6.1 Class Notes
advertisement

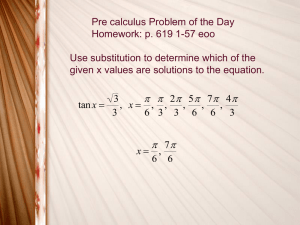
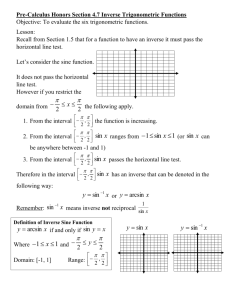
Section 6.1 – Inverse Trigonometric Functions Objective: In this section you will learn how to evaluate the inverse trigonometric functions and compositions of trigonometric functions and inverse trigonometric functions. I. Inverse Sine Function The sine function is not a one-to-one function. We know this because the graph of y sin x fails the _______________________________________. Therefore, to define an inverse function for sine we must restrict the domain. The domain of y sin x is restricted to ______________________________ in order to have a one-to-one function that obtains all possible values of y sin x . The inverse sine function is defined by: y sin 1 x if and only if _____________________ where _____ x _____ and _____ y ______. That is, the domain of y arcsin x is ___________________ and the range is ______________________. Example 1: Find the exact value: a. arcsin( 1) = ______________ c. II. b. sin 1 (1/ 2) = _______________ arcsin( 3 / 2) = _____________ Inverse Cosine Function The inverse cosine function is defined by: y cos 1 x if and only if _____________________ where _____ x _____ and _____ y ______. That is, the domain of y arccos x is ___________________ and the range is ______________________. Example 2: Find the exact value: a. arccos(1 / 2) = ______________ c. arccos( ) = _______________ b. cos 1 ( 2 / 2) = __________ III. Inverse Tangent Function The inverse tangent function is defined by: y tan 1 x if and only if _____________________ where _____ x _____ and _____ y ______. That is, the domain of y arctan x is ___________________ and the range is ______________________. Example 3: Find the exact value: a. arctan( 3 ) = ___________ tan 1 (1) = _______________ b. Example 4: Use a calculator to approximate to four decimal places. IV. a. arccos( 0.85) = ________________ c. arctan( 8) = __________________ b. sin 1 (4.215) = ________________ Other Inverse Trigonometric Functions I will not expect you to memorize the domains and ranges for the other inverse trigonometric functions. You may refer to the chart on p.265 of your text to assist you in evaluating these functions. I do expect you to memorize the domain and range for the inverse functions of sine, cosine, and tangent. V. Compositions of Functions Example 5: a. 1 sin sin 1 = _________________ 2 c. sin sin 1 = __________________ tan tan 1 1 = _______________ sin sin 1 x = _____________. Similarly, as long as ___________________________, a. 2 = ___________________ sin arcsin 2 Hence, as long as ___________________________, Example 6: b. cos cos1 x = _____________. b. tan arctan 3 = ____________________ Hence, as long as ____________________________, tan(arctan x ) = __________________. Example 7: Hence, a. sin 1 sin = _________________ 4 c. 11 sin 1 sin = ________________ 6 b. 2 arcsin sin = ___________________ 3 sin 1 sin x x only when ____________________________. If x is not in this interval, BE CAREFUL! Similarly, arctan tan x x only when __________________________. Example 8: a. arctan tan = _______________ 3 b. tan tan Example 9: a. cos 1 cos = ______________ 3 b. arccos cos Hence, 1 3 = _________________ 4 7 = _________________ 6 cos 1 cos x x only when ____________________________. If x is not in this interval, BE CAREFUL! What if you need to find the composition of a trig function and the inverse of a different trig function? Example 10: a. 3 sin cos 1 = _________________ 7 b. 3 5 cos sin 1 cos 1 = _________________ 4 13