Stroke Checklist
advertisement
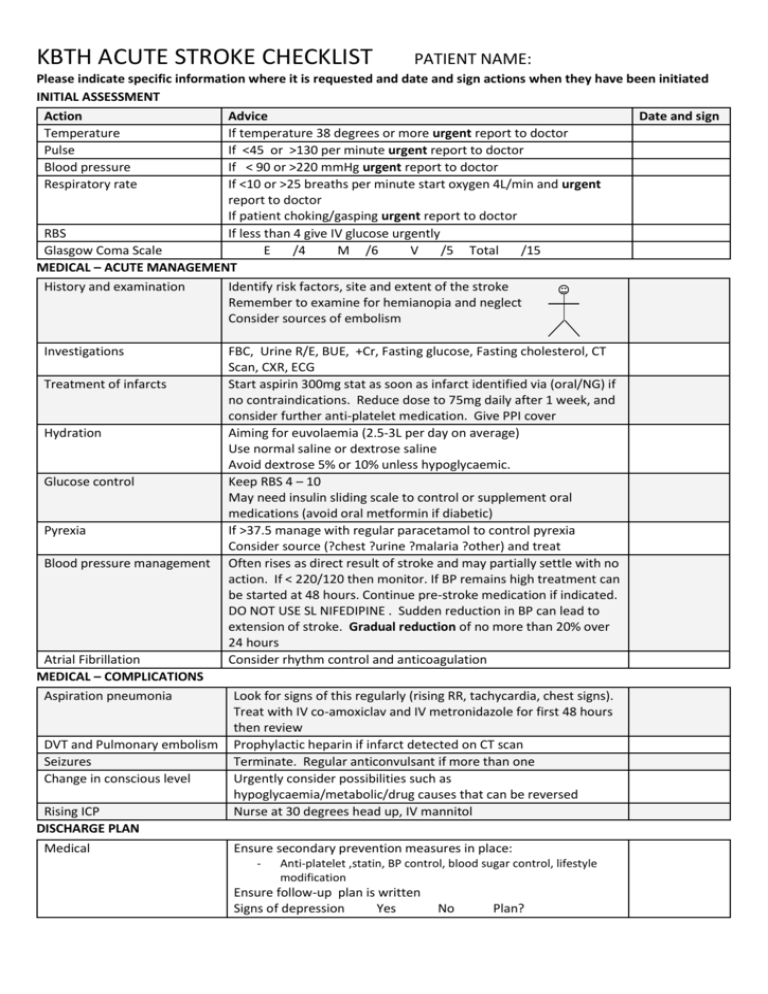
KBTH ACUTE STROKE CHECKLIST PATIENT NAME: Please indicate specific information where it is requested and date and sign actions when they have been initiated INITIAL ASSESSMENT Action Advice Date and sign Temperature If temperature 38 degrees or more urgent report to doctor Pulse If <45 or >130 per minute urgent report to doctor Blood pressure If < 90 or >220 mmHg urgent report to doctor Respiratory rate If <10 or >25 breaths per minute start oxygen 4L/min and urgent report to doctor If patient choking/gasping urgent report to doctor RBS If less than 4 give IV glucose urgently Glasgow Coma Scale E /4 M /6 V /5 Total /15 MEDICAL – ACUTE MANAGEMENT History and examination Identify risk factors, site and extent of the stroke Remember to examine for hemianopia and neglect Consider sources of embolism Investigations Treatment of infarcts Hydration Glucose control Pyrexia Blood pressure management Atrial Fibrillation MEDICAL – COMPLICATIONS Aspiration pneumonia DVT and Pulmonary embolism Seizures Change in conscious level Rising ICP DISCHARGE PLAN Medical FBC, Urine R/E, BUE, +Cr, Fasting glucose, Fasting cholesterol, CT Scan, CXR, ECG Start aspirin 300mg stat as soon as infarct identified via (oral/NG) if no contraindications. Reduce dose to 75mg daily after 1 week, and consider further anti-platelet medication. Give PPI cover Aiming for euvolaemia (2.5-3L per day on average) Use normal saline or dextrose saline Avoid dextrose 5% or 10% unless hypoglycaemic. Keep RBS 4 – 10 May need insulin sliding scale to control or supplement oral medications (avoid oral metformin if diabetic) If >37.5 manage with regular paracetamol to control pyrexia Consider source (?chest ?urine ?malaria ?other) and treat Often rises as direct result of stroke and may partially settle with no action. If < 220/120 then monitor. If BP remains high treatment can be started at 48 hours. Continue pre-stroke medication if indicated. DO NOT USE SL NIFEDIPINE . Sudden reduction in BP can lead to extension of stroke. Gradual reduction of no more than 20% over 24 hours Consider rhythm control and anticoagulation Look for signs of this regularly (rising RR, tachycardia, chest signs). Treat with IV co-amoxiclav and IV metronidazole for first 48 hours then review Prophylactic heparin if infarct detected on CT scan Terminate. Regular anticonvulsant if more than one Urgently consider possibilities such as hypoglycaemia/metabolic/drug causes that can be reversed Nurse at 30 degrees head up, IV mannitol Ensure secondary prevention measures in place: - Anti-platelet ,statin, BP control, blood sugar control, lifestyle modification Ensure follow-up plan is written Signs of depression Yes No Plan? KBTH ACUTE STROKE CHECKLIST PATIENT NAME: PAY SPECIAL ATTENTION TO THE HEMIPLEGIC SIDE DURING ALL ACTIVITIES Physiotherapy and Nursing Care Swallow Assessment Performed by…………………………………………….. Date………………. To be done within 2 Passed days of admission to Failed medical ward, by (Please circle) trained nurse Plan: (please document)………………………………… Positioning/Manual Handling Assessment To be done within 2 days of admission to medical ward Communication Assessment To be done within 2 days of admission to medical ward Performed by…………………………………………………. Mobile Assistance required to mobilise To remain in bed - needs positioning chart (Please circle) Plan: (please document plan eg arjo)………………. Date………………… Performed by…………………………………………………….. Communication normal Slurred speech/dysarthria Aphasia (Please circle) Plan: (please document aids needed) Date……………….. Performed by………………………………………………….. Continent Incontinent: (offer timed toileting) Catheter: (if in retention – treat cause; remove catheter if possible) (please circle) Plan: (Please document)…………………………………….. Date………………… Performed by………………………………………………………. Please document what information has been given to the family/patient prior to discharge Date…………………. Continence Assessment Patient and Family Education To be done prior to discharge Verbal Leaflet (Please circle) IMPORTANT ALL OF THE ABOVE SHOULD BE REASSESSED AS NECESSARY