Ways of Thinking: Scientific Reasoning in the Natural Sciences
advertisement

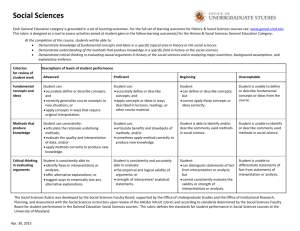
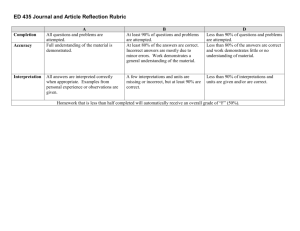
Ways of Thinking: Scientific Reasoning in the Natural Sciences Learning outcomes and rubric Instructions [Course Parameters and Assignment Guidelines] Use the following rubric to assist in the evaluation of skill performance related to Learning Outcomes 1 and 2. Different courses will aspire to either the novice or apprentice level depending on the population and aims of the course. Students can successfully demonstrate novice-level abilities through adequate performance on scripted or “canned” lab assignments, whereas apprentice or proficient levels require open-ended or “exploratory” labs. Learning Outcome Subcategory Rationale Application of the Scientific Method Hypotheses Experimental Design Proficient Performance Apprentice Novice The purpose of the lab or The purpose of the lab or the question to be the question to be answered during the lab is answered during the lab is clearly identified and identified, but is stated in a stated. somewhat unclear manner. Many reputable Several reputable background sources were background sources are used and cited correctly. used and cited correctly. Material is translated into Material is translated into student's own words. student's own words. Deficient The purpose of the lab or the question to be The purpose of the lab or answered during the lab is the question to be partially identified, and is answered during the lab is stated in a somewhat erroneous or irrelevant. unclear manner. Material is directly copied One or more background rather than put into sources are used and cited student’s own words correctly, but some are not and/or background reputable sources. Material sources are cited is translated into student’s incorrectly. own words. Hypothesized relationship Hypothesized relationship between the variables and Hypothesized relationship No hypothesized between the variables and the predicted results is between the variables and relationship has been the predicted results is reasonable based on the predicted results is stated, or demonstration clear and reasonable based general knowledge, clearly stated and of substantial inaccuracies on previous findings. observations, and previous appropriate. in logic. findings. An appropriate experimental design with An appropriate The experimental design The experimental design controls is reported and experimental design including controls is is not defined and/or thoroughly explained. including controls is reported and minimally lacks appropriate Alternative designs or reported and thoroughly explained. structure or controls. modifications are discussed explained. and explained. 1 Document1 Ways of Thinking: Scientific Reasoning in the Natural Sciences Conclusions Learning Outcome Subcategory Materials Collection, Analysis, and Interpretation of Quantitative Data Procedures Statistical Analysis Conclusion includes whether the findings supported the hypothesis, possible sources of error, and what was learned from the experiment. The relationship between the variables is discussed and trends/patterns logically analyzed. Predictions are made about what might happen if part of the lab were changed or how the experimental design could be changed. Results are thoroughly compared to previous findings. Proficient Learning outcomes and rubric Conclusion includes Conclusion includes what whether the findings was learned from the supported the hypothesis experiment. and what was learned from The relationship between the experiment. the variables is discussed The relationship between but no patterns, trends or the variables is discussed predictions are made based and trends/patterns on the data. Minimal logically analyzed. relation to previous Some relation to previous findings. findings mentioned. Performance Apprentice Novice All materials and setup Almost all materials and Most of the materials and used in the experiment are the setup used in the the setup used in the clearly and accurately experiment are clearly and experiment are accurately described. accurately described. described. Procedures are listed in clear steps. Each step is numbered and described in a complete sentence. Procedures appear to be replicable. Steps are outlined sequentially and are adequately detailed. Appropriate descriptive and inferential statistical analyses are reported and thoroughly explained. Experimental errors and outliers, their possible effects, and ways to reduce them are discussed. No conclusion was included in the report OR shows little effort and reflection. The relationship between the variables is minimally discussed. Little or no relation to previous findings noted. Deficient Many materials are described inaccurately or are not described at all. Procedures are listed in a Procedures do not logical order, but steps are Procedures are listed but accurately list the steps of not numbered and/or are are not in a logical order or the experiment. not in complete sentences. are difficult to follow. Several steps are not Procedures appear to be All steps are outlined, but outlined and there is not replicable. Steps are there is not enough detail enough detail to replicate outlined and are to replicate procedures. procedures. adequately detailed. Both descriptive and inferential statistical analyses are reported and explained. Experimental errors and outliers and their possible effects are discussed. Both descriptive and inferential statistical analyses are reported but minimally explained. Experimental errors and outliers are mentioned. Statistical analyses are not reported or are erroneous. There is no discussion of errors or outliers. 2 Document1 Ways of Thinking: Scientific Reasoning in the Natural Sciences Ethical Considerations Limitations Safety Outcome Subcategory Data Communication of Findings Appearance/ Organization Learning outcomes and rubric Thorough identification Thorough identification of Inadequately identifies key and discussion of Identifies key ethical applicable ethical applicable ethical applicable ethical considerations related to considerations related to considerations related to considerations related to data collection, human data collection, human data collection, human data collection, human subjects and organisms, subjects and organism, subjects and organisms, subjects and organism, health and safety, use of health and safety, use of health and safety, use of health and safety, use of others work, and/or bias. others work, and/or bias. others work and/or bias. others work, and/or bias. Clearly articulates a firm Articulates an understanding of Does not articulate an understanding of the Identifies either assumptions and provides understanding of assumptions and specifies assumptions or limitations. a thorough analysis of the assumptions or limitations. several limitations. limitations. Lab is carried out with Lab is generally carried out some attention to relevant Lab is carried out with full with attention to relevant safety procedures. The set- Safety procedures were attention to relevant safety safety procedures. The setup, experiment, and tearignored and/or some procedures. The set-up, up, experiment, and teardown posed no safety aspect of the experiment experiment, and tear-down down posed no safety threat to any individual, posed a threat to the safety posed no safety threat to threat to any individual, but several safety of the student or others. any individual. but one safety procedure procedures need to be needs to be reviewed. reviewed. Proficient Performance Apprentice Novice Deficient Professional-looking and Accurate representation of Accurate representation of accurate representation of the data in tables and/or the data in written form, the data in tables and/or graphs. Graphs and tables but no graphs or tables are graphs. Graphs and tables are labeled and titled. presented. are labeled and titled. Data are not reported or are inaccurate. Written or oral report contains all necessary sections and information, but some organizational problems remain. Written or oral report is incomplete and poorly organized. Written or oral report is Written or oral report is complete, superbly complete, well-organized, organized, and appears and largely professional in professional in all respects. appearance. 3 Document1 Ways of Thinking: Scientific Reasoning in the Natural Sciences Format Superbly utilizes an appropriate professional communication format suitable to the discipline and nature of the experiment. Utilizes an appropriate professional communication format suitable to the discipline and nature of the experiment. Learning outcomes and rubric Utilizes appropriate communication format suitable to the discipline and nature of the experiment, but lacks a professional polish. Does not utilize communication format suitable to the discipline. 4 Document1 Ways of Thinking: Scientific Reasoning in the Natural Sciences Learning outcomes and rubric Problem Solving Rubric for Scientific Reasoning in the Natural Sciences Strategic Approach Implementation Calculations (if appropriate) Evaluation of the Solution Communication of the Solution Proficient Determines appropriate and complete strategies to solve problems independently. Employs scientific principles correctly and independently. Correctly performs complex mathematical manipulation of algebraic equations when required. Provides broad interpretations of results independently and can perform advanced checks properly. Consistently communicates solutions in an effective format with high quality. Apprentice Determines appropriate and complete strategies to solve problems based upon examples. Employs scientific principles correctly to solve problems similar to examples. Correctly performs simple mathematical manipulation of algebraic equations when required. Can broaden interpretations of results with some direction and perform checks properly. Novice Chooses the correct strategy to solve a problem from a limited set of options. Employs scientific principles correctly to solve problems identical to examples. Correctly converts units, plugs numbers into equations and calculates quantities. Deficient Unable to choose the correct strategy to solve a problem. Provides narrow but correct interpretations of results and performs basic checks properly. Unable to interpret solutions or perform basic checks. Consistently communicates solutions in an effective format with average quality. Generally communicates solutions in an effective format with average quality. Unable to communicate solutions effectively. Unable to employ scientific principles correctly. Unable to perform calculations correctly. 5 Document1