Diuretics and Discharge Handout Alexander T. Limkakeng, Jr. MD
advertisement
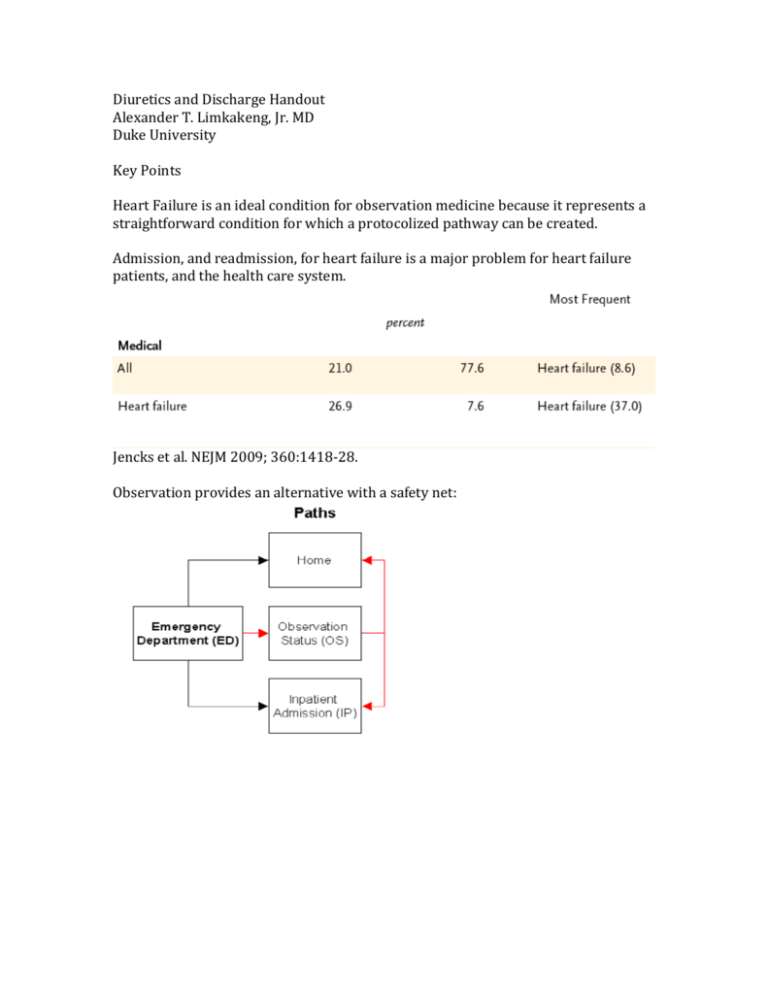
Diuretics and Discharge Handout Alexander T. Limkakeng, Jr. MD Duke University Key Points Heart Failure is an ideal condition for observation medicine because it represents a straightforward condition for which a protocolized pathway can be created. Admission, and readmission, for heart failure is a major problem for heart failure patients, and the health care system. Jencks et al. NEJM 2009; 360:1418-28. Observation provides an alternative with a safety net: An ideal observation unit pathway for heart failure patients can be summarized by the 7 “P”’s Patients Pick the right ones. Protocolized Care Use one and stick to it, if patients do not fit in your pathway then admit them (see #1) imProved? (Ensure your pathway has mandated reassessments, ideally semiobjective ones like lying them supine). Precipitants Addressed: Look into, for example, whether the patient has unaddressed hypertension. Be cautious and consider excluding patients with ACS, arrhythmias, pneumonias, or worsening renal function as the cause of their CHF. Prescriptions (BB and ACE-I) Ensure patients are started on or continued on these medications. Preach (Education) Provide education on medications, lifesetyle, diet, accounting for patient learning challenges. Physicians (Follow up) Patients should have a Primary care and Cardiologist involved in follow up care. Fonarow et al. Arch Intern Med 2008;168:847-54. Lee et al. Circulation 2010;122:1806-14 DUKE UNIVERSITY: A SIMPLE CHF PROTOCOL I. INCLUSION CRITERIA 1. History of heart failure 2. Signs and symptoms of heart failure II. EXCLUSION CRITERIA 1. EKG shows evidence of acute MI or ischemic pattern 2. Unstable vital signs 3. Arrythmias 4. Respiratory failure 5. Co-morbid conditions/causes: ESRD, pneumonia, thyrotoxicosis, pulmonary HTN, anemia III. OBSERVATION INTERVENTIONS 1. Serial cardiac enzymes and ECGs 2. Cardiopulmonary monitoring 3. Serial exams at least every 4 hrs, as clinically indicated 4. Diuresis 5. Supplemental oxygen, if needed 6. Correction of electrolyte imbalances 7. Consider echocardiography and/or non-invasive hemodynamic assessment 8. Education regarding diet and behavioral modification 9. Consult Social Worker for discharge planning and follow-up care IV. DISPOSITION CRITERIA 1. Home 1. Normal serial enzymes and ECGs 2. Stable vital signs, pulse oximetry back to baseline 3. Improvement in symptoms to baseline 4. Adequate diuresis 5. Unremarkable echocardiography 6. Appropriate and understood discharge plans for follow up care 2. Hospital 1. Significant elevation of cardiac enzymes 2. Rule in of exclusion criteria 3. Minimal improvement or worsening symptoms 4. Significant finding on functional study 5. Significant EKG changes 6. Unstable vital signs V. TIME FRAME - Up to 12-18 hours for evaluation and treatment SCPC OBSERVATION INCLUSION/EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Fermann and Collins. Curr Heart Fail Rep 2010;7:125–33 OTHER RESOURCES: Fermann GJ, Collins SP. Observation units in the management of acute heart failure syndromes. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2010 Sep;7(3):125-33. doi: 10.1007/s11897-0100020-x. Review. PubMed PMID: 20625946. Heart Failure Executive Committee, Peacock WF, Fonarow GC; Heart Failure Diagnosis Subcommittee, Ander DS, Maisel A, Hollander JE, Januzzi JL Jr, Yancy CW; Heart Failure Risk Stratification Subcommittee, Collins SP, Gheorghiade M, Weintraub NL, Storrow AB, Pang PS, Abraham WT, Hiestand B; Heart Failure Treatment Subcommittee, Kirk JD, Filippatos G, Gheorghiade M, Pang PS, Levy P, Amsterdam EA. Society of Chest Pain Centers Recommendations for the evaluation and management of the observation stay acute heart failure patient: a report from the Society of Chest Pain Centers Acute Heart Failure Committee. Crit Pathw Cardiol. 2008 Jun;7(2):83-6. doi: 10.1097/01.hpc.0000317706.54479.a4. PubMed PMID: 18520521.
![Major Change to a Course or Pathway [DOCX 31.06KB]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006879957_1-7d46b1f6b93d0bf5c854352080131369-300x300.png)