1-what changes Earth
advertisement

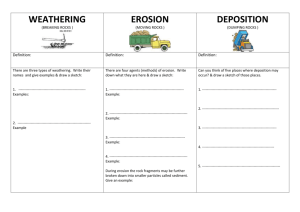
Extra Support for Name _____________________________________________ Vocabulary and Concepts Unit 8: Changes to the Earth’s surface Weathering is the breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces. The small pieces are called sediments. Sediment bits of rock carried by slow-moving water or wind. Weathering has changed the shape of these rocks. Erosion is the removal and transportation of weathered material. Deposition is the dropping or settling of the eroded material. Ice changes Earth surface. -Agents of weathering, erosion and deposition: 1. Roots can grow into rocks and break them apart; wind and water can wear away rocks. 2. Gravity can cause rocks to fall and break; flowing water can cause rocks to scrape each other. 3. Chemicals in water and rain can combine with rock to break it down and wear it away. 4. Wind and rain can cause erosion, the moving of weathered rock from one place to another. 5. Fast-flowing river water pulls rocks along the bottom of the river. 6. Slow-moving water deposits rocks on the river bottom in a process called deposition. 7. Slow-moving water carries along tiny bits of sand and silt, called sediment. 8. Sand dunes form when wind deposits a lot of sand in one area. 9. 1 Huge sheets of ice called glaciers pick up rocks as they move along like very slow rivers Extra Support for Name _____________________________________________ Vocabulary and Concepts The Earth’s layers: 1-Crust [KRUHST] the thin, rocky outer layer of Earth 2-Mantle [MAN•tuhl] the thickest layer of Earth, just below the crust -Core [KAWR] the center of Earth, made of metal 3-Outer core :molten, or liquid metal. 4-Inner core : solid metal. -Earth’s plates: -Earth’s crust and uppermost mantle are divided into sections, called plates. -Plates are blocks of crust and upper mantle rock that fit together like puzzle pieces. At different places, plates move toward each other, move away from each other, or slide past each other. These plate movements cause many changes in Earth’s surface. 1-Earthquakes -An Earthquake is a vibration in Earth’s crust, caused by the release of energy at a fault. -A fault is a break in the crust where rock moves. -The point inside Earth where an Earthquake begins is called the focus. -The point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus of an earthquake is the epicenter. 2-Volcanoes A Volcanoes is a mountain formed by lava and ash. Magma is liquid rock inside a volcano. Lava is liquid rock (magma) that flows out of a volcano. 2 Extra Support for Name _____________________________________________ Vocabulary and Concepts How Mountains Form -Plates moving toward each other push up mountains A-Match the clue to the simple machine. 1 a break in Earth’s crust A. lava 2 molten rock that flows out of a vent and arrives at Earth’s surface B. fault 3 the point on Earth’s surface that is directly above where an earthquake’s energy is released C. magma 4 molten rock under Earth’s surface D. epicenter B-Complete the following: (fault-volcano-magma-Earthquake) 1-Molten rock beneath Earth’s surface is _______. 2-A movement of the ground, caused by the sudden release of energy in Earth’s crust, is an _______. 3-A break in Earth’s crust is called a _______. 4-A mountain made of lava and ash is a _______. 3 Extra Support for Name _____________________________________________ Vocabulary and Concepts C-Choose the best answer 1- In which order are the processes listed below most likely to occur? A. erosion—deposition—weathering B. deposition—erosion—weathering C. weathering—deposition—erosion D. weathering—erosion—deposition 2-The point inside Earth where an earthquake begins is a-epicenter b-focus c-Fault d-plate tectonics 3-A break in the Earth’s crust where rocks can move is called a-earthquake b-Volcano c-Fault d-plate tectonics 4-The point on Earth’s surface directly above an earthquake is a-epicenter b-focus c-Fault d-plate tectonics 5-which of these is being released as rocks in a fault slide past one another? a-earthquake b-Volcano c-Fault d-plate tectonics 6-Certain land features form where plates meet. Which land feature forms where two continental plates move toward each other? glaciers mountains oceans trenches 7-Notice the ice splitting the rock.To which process does the ice contribute? deposition erosion polishing weathering 4 Extra Support for Name _____________________________________________ Vocabulary and Concepts 8-Earth consists of the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core. Which label do scientists use when they refer to the four parts of Earth shown in the image? faults layers plates rings 9-weathering and erosion are two different processes. Which sentence states a difference between weathering and erosion? Erosion moves rocks while weathering breaks them down. Weathering and erosion move rocks to new locations. Erosion breaks down rocks but doesn’t move them. Weathering moves rocks without breaking them down. 10-Sometimes, magma forces plates to push apart. Which statement best explains how magma reaches Earth’s surface? Gravity pulls the magma to the surface. Plate movement forces the magma upward. Heat and pressure cause the magma to rise. Magnetism attracts the magma to the surface. 11-Plates cause changes to Earth’s surface as they move and shift. Which type of plate movement forms mountains? Plates drift apart. Plates slide by each other. Plates push against each other. Plates blend to form one large plate. D-Match the term to the words that tell about it. 1.erosion wind and water break down rock into smaller pieces 2.weathering a place where lava comes out of the ground 3.earthquake wind or moving water moves sand and small rocks 4.volcano a shaking of Earth’s surface 5 Extra Support for Name _____________________________________________ Vocabulary and Concepts E-Match the clue on the left to the term on the right. 1-This occurs when rivers drop bits of rocks and soils. 2-They are made of layers of lava, rock, and ash. 3-This causes shaking, rolling, and cracking in the crust and Earth’s surface. T F-Fill this chart G-Match the clue on the left to the term on the right. Layer extending from the mantle to the center of the Earth Earth’s thin outer skin The breaking down of rock into smaller pieces The dropping or settling of eroded material H-Use this space to complete the graphic organizer. I-abel the layers of Earth 1-……………….…… 2-……………………… 3-…………..………… 4-…………………………. 6 Volcano Earthquake Deposition A. crust B. weathering C. deposition D. core