Experiment 02: Power Gain and Beam

Yarmouk University
Hijjawi Faculty of Engineering and Technology
Department of Communication Engineering
Microwave Systems Lab (CME447a)
Part 2: Microwave Antennas
[1].
[2].
[3].
Experiment 4:
Power Gain and Beamwidth Horn measurements
Objectives:
Upon completion of the laboratory study and experimentation, the student will be able to:
Background Discussion
Microwave Antennas Page 1
Material Required
Experimental Procedures
Yarmouk University
Hijjawi Faculty of Engineering and Technology
Department of Communication Engineering
Beamwidth measurements
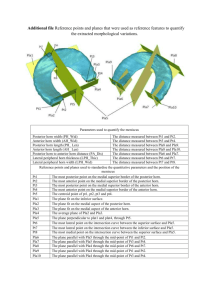
[1].Determine the radiated beamwidth by locating the – 3 dB points on both sides of the center line
.Maintain the receiver horn on the 3 dB line and move sideways to the left while maximizing current.
[2]. Determine the right-angle by moving the receiving horn to the right until the meter reading decreases to 50 % (- 3 dB power point) or the attenuator equal 3 dB.
Record the angle _______________________ (deg)
Microwave Antennas Page 2
Yarmouk University
Hijjawi Faculty of Engineering and Technology
Department of Communication Engineering
[3].repeat the step above while using a 10 dB transmitting horn, the 15 db receiver horn remain attached and determine the -3 dB beamwidth for both left and right.
______________________ L(deg), ______________________ R(deg).
[4].what is the total beamwidth between the two -3 Db points for both 10 and 15 dB horn?
10 dB horn: BW = _________________ (deg)
15 dB horn: BW = _________________ (deg)
Experiment 5:
Plotting the radiation patterns of the E and H Planes
Objectives:
Upon completion of the laboratory study and experimentation, the student will be able to:
[1].
[2].
[3].
Background Discussion
Microwave Antennas Page 3
Yarmouk University
Hijjawi Faculty of Engineering and Technology
Department of Communication Engineering
Material Required
Experimental Procedures
[1]. A 15 Db horn is attached to the transmitter module and another 15 dB horn is used at the receiver.
Start with the receiver located at the PO line and set meter current to .
[2] Plot the H plane radiation pattern of the 10 dB transmitter horn. Leave the 15 dB horn attached to the receiver but change its polarization to be vertical.
[3]. for the last plot, remove the 10 dB horn from the transmitter, leaving only the waveguide connected. Repositioning the receiver horn so that it is in line with the axis of transmits horn and a gain tries plotting output of the waveguide.
[4]. from equation below, compute the minimum measurement distance.
___________________________.
Microwave Antennas Page 4
Yarmouk University
Hijjawi Faculty of Engineering and Technology
Department of Communication Engineering
Experiment 6:
Flare horn antenna measurements
Objectives:
Upon completion of the laboratory study and experimentation, the student will be able to:
[1].
[2].
Background Discussion
Microwave Antennas Page 5
Yarmouk University
Hijjawi Faculty of Engineering and Technology
Department of Communication Engineering
Material Required
Experimental Procedures
[1]. physically measure the flare-horn and calculate its db gain. Assume a frequency of operation 10.5
GHz and an efficiency of 66%. a =_________________ cm b =_________________ cm
G =_________________
[2]. Attach the flare-horn to the transmitting module and align to the apex. Connect the 15 Db horn
(with its “a” dimension parallel to the table) to the detector waveguide and stand. Determine the beamwidth of the flare horn in this position.
Microwave Antennas Page 6
Yarmouk University
Hijjawi Faculty of Engineering and Technology
Department of Communication Engineering
[3]. From the E-plane and H-plane measurements, determine the beamwidth of the radiation pattern in each of these planes.
E plane:_____________ degrees.
H plane:_____________ degrees.
[4].what is the ratio in beamwidth (BW) between the two different pattern?________________.
Conclusion
Microwave Antennas Page 7