Appendix 2 - Rode Rage
advertisement

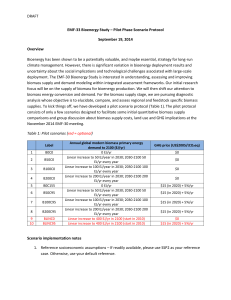
APPENDIX 2 “Bioenergy is energy derived from biomass, which is organic material such as wood, plants, or animal wastes. Bioenergy can be used to generate electricity, produce heat, and also for the production of biofuels.” (Bioenergy WM, 2006. http://www.bioenergywm.co.uk/default.aspx) Bioenergy involves taking conventional power generation to extract considerable amounts of clean, low-emission electricity from many different agricultural crop wastes, plantation wood waste, garden and food waste, sugar cane, sewage and animal wastes. It generates power through a renewable source that is stored and well controlled. ‘Throughout Australian capital cities landfill gas plants are already in operation for over 90% of the year which is comparable to traditional energy power stations. By using Bioenergy, one mega watt hour saves one tone of CO2.’ (Clean Energy Council, 2007. www.cleanenergycouncil.org.au) Bioenergy can be classified according to either fuel or the type of technology used to generate the electricity. Bioenergy type Examples methane gas landfills and sewage treatment plants wet wastes abattoirs, feedlots and food processing dry agricultural byproducts sugar cane waste municipal mixed wastes household garbage and pruning’s with recyclables removed forestry by-products remnant material from existing sawmills and managed forestry operation (NSW Government Department of Water and Energy, 2009 http://www.dwe.nsw.gov.au/energy/sustain_renew_bioenergy.shtml) Some advantages include: It can be produced using waste matter Save the environmental and economic costs Possibility of increasing the economy if used in mass amounts, reducing the need to import fossil fuels Reduces carbon dioxide in the atmosphere It is a potentially renewable natural resource that would help supply energy indefinitely. The Disadvantages include: Biomass has smaller energy content then fossil fuels Higher cost of labor, transportation and storage With the drought, water and nutrients are in short supply are needed for biomass crops There is no demand for Bioenergy until there are cost saving initiatives, but these initiative will not been seen until there is a demand for Bioenergy, or non-renewable resources are more expensive (Primary ways of using Bioenergy, 2009. http://science.jrank.org/pages/867/Bioenergy.html) How it reduces green house emissions? (NSW Government Department of Water and Energy, 2009 http://www.dwe.nsw.gov.au/energy/sustain_renew_bioenergy.shtml) Black balloons are used to describe measure and visualize greenhouse emissions. It is a recent Victorian campaign to advertise the reduction of greenhouse emissions. A balloon is estimated to hold 50 g of green house gasses. (Resource smart, 2009. http://www.saveenergy.vic.gov.au/getthefacts/whatisblackballoon.aspx) Reference: Bioenergy WM, 2006. http://www.bioenergywm.co.uk/default.aspx Clean Energy Council, 2007. www.cleanenergycouncil.org.au NSW Government Department of Water and Energy, 2009. http://www.dwe.nsw.gov.au/ energy/sustain_renew_bioenergy.shtml Primary ways of using Bioenergy, 2009. http://science.jrank.org/pages/867/Bioenergy.html Resource smart, 2009. http://www.saveenergy.vic.gov.au/getthefacts/whatisblackballoon.aspx