STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 4, ROCKS TEST __TUESDAY
advertisement

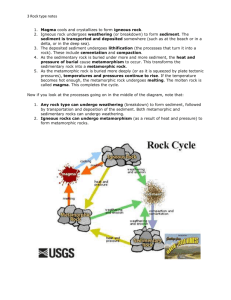
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 4, ROCKS TEST __TUESDAY, DECEMBER 15TH ____ VOCABULARY: 1. Cementation: process that glues compacted sediment to form sedimentary rock 2. Weathering: process which wind, water, ice & heat BREAK DOWN rock into sediment (small pieces) 3. Erosion: process which wind, water, ice & heat TRANSPORT soil & sediment from one location to another. 4. Deposition: process in which material is laid down. 5. Compacting: squeezing (pressure) sediment to form sedimentary rock 6. Intrusive igneous rock: rock formed from cooling and hardening of magma beneath Earth’s surface (interior) 7. Extrusive igneous rock: rock formed from volcanic activity at or near Earth’s surface (exit) 8. Felsic: light colored, igneous rocks that are less dense and rich in aluminum, potassium, silicon, and sodium. 9. Mafic: dark colored, igneous rocks, rich in calcium, iron, and magnesium. 10. Foliated: texture of metamorphic rock in which the mineral grains are arranged in planes or bands. 11. Non foliated: texture of metamorphic rock in which the mineral grains are NOT arranged in planes or bands. 12. Deformation: change in the shape of a rock caused by a force placed on it. Forces may squeeze or stretch the rock. 13. Rock cycle: series of processes in which a rock forms, changes from one type to another, is destroyed and forms again by geological processes. 14. Rock: naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals or organic matter. 15. Texture: size, shape, and position of the grains that make up a rock 16. Composition: chemical makeup of a rock ( or other materials) 17. Strata: layers 18. Stratification: process in which sedimentary rocks are arranged (aligned) in layers. 19. Magma: hot liquid that forms when rock partially or completely melts. 20. Igneous: magma cools and hardens to become igneous rock. 21. Sedimentary: grains of sediment are compacted and cemented together. Forms at or near Earth’s surface 22. Metamorphic: intense heat and pressure form metamorphic rock in the Earth’s interior. 23. Sediment: weathering breaks down rock into small pieces 24. Metamorphism: meta means “change” morphos means “shape”. In order for metamorphism to take place you need changes in temperature and pressure. Short Answer Questions/ Processes for Change: 1. How does the rate of cooling of magma affect the texture of igneous rock? (Rapid cooling vs. cooling slowly) Rapid cooling magma results in fine-grain texture. Likely formed at Earth’s surface. Slowly cooling magma results in coarse-grain texture because crystals have time to form. 2. What happens to minerals when temperature and pressure change? (From section 4 of the chapter and our Warm Up – how does the mineral composition of rocks change as it undergoes metamorphism?) Metamorphism (rocks “change shape”) occurs when temperature and pressure inside Earth’s crust change. Minerals form and are stable at specific temperatures and pressures so when there is a change in temperature and pressure minerals become unstable and change into a new mineral that is more stable at that new condition. 3. What are the 3 types of sedimentary rock? Define each type. 1. Clastic Sedimentary Rock: form when rock or mineral fragments, called clasts, are cemented together. 2. Chemical Sedimentary Rock: formed when minerals crystallize out of a solution, such as sea water, to become rock. 3. Organic Sedimentary Rock: forms from the remains of once-living plants & animals. 4. How to scientists classify rocks? By texture and composition. 5. What causes magma to form? Understand this process so you can answer what DOES NOT cause magma to form. Melting 6. Know the Rock Cycle – what processes change igneous rock into metamorphic or sedimentary? Metamorphic into igneous or sedimentary? How is sediment formed? Draw the Rock Cycle and label each process and the new rock formed. Igneous + HEAT & PRESSURE = metamorphic rock Igneous + COMPACTION & CEMENTATION = sedimentary rock Igneous + WEATHERING & EROSION = sediment Metamorphic + COMPACTION & CEMENTATION = sedimentary rock Metamorphic + MELTING & COOLING = igneous rock Metamorphic + WEATHERING & EROSION = sediment Sedimentary + MELTING & COOLING = igneous Sedimentary + HEAT & PRESSURE = metamorphic rock Sedimentary + WEATHERING & EROSION = sediment To make sedimentary rock you need COMPACTION & CEMENTATION To make igneous rock you need MELTING & COOLING To make metamorphic rock you need HEAT & PRESSURE To make sediment you need WEATHERING & EROSION To make magma you need MELTING NOTE: As part of the rock cycle process you have to go through a series of steps. In order to make sedimentary rock, you first need to make sediment. In order to make igneous rock, you first need to make magma.