pedigree maternal
advertisement
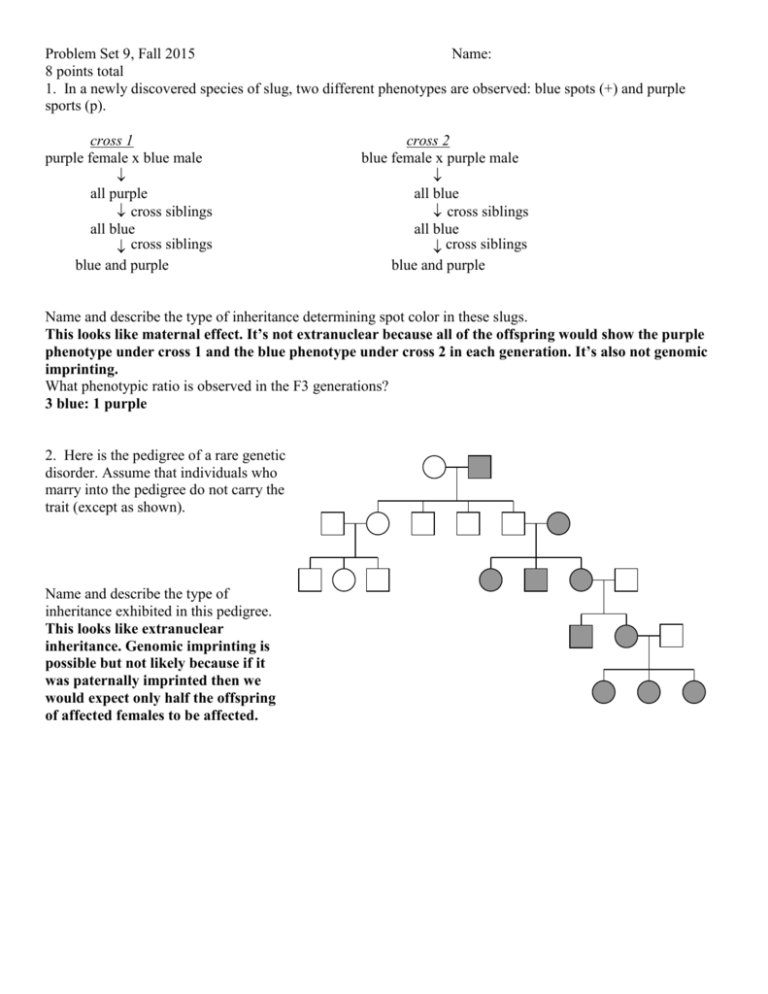
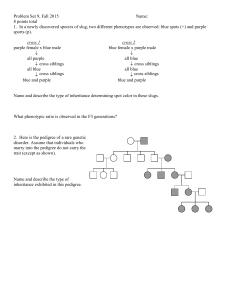
Problem Set 9, Fall 2015 Name: 8 points total 1. In a newly discovered species of slug, two different phenotypes are observed: blue spots (+) and purple sports (p). cross 1 purple female x blue male all purple cross siblings all blue cross siblings blue and purple cross 2 blue female x purple male all blue cross siblings all blue cross siblings blue and purple Name and describe the type of inheritance determining spot color in these slugs. This looks like maternal effect. It’s not extranuclear because all of the offspring would show the purple phenotype under cross 1 and the blue phenotype under cross 2 in each generation. It’s also not genomic imprinting. What phenotypic ratio is observed in the F3 generations? 3 blue: 1 purple 2. Here is the pedigree of a rare genetic disorder. Assume that individuals who marry into the pedigree do not carry the trait (except as shown). Name and describe the type of inheritance exhibited in this pedigree. This looks like extranuclear inheritance. Genomic imprinting is possible but not likely because if it was paternally imprinted then we would expect only half the offspring of affected females to be affected. Problem Set 9, Fall 2015 Name: 8 points total 3. In a newly discovered species of sexually-reproducing money tree, you discover that 5 dollar bill (db+) producing trees are dominant to 10 dollar bill producing trees (db-). The following crosses yield the outcomes shown. 10 dollar bill females x 5 dollar bill males F1 all 10 dollar bill cross siblings F2 all 5 dollar bill cross siblings F3 5 dollar bill and 10 dollar bill a. What is the mode of inheritance? maternal effect b. What is the phenotypic ratio in the F3 generation? 3 $5:1 $10 c. Why couldn’t it be either of the other two non-mendelian methods of inheritance? Extranuclear inheritance would produce all $10 in the F2. Imprinting would produce ½ $5 and ½ $10. 4. In a transduction mapping experiment, you get the following result Experiment selected marker unselected marker + 1 a 45% b+, 5% c+ + 2 b 40% a+, 10% c+ Draw the relative position of a, b, and c. Problem Set 9, Fall 2015 Name: 8 points total 5. You join a Tollan research group on planet Tollana in studying a gene called green which causes green eyes instead of blue in a native insect species. This is very important research as the rare green-eyed individuals are believed to hold special medicinal properties. You know that green is not dominant. You perform the following crosses to gain insight into the green mode of inheritance: green-eyed ♀ x blue-eyed ♂ all green-eyed (cross siblings) all green-eyed a. What possible mode(s) of inheritance does eye color exhibit? extranuclear b. In a different species of insects you find that there are no maternally inherited organelles. However, you do see organelles that are inherited strictly from a father. A wild-type organelle is required for large wings. What happens if you cross a large-winged female with a small-winged male? Draw the crosses for enough generations to make it clear that this is extranuclear inheritance. Assume that you are crossing siblings after the first cross. By F2 generation you can distinguish between these possibilities. What happens if you do a cross reciprocal to the one above? Once again, draw the crosses for enough generations to make it clear that this is extranuclear inheritance. Have to carry crosses to F3 to distinguish between these possibilities. (in both cases the F2 are wild type) 6. In a transduction mapping experiment, you get the following results: Problem Set 9, Fall 2015 Name: 8 points total When you select for presence of wt gene X, you find that gene Y cotransduces 47% of the time, and gene Z cotransduces 3% of the time. When you select for presence of wt gene Z, you find that gene X cotransduces 5% of the time and you never see gene Y cotransduce with gene Z. What are the relative map positions of genes X, Y, and Z? 7. In the rare musical lemurs of Madagascar, K. badgerae, you observe two distinct phenotypes: golden fur and brown fur. To study the transmission of this trait you obtain permission from the Madagascar government to collect a few animals and perform crosses that yield the results shown below. Golden female X Brown male All Golden Cross siblings All Golden Cross siblings Golden and Brown A. Name and describe the type of inheritance determining the fur color in these lemurs (6 points). This looks like a maternal effect gene controls fur color. In maternal effect, the mother’s genotype determines the offsprings phenotype through factors deposited in the egg either as RNA or protein. B. What phenotypic ratio is observed in the F3 generations (4 points)? 3:1 8. You are attempting to find the map distance between two genes in a specific species of phage. The r+ gene is responsible for large plaques, and r- is responsible for small plaques. The b+ gene gives a bluish color to the plaques, while b- makes them clear. a. How would you perform this phage recombination mapping experiment in order to determine the distance between the two genes? Infect relatively few bacterial cells with many phage, then add more cells, spread on plate and examine plaques after they’ve had time to grow. b. After plating out the infected cells, you find the following: 4 large, blue plaques r+ b+ 5 small, clear plaques r– b– 36 large, clear plaques r+ b– 38 small, blue plaques r– b+ What are the genotypes of these plaques? What are the genotypes of the original phage? Originals are r+b– and r–b+ c. What is the recombination frequency between the r and b genes in this species of phage? (4 + 5)/(4 + 5 + 36 + 38) = 9/83 = 0.11