Original Research Article Functional and Structural Impact of ATP
advertisement

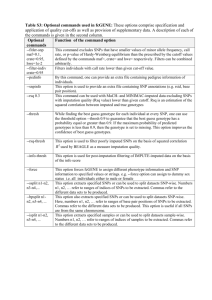
Original Research Article Functional and Structural Impact of ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter A1 R219K and I883M gene polymorphisms in obese children and adolescents Manal S. Fawzy 1*, Osama Alhadramy2, Mohammad H Hussein3, Hussein M. Ismail2,4, Nesreen M. Ismail5, Nouran M. Biomy6, Eman A. Toraih7* Supplementary Fig. 1. Human ABCA1 gene structure and transcripts. Reference GRCh38.p2 Primary Assembly, Homo sapiens Annotation Release 106 (updated December 2013). ABCA1 gene coordinates at 104781002 to 104928237. Transcription of ABCA1 gene produces 15 different mRNAs, 8 alternatively spliced variants and 7 unspliced forms. The mRNAs appear to differ by truncation of the 5' end, truncation of the 3' end, presence or absence of a cassette exon, overlapping exons with different boundaries, splicing versus retention of 3 introns. The current figure shows 4 common alternative transcripts of ABCA1 gene produced by alternative splicing. The longest ABCA1-002 transcript spans 49 coding exons of 10494 bp length. It encodes an open reading frame (ORF) of 6,783 bp, thus, translated to 2,261 residue protein. (Data source from ECgene software: Genome Annotation for Alternative Splicing and Ensembl). (a) (b) (c) [ Supplementary Fig. 2. Functional annotations of human ABCA1 protein. (a) Gene ontology (GO) of human ABCA1. The transmembrane ABCA1 protein participates in multiple cellular processes, including phospholipid translocation, positive regulation of cholesterol efflux, steroid metabolic process, protein amino acid lipidation, peptide secretion, phagocytosis, engulfment, and transport. (Data from: Ontologies according to Gene Ontology Consortium 01 Apr 2014 via Entrez Gene). (b) The STRING network view of ABCA1 protein. The network nodes are proteins. Predicted functional links between the proteins are indicated by edges. Modes of action are shown in different colored lines. A blue line indicates binding interaction; a grey line with green arrow shows proteins which activate ABCA1 protein; black edge states for reaction evidence. The string global score (confidence score) was adjusted to be greater than 0.95. ABCA1, ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 1; APOA1, apolipoprotein A-I; PLTP, phospholipid transfer protein; APOE, apolipoprotein E; NR1H2, nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group H, member 2; ARHGEF11, Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 11; APOB, apolipoprotein B; PRARA, peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptor alpha; SPTLC1, serine palmitoyltransferase, long chain base subunit 1. (http://string.embl.de/) (c) Subcellular localization of ABCA1 protein. The ABCA1 transmembrane protein is localized in various components (endoplasmic reticulum membrane, plasma membrane, Golgi apparatus). Within cells, ABCA1 is present in early and late endosomes and lysosomes, and ABCA1-containing vesicles recycle between the plasma membrane and intracellular sites. The confidence of each association is noted by the grade of green color with the highest confidence shown by darker color. (Derived from Compartment database annotations, automatic text mining of the biomedical literature, and sequence-based predictions). (a) 300 Number of coding SNP 250 200 150 100 50 0 Silent (b) Missense Nonsense (c) C HW M L Y S Q R N V Probably damaging 29% P G D K F E I A Possibly damaging 12% Benign 59% T (d) Supplementary Fig. 3. Distribution of coding single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the human ABCA1 gene. (a) Distribution of coding SNPs according to their molecular consequence. (Data source: SNPs/Variants are retrieved from the NCBI SNP Database of short genetic variations, Ensembl, and PupaSUITE, with descriptions from UniProtKB). (b) Frequency of mutated amino acid residue in non-synonymous variants. The two most frequent amino acids that are changed into alternative ones were Arginine and Glycine, representing 17.7% and 10.3% respectively. (Data source: Ncbi: dbSNP) (c) Distribution of missense variants in the coding region according to the predicted functional effect of amino acids substitution using PolyPhen-2 (Polymorphism Phenotyping v2) program. The predicted mutation outcome is classified as benign, possibly damaging, or probably damaging. Half of the variants in the Arginine residues and all the Isoleucine amino acid mutations were benign. The studied SNP in particular was predicted to be benign by both PolyPhen (http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/) and MutPred (http://mutpred.mutdb.org/) algorithms. (d) Location of coding missense polymorphisms in the ABCA1 protein. Schematic representation of the graduated 2261 residue protein is indicated in black line. Location of important domains is colored. Boxes in red: cytoplasmic loop, blue: extracellular loops, yellow: transmembrane domains. Coding SNPs (cSNPs) are described according to the Standard Nomenclature Recommendations of the Human Genome Variation Society (HGVS). The first one letter amino acid residue is substituted with the last letter at the codon position described. More than 50 mutations are described, many of which show a nonrandom distribution and cluster in specific regions of the protein. cSNPs causing the autosomal recessive high density lipoprotein deficiency 1 (HDLD1) in blue, dominant HDLD2 disorder in light blue, known to be associated with higher risk of atherosclerosis, premature coronary heart disease, and ischemic heart disease in orange, associated with increased plasma HDL-c levels in green, deficient plasma HDL-c levels in red, decreased cellular cholesterol efflux is underlined. *Mutant protein is trapped in endoplasmic reticulum. & Impaired trafficking of mutant version to plasma membrane. (a) (b) (c) (d) Supplementary Fig. 4. Haplotype block structure in ABCA1 gene in African Ancestry. (a) Haplotype block structure is indicated by triangular segments; shading indicates strength of linkage disequilibrium (LD) as measured by D′, which is provided in the intersecting squares. Squares with significant linkage disequilibrium (LOD ≥ 2) are shaded from light pink to red with D′ = 1 being bright red. Black triangle is enlarged. R219K (rs2230806) is shown by yellow arrow. Linkage disequilibrium data of ensemble: 1000GENOMES:phase_3: African Ancestry in Southwest US. (b) Enlarged triangle for R219K SNP (shaded in black). Spacing of nearby SNPs along gene is given at the top of the plot. Yellow SNPs are missense while Blue SNPs are intronic variants. (c) Haplotype block structure of I883M (rs2066714). (d) Enlargement of the black triangle showing LD with nearby SNPs. (a) (b) (c) Supplementary Fig.5. General information about the genotyped single nucleotide polymorphisms in ABCA1 gene. ABCA1: ATP binding cassette transporter A1; R219K: Arginine to Lysine at position 219; I883M: Isoleucine to methionine at position 883; bp: base pair; aa: amino acids. (a) Position of R219K and I883M SNPs in ABCA1 gene (NC_000009.12) at chromosome 9q31.1: Reference GRCh38 human assembly, Annotation release 107 (updated December 2013). ABCA1 gene coordinates at 104781002 to 104928237, reverse strand. Thus the gene spans 147,235 bp. Green line shows the longest ABCA1-002 protein-coding transcript spans 49 coding exons of 10494 bp length and encodes an open reading frame (ORF) of 6,783 bp. The first SNP (rs2230806, R219K) in red: exists in exon 7 position 113, having nucleotide substitution (1051G>A, c.656G>A). The second SNP (rs2066714, I883M) in blue: exists in exon 18 position 107, having nucleotide substitution (3044A>G, c.2649A>G). (b) Schematic representation of domains and motifs of ABCA1 protein (ENSP00000363868, O95477). The whole protein of ABCA1-002 transcript consists of 2261 amino acids (254,302 Da) represented in black box, membrane-spanning regions in yellow boxes, two ATP-binding domains in grey, Walker A motif/P-loop in violet, Q-loop in blue, Walker B motif in red, D-loop in green, and H-loop/switch region in brown. Position of the two studied missense mutations is allocated R219: p.Arg219Lys (red arrow) and I883M: p.Ile883Met (blue arrow). (Data orginate from Protein Database and UniProtKB). (c) Model for secondary structure of human ABCA1 protein. Graphical representation of the topology of ABCA1 generated with ProtterServer. ABCA1 protein is predicted to have 15 transmembrane domains (numbered), in addition to 8 intracellular and 8 extracellular domains. The two experimentally tested variants in the study are shown in red (R219K) and blue (I883M). Both are located in the extracellular domains. (Annotation data sources: UniProtKB, Phobius predictions, ExPASy PeptideCutter, PeptideAtlas database) [11]. (b) * 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% F M Ch Ad Normal weight control group GG GA AA 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% F M AA Ch Overweight/Obese group Ad AG GG * 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% F M Ch Ad Normal weight control group (d) * 100% Frequency of I883M genotypes Frequency of R219K genotypes AA 100% (c) Frequency of R219K genotypes GA Frequency of I883M genotypes GG (a) AA AG GG 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% F M Ch Ad Overweight/Obese group Supplementary Fig. 6. Genotype frequencies of R219K and I883M polymorphisms in the study groups stratified by age and gender. F; female, M; male, Ch; children, Ad; adolescents. Chi square test (two-sided) was used. (*) P-values <0.05 are statistically significant. (a) R219K polymorphism GG (n=10) GA (n=67) AA (n=51) 5 *# 4 *# 3 *# 2 * 1 0 TC/HDL-c TG/HDL-c LDL/HDL-c (b) I883M polymorphism AA(n=66) AG (n=52) GG (n=10) 5 4 3 2 1 0 TC/HDL-c TG/HDL-c LDL/HDL-c Supplementary Fig. 7. Cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight/obese subjects with different ABCA1 genotypes. Values are expressed as means. TC, Total cholesterol; TG, Triglycerides; HDL-c, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-c, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Comparison between genotypes of R219K (a) and I883M (b) polymorphisms were performed by one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test. (*), Indicates significant difference from homozygous carriers of the wild allele in the same group at P < 0.05. (#), Indicates significant difference from heterozygous carriers in the same group at P < 0.05. (a) R219K (b) I883M 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% Egyptian (Current study) Egyptian (Current study) Tunisian Chinese Iranians Singaporean Chinese Spanish Japanese Danish Canadians French Americans Hungarian Spanish Americans Hungarian I Germans M Danish French Polish R K Supplementary Fig. 8. Allele frequencies of R219K and I883M polymorphisms of ABCA1 gene in various populations [47, 48].