emitter, so no radiation will be detected if the pipe has not sprung a leak as the radiation emitted will not be able to penetrate the pipe's thick walls. Sodium-24, being a beta emitter, may potentially be harmful to humans and animals if ingested or directly injected into the bloodstream. However, having a short half-life of roughly 15 hours, Sodium-24 does not pose a significant threat to humans or animals. Disadvantages of using Sodium-24 Sodium-24 is a non-naturally occurring radioisotope, so it relies on commercial production in nuclear reactors and poses the same threats that nuclear reactors have. i.e. nuclear fallout and disasters. Having a short half-life prevents the point of use from being very far from the source of production of the isotope. Radioisotopes have long term effects and implications to workers handling them. Without proper care in transportation and handling, Sodium-24 can cause biological damage, which may result in tissue damage or cancer. In conclusion: Sodium-24 is a very effective means of detecting leaks in industry. Although suffering from some minor disadvantages, it is widely used in industry because of its ability to efficiently detect of leaks. More info about radioisotopes here: http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/inf56.html