Air Pressure and Wind FactSheet
Name
Class
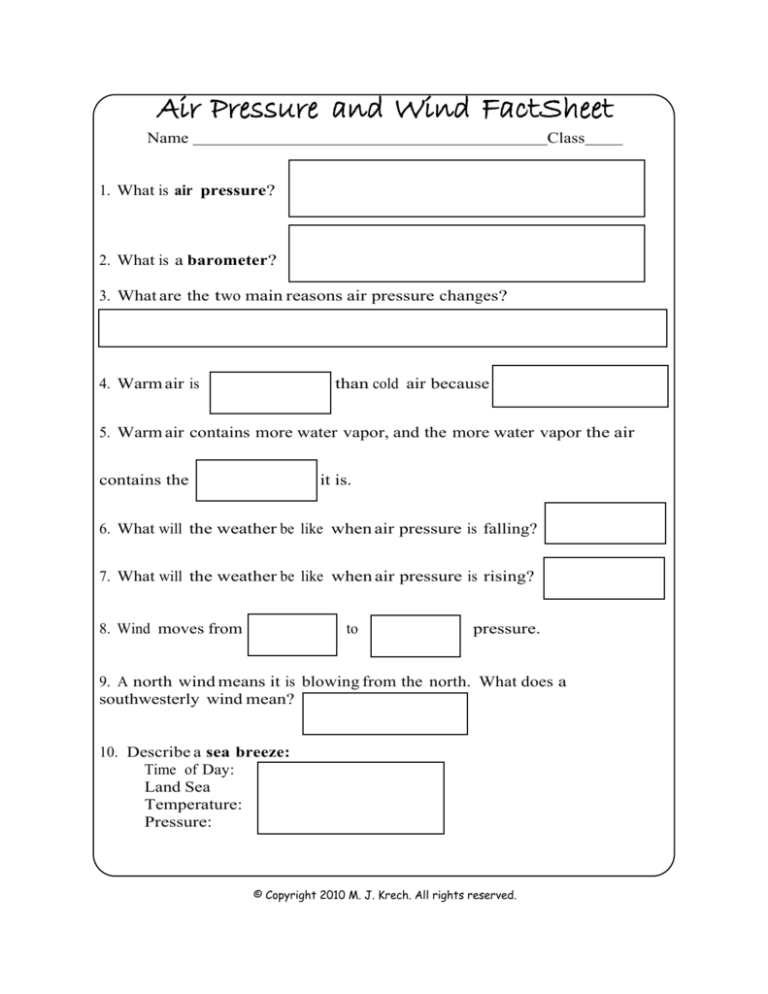
1. What is air pressure?
2. What is a barometer?
3. What are the two main reasons air pressure changes?
4. Warm air is
than cold air because
5. Warm air contains more water vapor, and the more water vapor the air
contains the
it is.
6. What will the weather be like when air pressure is falling?
7. What will the weather be like when air pressure is rising?
8. Wind moves from
to
pressure.
9. A north wind means it is blowing from the north. What does a
southwesterly wind mean?
10. Describe a sea breeze:
Time of Day:
Land Sea
Temperature:
Pressure:
© Copyright 2010 M. J. Krech. All rights reserved.
11. Describe a land breeze:
Time of Day:
Land Sea
Temperature:
Pressure:
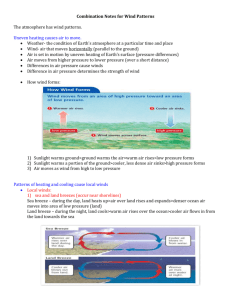
12. Describe mountain and valley winds.
13. The arrows show how air moves during the day. Cool night temperatures
affect air pressure. Air moves in the opposite direction at night. Draw arrows
on the bottom diagrams to show how the air moves at night.
14. What is the coriolis effect?
15. What does the Coriolis Effect do to wind in the Northern Hemisphere?
© Copyright 2010 M. J. Krech. All rights reserved.
Weight of the atmosphere per
unit area
An instrument that measures
atmospheric pressure
Changes in air temperature. AND Changes in Humidity.
molecules of warm air
are farther apart
lighter
warmer and
more humid
cooler and
drier
blowing from the
southwest
lighter
high
Occurs in the Day
Comes from the Sea
Cooler Air
High Pressure on Sea
low
Occurs in the Day
Comes from the Sea
Cooler Air
Low Pressure on Land
Mountain: At night cold air sinks and blows
from mountain into valley.
Valley: In the day, warm air rises from valley
and blows up the mountain.
effect of Earth’s rotation which
deflects objects toward or away
from Equator
Winds are turned to the right relative to the Earth’’s surface
© Copyright 2010 M. J. Krech. All rights reserved.
Master Transparency:
© Copyright 2010 M. J. Krech. All rights reserved.
Air Pressure and Wind FactSheet
Name
Class
1. What is air pressure?
Weight of the atmosphere per
unit area
2. What is a barometer?
An instrument that measures
atmospheric pressure
3. What are the two main reasons air pressure changes?
Changes in air temperature. AND Changes in Humidity.
4. Warm air is
lighter
molecules of warm air
than cold air because are farther apart
5. Warm air contains more water vapor, and the more water vapor the air
contains the
lighter
it is.
warmer and
6. What will the weather be like when air pressure is falling? more humid
7. What will the weather be like when air pressure is rising?
8. Wind moves from
high
to
low
cooler and
drier
pressure.
9. A north wind means it is blowing from the north. What does a
blowing from the
southwesterly wind mean?
southwest
10. Describe a sea breeze:
Occurs in the Day
Time of Day:
Comes from the Sea
Land Sea
Cooler Air
Temperature:
High Pressure on Sea
Pressure:
© Copyright 2010 M. J. Krech. All rights reserved.
11. Describe a land breeze:
Time of Day: Occurs in the Day
Comes from the Sea
Land Sea
Temperature: Cooler Air
Low Pressure on Land
Pressure:
12. Describe mountain and valley winds.
Mountain: At night cold air sinks and blows
from mountain into valley.
Valley: In the day, warm air rises from valley
and blows up the mountain.
13. The arrows show how air moves during the day. Cool night temperatures
affect air pressure. Air moves in the opposite direction at night. Draw arrows
on the bottom diagrams to show how the air moves at night.
14. What is the coriolis effect?
effect of Earth’s rotation which
deflects objects toward or away
from Equator
15. What does the Coriolis Effect do to wind in the Northern Hemisphere?
Winds are turned to the right relative to the Earth’’s surface
© Copyright 2010 M. J. Krech. All rights reserved.
Right Side
Breezes Reflection
Label and explain Land and Sea Breezes. Hint: Use the
Crushing Can lab and the Solar Radiation Lab to help you.
© Copyright 2010.! M. J. Krech. All rights reserved.
Right Side
Breezes Reflection
Label and explain Land and Sea Breezes. Hint: Use the
Crushing Can lab and the Solar Radiation Lab to help you.
© Copyright 2010.! M. J. Krech. All rights reserved.