Student Notes-
advertisement
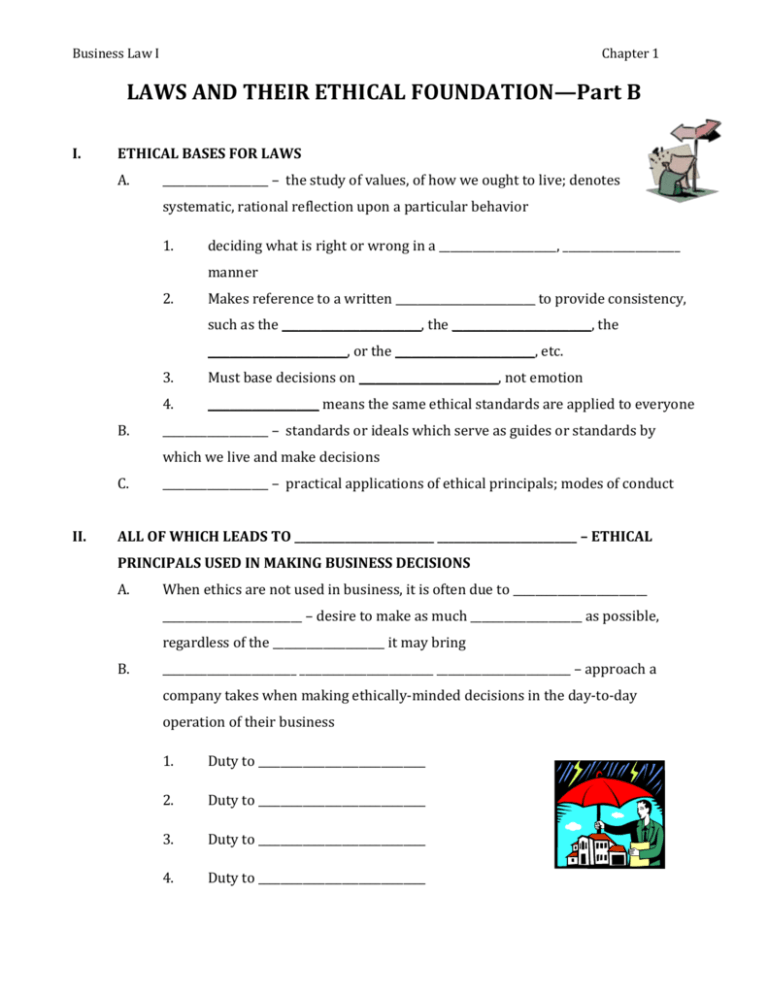
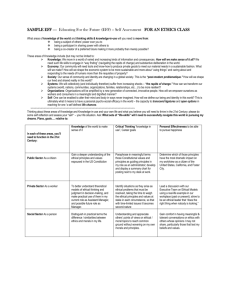
Business Law I Chapter 1 LAWS AND THEIR ETHICAL FOUNDATION—Part B I. ETHICAL BASES FOR LAWS A. ___________________ – the study of values, of how we ought to live; denotes systematic, rational reflection upon a particular behavior 1. deciding what is right or wrong in a _____________________, _____________________ manner 2. Makes reference to a written _________________________ to provide consistency, such as the _________________________, the _________________________, the _________________________, or the _________________________, etc. B. 3. Must base decisions on _________________________, not emotion 4. ____________________ means the same ethical standards are applied to everyone ___________________ – standards or ideals which serve as guides or standards by which we live and make decisions C. II. ___________________ – practical applications of ethical principals; modes of conduct ALL OF WHICH LEADS TO _________________________ _________________________ – ETHICAL PRINCIPALS USED IN MAKING BUSINESS DECISIONS A. When ethics are not used in business, it is often due to ________________________ _________________________ – desire to make as much ____________________ as possible, regardless of the ____________________ it may bring B. ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ – approach a company takes when making ethically-minded decisions in the day-to-day operation of their business 1. Duty to ______________________________ 2. Duty to ______________________________ 3. Duty to ______________________________ 4. Duty to ______________________________ Business Law I III. Chapter 1 BASIC FORMS OF ETHICAL REASONING – TAKES TWO BASIC FORMS A. _________________________ -________________________ Ethical Reasoning where right or wrong is based only on the _________________________ of the action (acts themselves have no ethical or moral character) B. __________________________ -_________________________ Ethical Reasoning where the __________________________ __________________________ are judged as right or wrong; standards for judging can come from: 1. An _________________________ – often a religious source 2. ____________________ ____________________ – some use ________________________ where everyone is pictured doing the same thing (is the result irrational, illogical or demeaning?) IV. ETHICS REFLECTED IN LAWS A. Process of electing _________________________ comes from majority rule and includes many features of consequence-based ethics (providing the greatest good for the greatest number) B. _________________________ preserved by the Bill of Rights and other civil rights laws reflect ethics based on rules C. Both conclude we are obligated to obey the law D. Why are we obligated to obey the law? 1. We consent to be _____________________ and gain benefits of the country 2. We want to avoid _____________________ – fines, community service, jail time, death penalty, etc. 3. Inability to get certain jobs a) Inability to get a _________________________ __________________________ b) Inability to get a _________________________ __________________________ (type of insurance policy that pays employer in case of theft/damage by employee) c) E. Closed ___________________ (attorney, CPA, educator, doctor, etc.) Unethical behavior isn’t always large-scale 1. ____________________ – individuals without ____________________ for the law a) Are often minor lawbreakers – never ethically justified Business Law I Chapter 1 b) Weigh risks of being caught vs. benefit gained c) Lack personal _________________________ – ability to do what is right, even under pressure 2. __________________________ _________________________ – open, peaceful violation one feels is unjust F. G. a) Passionate about a cause but not advancing their own self-interest b) Have tried every other means to change the law __________________________ 1. Employee who has reported on the ___________ activities of his/her employer 2. Whistleblowers Protection Act passed by Congress in 1989 __________________________ 1. Individual who contributes toward various causes 2. May do so with public knowledge, but many do so ________________________ 3. May also be a focus of the business itself, as a way of giving back to the ____________________________ in which it is located V. TOP TEN QUESTIONS TO ASK YOURSELF WHEN MAKING AN ETHICAL DECISION* 10. Could the decision become ______________ ______________? If so, don't do it. 9. Is it ______________? If it isn't, don't do it. 8. Is it ______________? If it isn't, don't do it. 7. Is it the ______________ ______________ thing to do? If it isn't, don't do it. 6. Will this stand the test of ______________ ______________? If it won't, don't do it. 5. If something terrible were to happen, could I defend ______________ ______________? If you can't, don't do it. 4. Is it ______________, ______________, and ______________? If it isn't, don't do it. 3. How will it make me feel about ______________? If it's lousy, don't do it. 2. Does this choice lead to the greatest ______________for the greatest ______________? If it doesn't, don't do it. And the #1 question you should ask yourself when making an ethical decision: 1. Would I do this in front of my ______________? If you wouldn't, don't do it. *Hopper, Carolyn. "Top Ten Questions You Should Ask Yourself When Making an Ethical Decision." (1998). University 101 Instructor's Resource Manual Middle Tennessee State University. http://www.mtsu.edu/~u101irm/ethicques.html (10 Oct. 2003)