Electricity Review - Integrated Science
advertisement

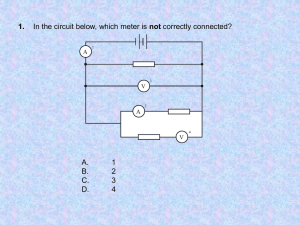
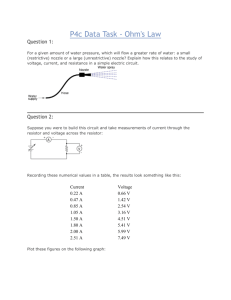
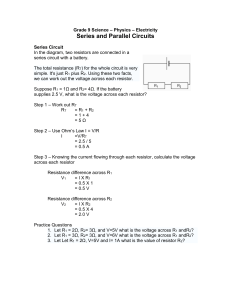
Ohm’s Law: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Class/circuits/u9l3c.cfm 1. Which of the following will cause the current through an electrical circuit to decrease? Choose all that apply. a. decrease the voltage b. decrease the resistance c. increase the voltage d. increase the resistance 2. A certain electrical circuit contains a battery with three cells, wires and a light bulb. Which of the following would cause the bulb to shine less brightly? Choose all that apply. a. increase the voltage of the battery (add another cell) b. decrease the voltage of the battery (remove a cell) c. decrease the resistance of the circuit d. increase the resistance of the circuit 3. You have likely been warned to avoid contact with electrical appliances or even electrical outlets when your hands are wet. Such contact is more dangerous when your hands are wet (vs. dry) because wet hands cause ____. a. the voltage of the circuit to be higher b. the voltage of the circuit to be lower c. your resistance to be higher d. your resistance to be lower e. the current through you to be lower 4. If the resistance of a circuit were tripled, then the current through the circuit would be ____. a. one-third as much b. three times as much c. unchanged d. ... nonsense! There would be no way to make such a prediction. 5. If the voltage across a circuit is quadrupled, then the current through the circuit would be ____. a. one-fourth as much b. four times as much c. unchanged d. ... nonsense! There would be no way to make such a prediction. 6. A circuit is wired with a power supply, a resistor and an ammeter (for measuring current). The ammeter reads a current of 24 mA (milliAmps). Determine the new current if the voltage of the power supply was ... a. ... increased by a factor of 2 and the resistance was held constant. b. ... increased by a factor of 3 and the resistance was held constant. c. ... decreased by a factor of 2 and the resistance was held constant. d. ... held constant and the resistance was increased by a factor of 2. e. ... held constant and the resistance was increased by a factor of 4. f. ... held constant and the resistance was decreased by a factor of 2. g. ... increased by a factor of 2 and the resistance was increased by a factor of 2. h. ... increased by a factor of 3 and the resistance was decreased by a factor of 2. i. ... decreased by a factor of 2 and the resistance was increased by a factor of 2. 7. Use the Ohm's law equation to provide numerical answers to the following questions: a. An electrical device with a resistance of 3.0 will allow a current of 4.0 amps to flow through it if a voltage drop of ________ Volts is impressed across the device. b. When a voltage of 120 V is impressed across an electric heater, a current of 10.0 amps will flow through the heater if the resistance is ________ . c. A flashlight that is powered by 3 Volts and uses a bulb with a resistance of 60 will have a current of ________ Amps 8. Use the Ohm's law equation to determine the missing values in the following circuits. 9. Refer to question 8 above. In the circuits of diagrams A and B, what method was used to control the current in the circuits? And in the circuits of diagrams C and D, what method was used to control the current in the circuits? Circuit Diagrams: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Class/circuits/u9l4a.cfm 1. Use circuit symbols to construct schematic diagrams for the following circuits: a. A single cell, light bulb and switch are placed together in a circuit such that the switch can be opened and closed to turn the light bulb on. b. A three-pack of D-cells is placed in a circuit to power a flashlight bulb. c. d. 2. Use the concept of conventional current to draw an unbroken line on the schematic diagram at the right that indicates the direction of the conventional current. Place an arrowhead on your unbroken line. Series vs. Parallel: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Class/circuits/U9l4b.cfm 1. Observe the electrical wiring below. Indicate whether the connections are series or parallel connections. Explain each choice. 2. Two electric circuits are diagrammed below. For each circuit, indicate which two devices are connected in series and which two devices are connected in parallel. In series? ___________________ In parallel? _________________ In series? ___________________ In parallel? _________________ SERIES Circuits: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Class/circuits/U9l4c.cfm 1. Use your understanding of equivalent resistance to complete the following statements: a. Two 3- resistors placed in series would provide a resistance that is equivalent to one _____- resistor. b. Three 3- resistors placed in series would provide a resistance that is equivalent to one _____- resistor. c. Three 5- resistors placed in series would provide a resistance that is equivalent to one _____- resistor. d. Three resistors with resistance values of 2- , 4- , and 6- are placed in series. These would provide a resistance that is equivalent to one _____- resistor. e. Three resistors with resistance values of 5- , 6- , and 7- are placed in series. These would provide a resistance that is equivalent to one _____- resistor. f. Three resistors with resistance values of 12- , 3- , and 21- are placed in series. These would provide a resistance that is equivalent to one _____- resistor. 2. As the number of resistors in a series circuit increases, the overall resistance __________ (increases, decreases, remains the same) and the current in the circuit __________ (increases, decreases, remains the same). 3. Consider the following two diagrams of series circuits. For each diagram, use arrows to indicate the direction of the conventional current. Then, make comparisons of the voltage and the current at the designated points for each diagram. 4. Three identical light bulbs are connected to a D-cell as shown at the right. Which one of the following statements is true? a. All three bulbs will have the same brightness. b. The bulb between X and Y will be the brightest. c. The bulb between Y and Z will be the brightest. d. The bulb between Z and the battery will be the brightest. 5. Three identical light bulbs are connected to a battery as shown at the right. Which adjustments could be made to the circuit that would increase the current being measured at X? List all that apply. a. Increase the resistance of one of the bulbs. b. Increase the resistance of two of the bulbs. c. Decrease the resistance of two of the bulbs. d. Increase the voltage of the battery. e. Decrease the voltage of the battery. f. Remove one of the bulbs. 6. Three identical light bulbs are connected to a battery as shown at the right. W, X,Y and Z represent locations along the circuit. Which one of the following statements is true? a. The potential difference between X and Y is greater than that between Y and Z. b. The potential difference between X and Y is greater than that between Y and W. c. The potential difference between Y and Z is greater than that between Y and W. d. The potential difference between X and Z is greater than that between Z and W. e. The potential difference between X and W is greater than that across the battery. f. The potential difference between X and Y is greater than that between Z and W. 7. Compare circuit X and Y below. Each is powered by a 12-volt battery. The voltage drop across the 12-ohm resistor in circuit Y is ____ the voltage drop across the single resistor in X. a. smaller than b. larger than c. the same as 8. A 12-V battery, a 12-ohm resistor and a light bulb are connected as shown in circuit X below. A 6-ohm resistor is added to the 12-ohm resistor and bulb to create circuit Y as shown. The bulb will appear ____. a. dimmer in circuit X b. dimmer in circuit Y c. the same brightness in both circuits 9. Three resistors are connected in series. If placed in a circuit with a 12-volt power supply. Determine the equivalent resistance, the total circuit current, and the voltage drop across and current at each resistor. In parallel: Case 1: Three 12 resistors are placed in parallel 1/Req = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 1/Req = 1/(12 ) + 1/(12 ) + 1/(12 ) Using a calculator ... 1/Req = 0.25 Req = 1 / (0.25 -1 -1) Req = 4.0 12 Case 2: A 5.0 , 7.0 , and resistor are placed in parallel 1/Req = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 1/Req = 1/(5.0 ) + 1/(7.0 ) + 1/(12 Using a calculator ... 1/Req = 0.42619 Req = 1 / (0.42619 -1 -1) Req = 2.3 1. As more and more resistors are added in parallel to a circuit, the equivalent resistance of the circuit ____________ (increases, decreases) and the total current of the circuit ____________ (increases, decreases). 2. Three identical light bulbs are connected to a D-cell as shown below. P, Q, X, Y and Z represent locations along the circuit. Which one of the following statements is true? a. The current at Y is greater than the current at Q. b. The current at Y is greater than the current at P. c. The current at Y is greater than the current at Z. d. The current at P is greater than the current at Q. e. The current at Q is greater than the current at P. f. The current is the same at all locations. 3. Three identical light bulbs are connected to a D-cell as shown below. P, Q, X, Y and Z represent locations along the circuit. At which location(s), if any, will the current be ... a. ... the same as at X? b. ... the same as at Q? c. ... the same as at Y? d. ... less than at Q? e. ... less than at P? f. ... twice that at Z? g. ... three times that at Y? ) 4. Which adjustments could be made to the circuit below that would decrease the current in the cell? List all that apply. a. Increase the resistance of bulb X. b. Decrease the resistance of bulb X. c. Increase the resistance of bulb Z. d. Decrease the resistance of bulb Z. e. Increase the voltage of the cell (somehow). f. Decrease the voltage of the cell (somehow). g. Remove bulb Y. 5. A 12-V battery , a 12-ohm resistor and a 4-ohm resistor are connected as shown. The current in the 12ohm resistor is ____ that in the 4-ohm resistor. a. 1/3 b. 1/2 c. 2/3 d. the same as e. 1.5 times f. twice g. three times h. four times 6. A 12-V battery , a 12-ohm resistor and a 4-ohm resistor are connected as shown. The voltage drop across the 12-ohm resistor is ____ that across the 4ohm resistor. a. 1/3 b. 1/2 c. 2/3 d. the same as e. 1.5 times f. twice g. three times h. four times 7. A 12-V battery and a 12-ohm resistor are connected as shown in circuit. A 6-ohm resistor is added to the 12-ohm resistor to create circuit Y as shown. The voltage drop across the 6-ohm resistor in circuit Y is ____ that across the resistor in X. a. larger than b. smaller than c. the same as 8. Use your understanding of equivalent resistance to complete the following statements: a. Two 6- resistors placed in parallel would provide a resistance that is equivalent to one _____- resistor. b. Three 6- resistors placed in parallel would provide a resistance that is equivalent to one _____- resistor. c. Three 8- resistors placed in parallel would provide a resistance that is equivalent to one _____- resistor. d. Three resistors with resistance values of 2- , 4- , and 6- are placed in parallel. These would provide a resistance that is equivalent to one _____- resistor. e. Three resistors with resistance values of 5- , 6- , and 7- are placed in parallel. These would provide a resistance that is equivalent to one _____- resistor. f. Three resistors with resistance values of 12- , 6- , and 21- are placed in parallel. These would provide a resistance that is equivalent to one _____- resistor. 9. Based on your answers to the above question, complete the following statement: The overall or equivalent resistance of three resistors placed in parallel will be _____. a. greater than the resistance of the biggest R value of the three. b. less than the resistance of the smallest R value of the three. c. somewhere in between the smallest R and the biggest R value of the three. d. ... nonsense! No such generalization can be made. The results vary. 10. Three resistors are connected in parallel. If placed in a circuit with a 12-volt power supply. Determine the equivalent resistance, the total circuit current, and the voltage drop across and current in each resistor. Combination Problems (Advanced): http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Class/circuits/U9l4e.cfm 1. A combination circuit is shown in the diagram at the right. Use the diagram to answer the following questions. a. The current at location A is _____ (greater than, equal to, less than) the current at location B. b. The current at location B is _____ (greater than, equal to, less than) the current at location E. c. The current at location G is _____ (greater than, equal to, less than) the current at location F. d. The current at location E is _____ (greater than, equal to, less than) the current at location G. e. The current at location B is _____ (greater than, equal to, less than) the current at location F. f. The current at location A is _____ (greater than, equal to, less than) the current at location L. f. The current at location H is _____ (greater than, equal to, less than) the current at location I. 2. Consider the combination circuit in the diagram at the right. Use the diagram to answer the following questions. (Assume that the voltage drops in the wires themselves in negligibly small.) a. The electric potential difference (voltage drop) between points B and C is _____ (greater than, equal to, less than) the electric potential difference (voltage drop) between points J and K. b. The electric potential difference (voltage drop) between points B and K is _____ (greater than, equal to, less than) the electric potential difference (voltage drop) between points D and I. c. The electric potential difference (voltage drop) between points E and F is _____ (greater than, equal to, less than) the electric potential difference (voltage drop) between points G and H. d. The electric potential difference (voltage drop) between points E and F is _____ (greater than, equal to, less than) the electric potential difference (voltage drop) between points D and I. e. The electric potential difference (voltage drop) between points J and K is _____ (greater than, equal to, less than) the electric potential difference (voltage drop) between points D and I. f. The electric potential difference between points L and A is _____ (greater than, equal to, less than) the electric potential difference (voltage drop) between points B and K. 3. Use the concept of equivalent resistance to determine the unknown resistance of the identified resistor that would make the circuits equivalent. 4. Analyze the following circuit and determine the values of the total resistance, total current, and the current at and voltage drops across each individual resistor. 5. Referring to the diagram in question #4, determine the ... a. ... power rating of resistor 4. b. ... rate at which energy is consumed by resistor 3.