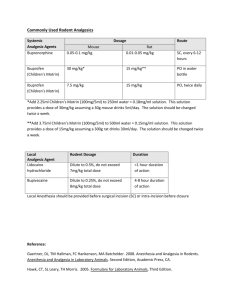
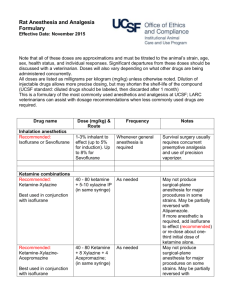
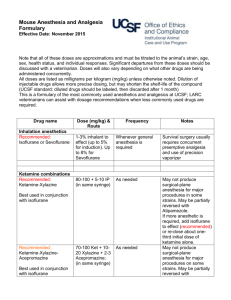
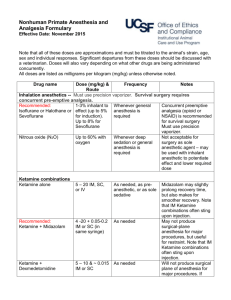
ウサギの麻酔・鎮痛剤 薬剤 用量(mg/kg) &投与方法 投与回数 注記
advertisement

ウサギの麻酔・鎮痛剤 薬剤 用量(mg/kg) &投与方法 注記 Anticholinergics – Prevents bradycardia and cardiac arrhythmias 0.02-0.05 Some rabbits have atropinase and atropine is quickly Atropine Once at induction. May need to administer booster dose. IM or SC metabolized 0.1 IM or SC Once at induction. May need to administer booster dose. Recommended: Glycopyrrolate 0.01 IV Inhalation anesthetics – Must use precision vaporizer. Survival surgery requires concurrent pre-emptive analgesia. Mask or chamber induction without injected pre-medication may result in breath-holding and injury. Recommended: Sevoflurane Isoflurane or 1-3% inhalant to effect (up to 5% for induction). Whenever general anesthesia is required Up to 8% for Sevoflurane Survival surgery requires concurrent pre-emptive analgesia. Not acceptable for surgery as sole agent – usually used with inhalant anesthetic to potentiate effect and lower required dose Ketamine combinations – May sting on IM injection. May be used for pre-anesthesia prior to intubation and induction of isoflurane anesthesia or as general anesthesia. May not produce surgical-plane anesthesia for major 35 – 50 As needed. If redosing use ¼ dose of each. procedures. May be partially reversed with Atipamezole or Recommended: Ketamine-Xylazine + 5 -10 IM or SC (in same syringe) Yohimbine. 35-50 May not produce surgical-plane anesthesia for major As needed. If redosing use ¼ dose each of ketamine and Recommended: + 5 -10 procedures. May be partially reversed with Atipamezole or xylazine only. Ketamine-Xylazine-Acepromazine + 0.75 – 1.0 IM or SC (in same syringe) Yohimbine. 35 – 50 + 0.25 -0.5 IM or SC (in same syringe, or with May not produce surgical-plane anesthesia for major Ketamine-Medetomidine As needed. If redosing use ¼ dose of each. medetomidine adm. 10-20 minutes in advance) procedures. May be partially reversed with Atipamezole. only if pre-medicated with an anticholinergic 35 – 50 May be useful for restraint for performing short, not painful Ketamine-Midazolam +2 – 5 IM or SC As needed procedures. (in same syringe) Reversal agents for alpha 2 agents – Atipamezole is more specific for medetomidine than for xylazine (as a general rule, Atipamezole is dosed at the same volume as Medetomidine, though they are manufactured at different concentrations) Atipamezole 0.1 – 1.0 SC, IM, IV Once. Repeat as needed. To reverse medetomidine or xylazine Yohimbine 0.2 – 2.0 IV or SC Once. Repeat as needed. For reversal of xylazine effects Other injectable anesthetics 20 – 50 IV to effect and maintained with intermittent bolus as needed Consider supplemental analgesia (opioid or NSAID) for Recommended for terminal/acute procedures only, with Sodium pentobarbital (Nembutal) or invasive procedures. Rabbits have a very narrow window of booster doses as needed 2-20 mg/kg/hr IV continuous infusion after safety for pentobarbital. Apnea is common at anesthetic doses. induction As needed. Very short acting unless administered as a an Only useful IV, so therefore limited usefulness. Respiratory Propofol 12-26 IV IV drip. depression upon induction is possible. Opioid analgesia Used pre-operatively for preemptive analgesia and For major procedures, require more frequent dosing than 12 0.01 – 0.1 SC or IP Recommended: Buprenorphine post-operatively every 6-12 hour hour intervals. Consider multi-modal analgesia with a NSAID Nitrous oxide (N2O) 投与回数 Up to 60% with oxygen Whenever deep sedation or general anesthesia is required Butorphanol Morphine 0.1 – 0.5 IM, IV, SC 0.5 -5 IV or IM Fentanyl patch Patch /B.Wt. 25 µg/hr Every 4-6 hours Every 2-4 hours for 8 hours Place patch 24 hours in advance of surgery and maintain for up to 3 days. Alternatively, place at induction, premedicate with morphine, adm. morphine at 4 and 8 hrs. Useful for minor, short procedures When fentanyl patch is placed at induction When severe post-surgical pain is anticipated. Best placed on the back at induction and covered by a bandage after surgery Reversal agents for opioids Naloxone 0.01 -0.02 IV, IM Once as needed to reverse respiratory depression Note that reversal will also remove the analgesic effect of the opioid Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for analgesia (NSAID) — Note that prolonged use may cause renal, gastrointestinal, or other problems. Used pre-operatively for preemptive analgesia and post-operatively for postoperative analgesia. Depending on the procedure, may be used as sole analgesic, or as multi-modal analgesia with buprenorphine. DRUG NAME DOSE (mg/kg) & ROUTE FREQUENCY NOTES Recommended: Carprofen Meloxicam Flunixin meglubin Banamine® 1.0 – 2.2 PO 0.1 – 0.3 PO, IM or SC Every 12 hours Adm. pre-op, then every 24 hours For supplemental postop analgesia 1.0 IM only Every 24 hours for no more than 3 days Adm. pre-op, then Ketorolac 0.3 – 0.5 IM, SC every 12-24 hour Ketoprofen 2 – 5 SC, IM Adm. pre-op, then every 12-24 hour Local anesthetic/analgesics (lidocaine and bupivacaine may be combined in one syringe for rapid onset and long duration analgesia) DRUG NAME DOSE (mg/kg) & ROUTE FREQUENCY Dilute to 0.5%, do not exceed 7 mg/kg total dose, SC or Use locally before making surgical Lidocaine hydrochloride intra-incisional incision Dilute to 0.25%, do not exceed 8 mg/kg total dose, SC or Use locally before making surgical Bupivacaine intra-incisional incision Useful for treating hyperthermia NOTES Faster onset than bupivacaine but short (<1 hour) duration of action Slower onset than lidocaine but longer (~ 4-8 hour) duration of action