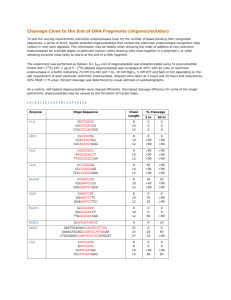
here
advertisement

Common Abbreviations and Acronyms These common abbreviations can be used in abstracts without explicitly defining them. For less-common abbreviations, spell the phrase in full the first time it appears, followed by the abbreviation in parentheses. For example: “Cleavage of genomic DNA at unintended positions—so-called ‘off-target cleavage’ (OTC)—hampers the use of engineered nucleases (EN) for gene therapy. We describe an assay to measure the extent of OTC by a variety of ENs…” aa amino acid In the context of protein: A Ala; alanine C Cys; cysteine D Asp; aspartic acid (aspartate) E Glu; glutamic acid (glutamate) F Phe; phenylalanine G Gly; glycine H His; histidine I Ile; isoleucine K Lys; lysine L Leu; leucine M Met; methionine N Asn; asparagine P Pro; proline Q Gln; glutamine R Arg; arginine S Ser; serine T Thr; threonine V Val; valine W Trp; tryptophan X any amino acid Y Tyr; tyrosine AdoMet (or SAM) EtBr ELISA EMSA GST IVC PCR SDS PAGE SDA RCA SELEX SMRT® DNA RNA oligo bp S-adenosylmethionine ethidium bromide enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay electrophoretic mobility-shift assay Glutathione S-transferase in vitro compartmentalization polymerase chain reaction sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis strand-displacement amplification rolling-circle amplification systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment single-molecule, real-time (sequencing) deoxyribonucleic acid ribonucleic acid oligonucleotide base pair nt ds ss nucleotide double-stranded single-stranded In the context of DNA or RNA: A adenine G guanine C cytosine T thymine U uracil Y C or T (pyrimidine) R A or G (purine) S C or G (strong H-bonds) W A or T (weak H-bonds) M A or C (commonly modified bases) K G or T (not commonly modified) H A, C, or T (not G) B C, G, or T (not A) V A, C, or G (not T) D A, G, or T (not C) N A, C, G, or T (any base) m or me 5mC 4mC 6mA 5hmC (or hmC) 5fC 5CaC 5hmU (or hmU) methyl 5-methylcytosine N4-metyhylcytosine N6-methyladenine 5-hydroxymethylcytosine 5-formylcytosine 5-carboxycytosine 5-hydroxymethyl uracil R M S R-M C V (or Vsr) ENase MTase Dnmt NEase REase CD DBD MBD TRD TET restriction modification specificity restriction-modification (system) control protein very short-patch repair: T:G and U:G mismatch endonuclease restriction enzyme, or restriction endonuclease modification enzyme; prokaryotic DNA-methyltransferase eukaryotic DNA-methyltransferase DNA-nicking endonuclease restriction endonuclease catalytic domain DNA-binding domain methyl-binding domain target recognition domain ten-eleven translocase GT HR gene-targeting homologous recombiunation NHEJ HDR DSB non-homologous end-joining homology-directed repair double-strand break HEase ZF ZFN TALE TALEN RVD RGN CRISPR Cas9 dCas9 crRNA PAM sgRNA tracrRNA homing endonuclease zinc-finger protein engineered zinc-finger nuclease transcription activator-like effector protein (from Xanthomonas) engineered TALE nuclease repeat-variable di-residue RNA-guided nuclease clustered, regularly interspaced, short palindromic repeats CRISPR-associated nuclease (from Streptococcus pyogenes) catalytically defective (inactive) Cas9 variant CRISPR RNA protospacer-adjacent motif single-guide RNA trans-acting crRNA