View
advertisement
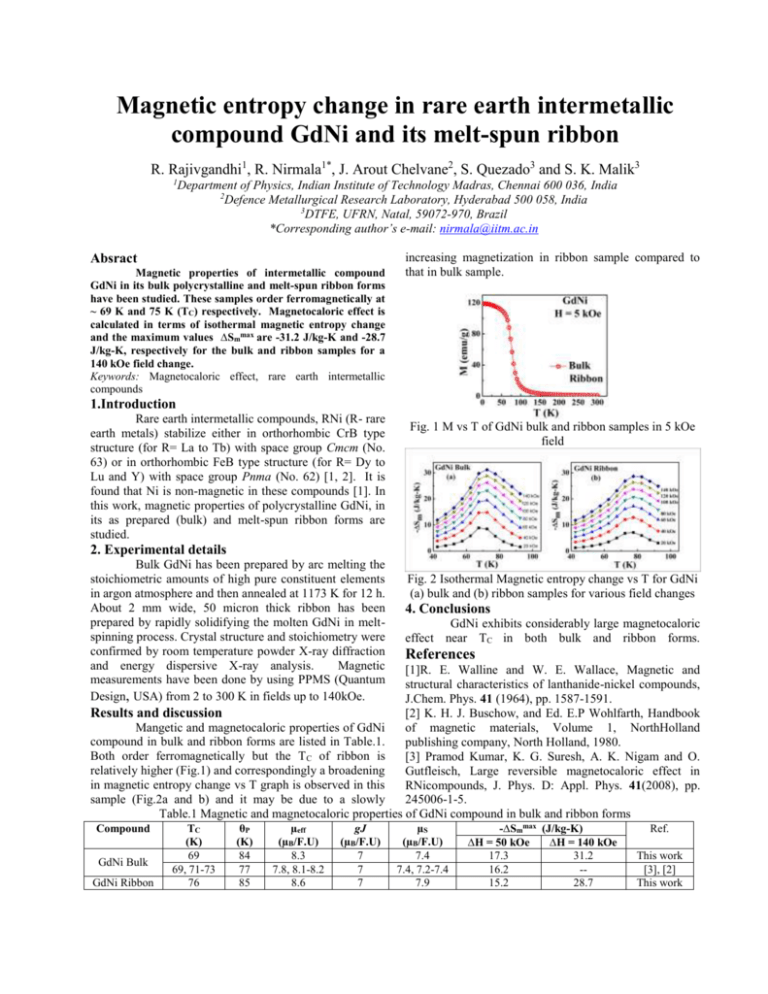
Magnetic entropy change in rare earth intermetallic compound GdNi and its melt-spun ribbon R. Rajivgandhi1, R. Nirmala1*, J. Arout Chelvane2, S. Quezado3 and S. K. Malik3 1 Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai 600 036, India 2 Defence Metallurgical Research Laboratory, Hyderabad 500 058, India 3 DTFE, UFRN, Natal, 59072-970, Brazil *Corresponding author’s e-mail: nirmala@iitm.ac.in Absract Magnetic properties of intermetallic compound GdNi in its bulk polycrystalline and melt-spun ribbon forms have been studied. These samples order ferromagnetically at ~ 69 K and 75 K (TC) respectively. Magnetocaloric effect is calculated in terms of isothermal magnetic entropy change and the maximum values ∆Smmax are -31.2 J/kg-K and -28.7 J/kg-K, respectively for the bulk and ribbon samples for a 140 kOe field change. Keywords: Magnetocaloric effect, rare earth intermetallic compounds increasing magnetization in ribbon sample compared to that in bulk sample. 1.Introduction Rare earth intermetallic compounds, RNi (R- rare earth metals) stabilize either in orthorhombic CrB type structure (for R= La to Tb) with space group Cmcm (No. 63) or in orthorhombic FeB type structure (for R= Dy to Lu and Y) with space group Pnma (No. 62) [1, 2]. It is found that Ni is non-magnetic in these compounds [1]. In this work, magnetic properties of polycrystalline GdNi, in its as prepared (bulk) and melt-spun ribbon forms are studied. Fig. 1 M vs T of GdNi bulk and ribbon samples in 5 kOe field 2. Experimental details Bulk GdNi has been prepared by arc melting the stoichiometric amounts of high pure constituent elements in argon atmosphere and then annealed at 1173 K for 12 h. About 2 mm wide, 50 micron thick ribbon has been prepared by rapidly solidifying the molten GdNi in meltspinning process. Crystal structure and stoichiometry were confirmed by room temperature powder X-ray diffraction and energy dispersive X-ray analysis. Magnetic measurements have been done by using PPMS (Quantum Design, USA) from 2 to 300 K in fields up to 140kOe. Fig. 2 Isothermal Magnetic entropy change vs T for GdNi (a) bulk and (b) ribbon samples for various field changes 4. Conclusions GdNi exhibits considerably large magnetocaloric effect near TC in both bulk and ribbon forms. References [1]R. E. Walline and W. E. Wallace, Magnetic and structural characteristics of lanthanide-nickel compounds, J.Chem. Phys. 41 (1964), pp. 1587-1591. Results and discussion [2] K. H. J. Buschow, and Ed. E.P Wohlfarth, Handbook Mangetic and magnetocaloric properties of GdNi of magnetic materials, Volume 1, NorthHolland compound in bulk and ribbon forms are listed in Table.1. publishing company, North Holland, 1980. Both order ferromagnetically but the T C of ribbon is [3] Pramod Kumar, K. G. Suresh, A. K. Nigam and O. relatively higher (Fig.1) and correspondingly a broadening Gutfleisch, Large reversible magnetocaloric effect in in magnetic entropy change vs T graph is observed in this RNicompounds, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 41(2008), pp. sample (Fig.2a and b) and it may be due to a slowly 245006-1-5. Table.1 Magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of GdNi compound in bulk and ribbon forms Compound GdNi Bulk GdNi Ribbon TC (K) 69 69, 71-73 76 θP (K) 84 77 85 µeff (µB/F.U) 8.3 7.8, 8.1-8.2 8.6 gJ (µB/F.U) 7 7 7 µS (µB/F.U) 7.4 7.4, 7.2-7.4 7.9 -∆Smmax (J/kg-K) ∆H = 50 kOe ∆H = 140 kOe 17.3 31.2 16.2 -15.2 28.7 Ref. This work [3], [2] This work