Communication Skills Test Questions: Culture & Nonverbal Cues
advertisement

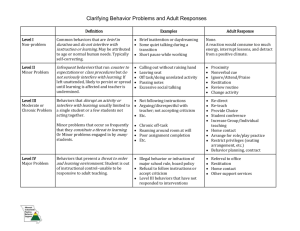
Hamilton, Communicating for Results, 10th Edition, Chapter 05 1. What level of culture refers to the behaviors we learn subconsciously through imitation and modeling? a. Formal level b. Informal level (CORRECT) c. Technical level d. Social level e. Personal level 2. At the technical level of culture, unintentional broken rules or behaviors result in very little emotional involvement. a. True (CORRECT) b. False 3. Some generally accepted workplace examples of the formal level of culture in the United States include: a. The executive sits at the head of the table b. Employees should arrive on time or early c. Office hours are 9 to 5, with lunch from 12 to 1 d. Higher ranking professionals have larger offices e. All of these (CORRECT) 4. At the informal level of culture, unintentional broken rules or behaviors result in very little emotional involvement. a. True b. False (CORRECT) 5. Facial expressions account for less than 10% of the meaning in nonverbal messages. a. True b. False (CORRECT) 6. The most expressive area of the face is/are the: a. Eyes (CORRECT) b. Mouth c. Nose d. Forehead e. No one area of the face is more expressive than another 7. The habitual gestures and movements we use in times of discomfort are called: a. Emblems b. Illustrators c. Regulators d. Adaptors (CORRECT) e. Pacifying behaviors 8. Research shows that overdressing (wearing higher authority symbols than the authority level of the actual position) is a way to make others trust you. a. True b. False (CORRECT) 9. Unlike the technical level, the formal level has rules a. Clearly stated, but the reasons for the rules are not * b. That are not clearly stated and the rules for them are clearly defined c. That are not clearly stated nor are the rules clearly stated d. None of the above 10. Ms. Bergen asks her team who is willing to be the team lead for the upcoming project. Mark looks directly at her and doesn’t break his gaze while the other people looked down or away. Ms. Bergen says, “Mark, how about you?” Mark’s eye contact communicated what? a. Understanding b. Willingness to participate (CORRECT) c. Acceptance of his boss d. Control of others e. Lack of motivation 11. What is casual confusion syndrome (CCS)? a. A phenomenon in which people are sometimes too informal in their gestures at work. b. Uncertainty about when touch is appropriate in the workplace. c. A theory that suggests that people are not as professional now as 30 years ago. d. A syndrome that applies to young workers who do not know the formal rules of a workplace. e. The lack of clarity workers have about what constitutes appropriate business casual attire. (CORRECT) 12. The monochromic dimension relative to understanding time and culture a. Refers to time as a scarce resource b. Can be found in the culture of the United States, Germany and Switzerland c. holds that time must be controlled and rationed d. Is indicated in phrases like, “Time is money.” e. All of the above (CORRECT) 13. Which of these behaviors convey power? a. Sitting upright and look serious or intense b. Sitting in a relaxed position (CORRECT) c. Keeping hands and feet together d. Useing small, well controlled movements e. Fidgeting 14. Which of these behaviors indicate weakness? a. Making large expansive movements b. Crossing your legs and lean slightly c. Playing with an object (CORRECT) d. A tall upright posture with feet slightly apart e. Sitting in a relaxed position 15. Suzanne and Lorainne are standing 2 feet apart. What kind of distance is between them? a. Intimate distance b. Professional distance c. Social distance d. Personal distance (CORRECT) e. Public distance