Affiliate Tax-Exempt Options - Indiana State 4-H
advertisement

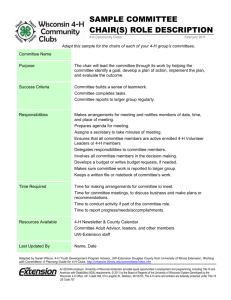
4-H Affiliate Tax Options Entities who are affiliated with the 4-H Youth Development program, and whose 501(c)(3) tax exemption has ended in 2011 as a result of the sunset of GEN 2704, will have four options to consider regarding their tax status. These options are listed below along with an outline of the advantages and disadvantages of each option. 4-H Affiliates are organizations which are authorized to use the 4-H Name & Emblem, but which do not operate as a 4-H Club. Examples of 4-H Affiliates include, but are not limited to, County 4-H Councils and 4-H Fair Boards. 4-H Affiliate Tax-Exempt Options 1. Join the Purdue Group Exemption Number (PU GEN) 2. Obtain status as separate 501(c)(3) Entity Advantages No financial cost for entity to join PU GEN. May accept charitable contributions from individuals, businesses, or organizations. Eligible to apply for grants as a non-profit entity using IRS 501(c)(3) tax recognition as subordinate organization under PU GEN. Not required to complete separate Form 1023 or Form 1024 application to obtain tax exempt status under 501(c)(3) or 501(c)(5) because of conferred status as subordinate organization under PU GEN. Exempt from paying taxes on entity income derived from tax-exempt function activities and sources of income exempt from unrelated business income tax. May accept charitable contributions from individuals, businesses, or organizations. Eligible to apply for grants as a non-profit entity using separate IRS 501(c)(3) determination letter issued to entity. Not asked to include specific general supervision and control language in governing document . Exempt from paying taxes on entity income derived from tax-exempt function activities and sources of income exempt from unrelated business income tax. Separate identification as 501(c)(3) organization in IRS Publication 78. Disadvantages Will agree to be under Purdue’s general supervision and control – specific language to be included in governing document. Governing document must be amended to satisfy IRS current organizational test for 501(c)(3) entities. Annual review to maintain participation in PU GEN; Purdue determines whether eligibility conditions to remain in PU GEN continue to be met. No separate identification as 501(c)(3) organization in IRS Publication 78. File Form 1023 Application http://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/f1023.pdf (30 pages); 38 pages of instructions available at: http://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/i1023.pdf; typical application package between 50-100 pages; estimated 100 hours preparation time for novice. Professional fees; attorney/accountant should be hired to complete/review of Form 1023 application and documents required to be submitted with application. Estimated professional fees are likely to be ~$3,000-$5,000 or more, depending on the facts in each situation and local resources available. REV: 1/5/2012 4-H Affiliate Tax-Exempt Options Advantages No annual determination by Purdue to continue 501(c)(3) status through PU GEN. 3. Obtain status as separate 501(c)(5) Entity (provides for exemption of labor, agricultural or horticultural organizations) Exempt from paying taxes on entity income derived from tax-exempt function activities and sources of income exempt from unrelated business income tax. Some IRS required provisions in governing document to obtain exempt status under 501(c)(3) are not required to be included in 501(c)(5) governing document. Not asked to include specific general supervision and control language in governing document. No annual determination by Purdue whether to continue exempt status under 501(c)(5). 4. Become taxable entity Not asked to include specific general supervision and control language in governing document. Not required to include IRS required 501(c)(3) provisions in governing document. Disadvantages Initial filing fee $850 for 2011 applications (for entities with gross receipts of at least $10,000). IRS may take as long as a year to process application. Will NOT be recognized as a 4-H Affiliate. May not have 4-H in its name or purpose, nor be granted use of 4-H Name & Emblem. File Form 1024 (3-4 page application + 20 pages of instructions) http://www.irs.gov/pub/irspdf/k1024.pdf. Initial filing fee $850 for 2011 applications (for entities with gross receipts of at least $10,000). Unable to acknowledge receipt of deductible charitable contributions from individuals, businesses, or organizations even if contributions promote charitable activity conducted by 501(c)(5) entity. May not be able to apply for grants as a non-profit entity if granting agency insists on 501(c)(3) status as condition for grant. Will NOT be recognized as a 4-H Affiliate. May not have 4-H in its name or purpose, nor be granted use of 4-H Name & Emblem. Pay taxes on income received. Pay taxes on any property owned. Unable to acknowledge receipt of deductible charitable contributions from individuals, businesses, or organizations. Ineligible to apply for grants as a non-profit entity. Annual IRS filing requirements as business or for-profit corporation/organization. Will NOT be recognized as a 4-H Affiliate. May not have 4-H in its name or purpose, nor be granted use of 4-H Name & Emblem. As a result of the sunset of GEN 2704, any 4-H Affiliate which derived its tax exempt status through GEN 2704 and which does not undertake option 1, 2, or 3 above, will be characterized by the IRS as a taxable entity. REV: 1/5/2012 *NOTE: The ability of 4-H Affiliates to participate in the PU GEN is subject to the final approval of the Purdue University Executive Vice President and Treasurer. Regardless of the tax option that the 4-H Affiliate chooses, the following obligations will be met: Annual IRS Form 990-series filing requirements (for Options 1-3 above): o Entities earning $50,000 or less in annual gross receipts will file an e-postcard (http://epostcard.form990.org/). o Entities earning over $50,000 in annual gross receipts will file a Form 990. This is typically a 20+ page report (http://www.irs.gov/pub/irspdf/f990.pdf), including conflict of interest statements, statement of unrelated board members, etc. o Need to file Form 990-T for sources of unrelated business income. Sign a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with the County 4-H program that outlines specific guidelines for the groups to collaborate with one another. Individuals serving as volunteers for the 4-H Affiliate will successfully complete the 4-H Volunteer Screening process and annually sign the Adult Behavioral Expectations Forms. Maintain an active Employer Identification Number (EIN) with the IRS (whether or not the entity handles any finances). Submit an annual report of the entity’s finances to the County Extension Office. May or may not be exempt from paying applicable property taxes. Indiana law controls entity’s eligibility for property tax exemption. Indiana application form required to request a property tax exemption tied to specific provisions of Indiana Code. REV: 1/5/2012