Algebra I - Fort Thomas Independent Schools

AP Statistics
Notes
Name: ____________
Date: ____________
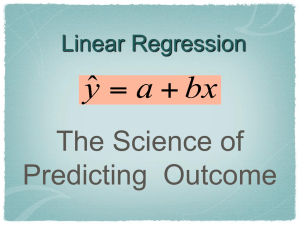
Lesson 3.1B: Correlation and Its Properties
Objectives:
F: Using a calculator, find the correlation r between two quantitative variables.
G: Know the basic properties of correlation: r measures the strength and direction of
linear relationships only;
relations; r
1
r
1 always; moves away from 0 towards
1 r
1 only for perfect straight-line as the linear relation gets stronger.
Vocabulary:
Correlation, r
Example:
How well does the number of beers a student drinks predict his or her blood alcohol content (BAC)? Sixteen student volunteers at The Ohio State University drank a randomly assigned number of cans of beer. Thirty minutes later, a police officer measured their BAC. Here are the data: [Example 3.5 page 177.]
Beers: 5
BAC: 0.10
2 9
0.03 0.19
8 3
0.12 0.04
7 3
0.095 0.07
5
0.06
Beers: 3
BAC: 0.02
5 4
0.05 0.07
6 5
0.10 0.085
7 1
0.09 0.01
4
0.05 a.
Below is a scatterplot of the data with “Number of Beers” (x) on the horizontal axis and “Blood Alcohol Content” (y) on the vertical axis.
0.20
Scatterplot of Blood Alcohol Content vs Number of Beers
0.15
0.10
0.05
0.00
0 1 2 3 4 5
Number of Beers
6 7 8 9 b. In general, how does the blood alcohol content score appear to be related to the number of beers consumed? [Form-Direction-Strength]
c. In order to measure the direction and strength of a linear relationship, we will
calculate the correlation coefficient, r.
Suppose that we have data on two quantitative variables x and y for n individuals.
The correlation r between x and y is r
n
1
1
x i s
x x
y i s
y y
Enter the “Number of Beers” and “BAC” data in your calculator.
Enter “Number of Beers” in L
1 and “BAC” in L
2
.
Using your calculator, complete the following table in order to calculate the correlation coefficient, r.
L
1
L
2 x
L
3
y
( x
x ) s x
L
4
( y
y ) s y
L
5
( x
x ) s x
( y
y ) s y d. Looking at your table and scatterplot, discuss how r measures the strength of the relationship between Number of Beers and BAC.
Correlation Coefficient, r
Linear Relationship?
Negative
Strong Moderate Weak None Weak
Positive
Moderate Strong
-1 -.8 -.5 0
Value of r
.5 .8 1
[Look at Figure 3.7 on page 192 of your text.] e. What is the correlation coefficient, r ?
What does this value of r tell you about the relationship between Number of
Beers consumed and BAC score?