Chapter 5, Sections 2, 3, 4 Matter in Motion Name
advertisement
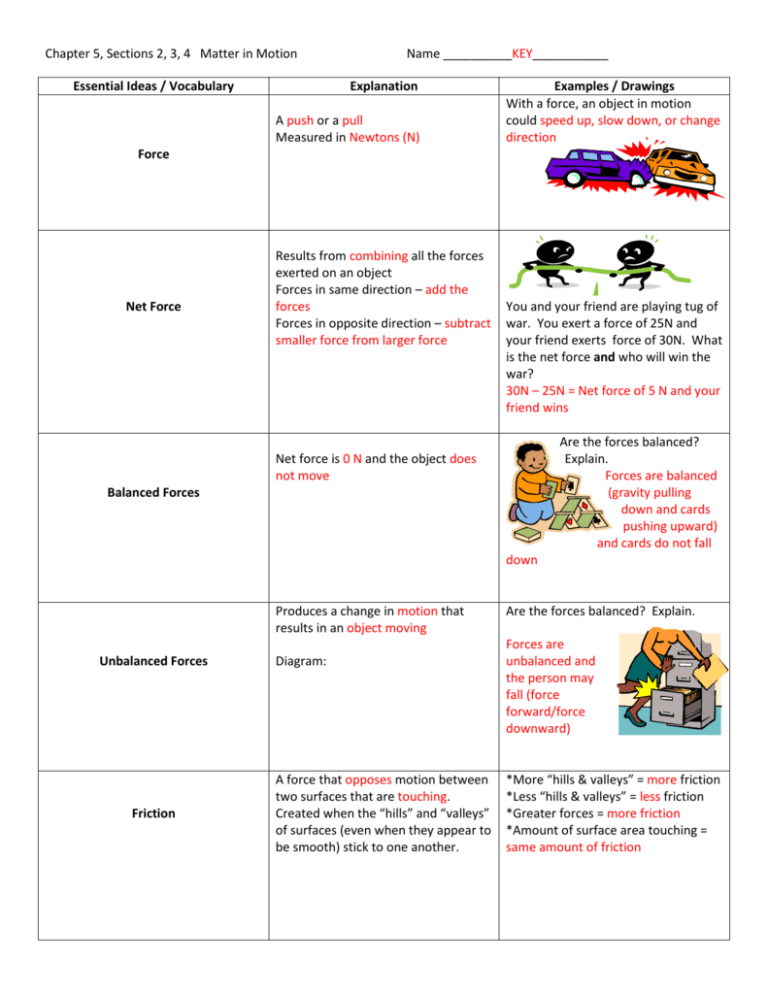
Chapter 5, Sections 2, 3, 4 Matter in Motion Essential Ideas / Vocabulary Name __________KEY___________ Explanation A push or a pull Measured in Newtons (N) Examples / Drawings With a force, an object in motion could speed up, slow down, or change direction Force Net Force Results from combining all the forces exerted on an object Forces in same direction – add the forces Forces in opposite direction – subtract smaller force from larger force You and your friend are playing tug of war. You exert a force of 25N and your friend exerts force of 30N. What is the net force and who will win the war? 30N – 25N = Net force of 5 N and your friend wins Are the forces balanced? Explain. Forces are balanced (gravity pulling down and cards pushing upward) and cards do not fall Net force is 0 N and the object does not move Balanced Forces down Produces a change in motion that results in an object moving Unbalanced Forces Friction Diagram: A force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching. Created when the “hills” and “valleys” of surfaces (even when they appear to be smooth) stick to one another. Are the forces balanced? Explain. Forces are unbalanced and the person may fall (force forward/force downward) *More “hills & valleys” = more friction *Less “hills & valleys” = less friction *Greater forces = more friction *Amount of surface area touching = same amount of friction Friction is necessary When is friction needed? Tires on Road, brakes, shoes on floor, rubber bottom on bath mat Increase Friction Ways to increase friction: rough up a surface, add sand/gravel, increase mass (greater force between surfaces) Tile is slick when wet, so getting out of shower you step on rug to dry your feet – friction keeps you from slipping / falling vs Race cars have slick tires to allow car to go faster, but less traction so they spin out more quickly… regular cars have “rougher” tires to be able to grip the road to increase friction and avoid spinouts Decrease Friction Gravity Law of Universal Gravitation Ways to decrease friction: lubricants (oils, grease, wax, water), smooth/sand surface, ball bearings (in skates/wheels) Force of attraction between objects due to their masses. Two factors that affect gravity are mass and distance. All objects in the universe attract each other through gravitational force. The size of the force depends on the mass of the objects and the distance between them. Define: amount of matter in an object Mass (review) Tool used to measure: balance scale Increase gravitational force by increasing mass and/or decreasing distance between objects. Decrease gravitational force by decreasing mass and/or increasing distance between objects. How change? Grow from baby Diet Pump iron (build muscle) SI Unit: g Define: amount of gravitational force on an object due to its mass Weight (review) Tool used to measure: spring scale SI Unit: N How change? Change mass Change location/leave planet






