Separating Mixtures: Methods & Examples
advertisement

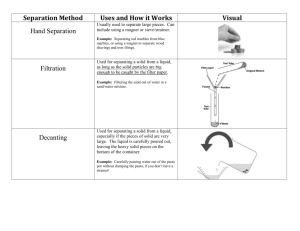
NOTES: Methods for Separating Mixtures Something is a MIXTURE if it contains two (or more) substances that are not chemically joined together. The substances in a mixture can often be easily separated from one another. A PURE substance only contains one material and so cannot be separated in any way (unless a chemical reaction takes place) PHYSICAL methods (no chemical reaction involved) of separating mixtures 1. A magnet can be used to separate solid substances, one of which is magnetic. How it works: The magnet sticks to the iron but not to the sand Example: separating of IRON from SAND. 2. Filtering (filtration) can be used to separate a solid from a liquid. How it works: The liquid (and anything dissolved in the liquid, ex. solid particles) passes through pores (holes) in a porous filter. If pores are smaller than solid particles, solid particles stay on filter (get stuck) and liquid components pass through Example: Filtration would be used to separate the dirt from some salty water or sand from water. 3. Evaporation This method is suitable to separate a soluble solid (ex. salt) from a liquid How it works: When salty water is warmed the water evaporates leaving behind crystals of salt. Example: Evaporation would be used to obtain some pure salt from salty water. 4. Distillation This method is used to separate a mixture of liquids with distinct boiling points that are far apart. How it works: Different liquids boil at different temperatures. When heated, they boil off and condense (turn into liquid) at different times. The apparatus features a fractionating column, which ensures that only the liquid boils at its boiling point will pass into the condenser. Example: separating ethanol and water 5. Crystallization This method results in the formation of pure solid particles of a substance from a solution containing the dissolved substance. How it works: When the solution contains as much dissolved substance as it can possibly hold (ex. 100g of water can dissolve only 250g of salt), the addition of a tiny amount more often causes the dissolved substance to come out of solution (“grow” out of the solution) because the solution is too concentrated for all the solid to remain dissolved at that temperature and collect as crystals on some available surface. Crystallisation is often done from a hot concentrated solution, because most substance are more soluble the hotter the liquid. Example: Rock Candy – as water evaporates from the sugar-water supersaturated solution (too concentrated), the sugar is left behind as a solid crystal on the string. 6. Chromatography This method is to separate different colored dyes. How it works: The dyes travel up the chromatography paper (filter paper) at different distances before they cannot remain in solution. The more soluble dyes move further up (travel faster across the filter paper b/c they are less attraction to the paper) than the less soluble ones (travel slower, b/c they are more attracted to the paper), hence separating from each other. The product is called chromatogram. Example: separating dyes in inks, or chlorophyll in plants Instructions for notes: Methods for separating mixtures Students separate their notebook page in 6 boxes (there are 6 methods) Give students guiding questions. Usually I have them on ppt. Students read for a purpose. What is the method? When is it used? Draw a picture. How does it work? Give an example Students read the notes. While they read they answer the guiding questions in their notebook in each of the 6 squares. Student page will look something like that…. You can apply the rule 4 colors minimum….. Magnet When? How? Picture Example