evolution and natural selection packet
advertisement

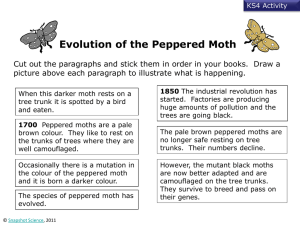
EVOLUTION AND NATURAL SELECTION PACKET Name: _____________________________________________ Period: ________________ Teacher: _________________________________ STUDENT UNIT PLAN LEARNING TARGETS : EVOLUTION AND NATURAL SELECTION VOCABULARY TERMS: Stasis Diversity Genetic Drift *Endosymbiotic Theory Fossil Record Carrying Capacity Adaptation Mutation Biogeography Natural Selection Species Founder Effect Gene Pool Homologies Evolution Speciation Bottleneck Effect Anatomical Population Gene Flow Recombination ****************************************************************************************** Assignment(s) 1. I can describe the contributions made to the Theory of Evolution by Charles Darwin. 2. Using molecular (DNA) evidence, physical and embryological similarities, I am able to analyze and evaluate common ancestry among living things. 3. I am able to analyze and evaluate the evolutional time line of life on earth through the fossil record. 4. I can analyze and evaluate the effects of natural selection on populations, including inherited variation, overpopulation, and limiting factors which produce favorable traits. 5. Given examples or diagrams, I can analyze and evaluate the effects of genetic drift, gene flow, and mutations on populations. 6. I am able to recognize that any living thing that adapts to its environment will ensure long term survival of its species? Page 2 STOCK QUESTIONS My level of understanding after discussion and assignments: or Theory of Evolution (Chapters 15 – 18) Evolution = process by which ______________ organisms have _______________ from _____________ ancient organisms. A change in populations over a long period of time. Scientific Theory = __________________________, ____________________ explanation of phenomena that have occurred in the natural world. Darwin: **In 1831, Darwin set sail from England aboard the __________________________________ for a voyage around the world. **During his travels, Darwin made numerous ________________________ and collected _______________________ that led him to propose a hypothesis about the way life changes over time known as _____________________ _____________________. Natural Selection also known as: ___________________ ______ ________ ____________________. Process by which individuals who are better __________________ for their environment ___________________ and _____________________ successfully. In the Galapagos Darwin notices that there were variations among members of the same species. Example: Finches, Giant Tortoise ________________________: the ability for an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment. It’s a ______________________________________________________________. For Example: Hummingbirds have adapted to their environment in two ways: 1. Very fast flight to keep them steady. 2. Long beak and tongue to reach into flowers and extract nectar. _____________________________: any inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chances for survival. Practice Question: 1. The Peppered Moth Scenario is an example of ________? a. Transcription b. Natural Selection c. Artificial Selection d. Translation Page 3 Evidence of Evolution: The Fossil Record What are fossils? ____________________________of once living organisms Homologous Structure: Similar in _________________ but _________________ differently Examples: flying, swimming, grasping etc. Analogous Structure: Structures that have a __________________ function, but _____________________ structures. Example: Butterfly and bird both use their wings for flying, but wings are structured differently, one has bones, one has network of veins. Vestigial Structure: Structures (organs) that serve __________________________________ in an organism. In whales, there is a vestigial pelvis and femur. Can you name any vestigial structures in humans? __________________________ Embryology: The early stages of ______________________ in organisms provides evidence that they share a _____________________ _______________________. Biochemistry: DNA and Proteins: shows that closely related species share common ______________ sequences. Speciation: the _____________________ of one or more _______________ from a single ancestor species. Geographic Isolation: When two populations of a species becomes _____________________ by _____________________ barriers such as ______________ or mountain ranges resulting in the formation of 2 separate gene pools. Genetic Drift: a change in _____________________ frequencies that occur in __________________ populations. These changes are associated with ____________________ events Bottleneck effect: ___________________________ “catastrophic event” (hunting, earthquake, volcanic eruption, etc. __________ _____ of the original population remains & repopulates ______diverse population Founder Effect: Small population gets _________________ by chance (storm, earthquake, etc.) Develop _________________ ____________________ over many generations If they come in contact later, they are too __________________ to interbreed Genetic Flow: (aka Gene Migration): the transfer of ____________________ or _________________ from one population to another Page 4 EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION PACKET Information: Much evidence has been found to indicate that living things have evolved or changed gradually during their natural history. The study of fossils as well as work in embryology, biochemistry, and comparative anatomy provides evidence of evolution. PART A: Fossil Footprints: Observe the fossil footprints in the diagram below and then answer the following questions. 1. How many different types of footprints do you observe in Section A? ___________ 2. During Section B, what do you believe might have occurred? ________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What has happened to the skull of the horse over time? ___________________________________________ 4. What has happened to the forefoot and toes over time? ____________________________________________ Page 5 Part B: Sedimentary Rock Layers 1. Observe the diagram below noticing the various fossils present in each layer. How many layers of rock are being observed? _________ A. B. C. D. 2. Which fossil is probably older, A or C ? _________ 3. Which fossil is the most structurally complex - A, B, C, or D? __________________ 4. Based off of the pictures shown, what was most likely the oldest environment? (circle one) OCEAN 5. DESERT LAKE FOREST Based off of the pictures shown, what is most likely the current environment? (circle one) OCEAN DESERT LAKE FOREST Part C: Homologous Structures 1. Carefully examine the drawings of the various bones below. Look for similarities among the various animals. 2. Describe the function (what it does) of each set of bones shown: 3. a. Human Arm____________________ d. Bat Wing__________________ b. Whale Flipper __________________ e. Bird Wing _________________ c. Cat Paw_______________________ f. Horse __________________ Structures that are formed in similar ways during embryonic development and share like arrangements but have different forms and functions are called _________________________________________________ structures. Page 6 Part D: Analogous Structures 1. Examine the butterfly wing and the bird wing shown below: veins bones 2. What function do these structures have? __________________________________________ 3. Name two ways these structures are different._______________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Some apparently unrelated animals have organs or structures with similar functions, yet are very different in structure and form. These structures are called ____________________________________________ structures. Part E: Vestigial Structures Gradual changes have occurred through time that have in some cases reduced or removed the function of some body structures and organs. The penguin’s wings and the leg bones of snakes are examples of this phenomenon. The cave fish and the minnow shown below are related, but the cave fish is blind. Minnow 1. Cave fish Explain why eyesight is not an important adaptation to life in a cave: ______________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Does the appearance of the cave fish and the minnow suggest common ancestry? ___________________________ 3. Explain your answer: ___________________________________________________________________________ 4. Organs or structures that have lost their function in organisms and become reduced in size are called _______________________________ structures. Page 7 5. Read the list of human vestigial structures and their functions shown in the table below and explain why it has become vestigial in humans. Record your answers in the table. Structure Function in Animals Appendix Aids in digestion of hair, bones, etc. Coccyx (tail bone) Used for communication and balance Muscles that move ears Used to increase awareness in their Why vestigial in humans environment 6. Based on lack of use, what organ or structure do you predict will become vestigial and why. ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ Part F: Embryology 1. Study the embryo diagrams below and look at the similarities between the early developments of the different animals. 2. Which of the different animals is most similar to the human? ____________________________ 3. As the embryos grow and develop, what happens to the similarity of the embryos? _________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. How does the comparison of embryos provide evidence of evolution? ____________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ Page 8 Part G: Molecular (DNA) similarities 1. According to the chart comparing molecular (DNA) similarities, who is most closely related to humans?__________________ 2. According to the chart comparing molecular (DNA) similarities, who is least closely related to humans? __________________ 3. What type of evidence is the best evidence of evolution demonstrating the relationship between two organisms? ___________ PEPPERED MOTH SURVEY INTRODUCTION: Industrial melanism is the term used to describe the adaptation of an organism in response to industrial pollution. One example of rapid industrial melanism occurred in the peppered moth in the area of Manchester, England from 1945 to 1990. Before the Industrial Revolution, the trees in the forest around Manchester were light grayish-green due to the presence of lichens on their trunks. Peppered moths, which live in the area, were light with dark spots. Their coloring served as camouflage against predators. As the Industrial Revolution progressed and pollution increased, the trees became covered with sulphur dioxide (soot), turning the tree trunks dark. Over a period of 45 years, the peppered moth became a predominantly dark species. It turns out that body and wing color in peppered moths is controlled by a single gene. Dark color is caused by a dominant mutation to the gene. Now the dark color is the dominant allele of the gene and light color is the recessive allele. In this investigation, you will observe the effects of industrial melanism in the peppered moth over a course of several years. I. II. III. IV. Title of Graph: Purpose/Objective: Materials Needed: Background: Peppered Moth Survey Understand Natural Selection Graph paper, ruler and 2 colored pencils Table A represents data from a ten-year study of two varieties of the same species of peppered moths. The numbers represent moths captured in traps for ten consecutive years. The traps were located in the same area each year. Page9 Table A: YEAR 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 NUMBERS OF LIGHT MOTHS CAPTURED 556 537 484 392 246 225 193 147 84 56 NUMBERS OF DARK MOTHS CAPTURED 64 112 196 210 281 357 412 503 594 636 V. Data/Results: Using the data provided, construct a graph comparing the numbers of each variety of peppered moth using one of your colored pencils to represent the light moths and one color to represent the dark moths. Label the Y-axis “Numbers of Moths Captured” and label the X-axis “Years. VI. Discussion: 1. If the bark of trees is dark and the moths that rest there are light, what do you predict will happen to the light colored moths? Use your notes and the information from your graph to help you answer the following questions. __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What historical event caused the tree trunks of many trees in England to turn from light green to dark? _________________ 3. Which variety of moths increased over the ten year period? ________________________________ 4. Which variety of moths decreased over the ten year period?________________________________________ 5. If the pollution is corrected and the air once again becomes clean, what can you predict will happen to the color of the trees? ________________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. What effect will this have on the moth population? Why? _____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ Page 10 SELF-QUIZ: 1. The bones in the wings of a bat are the same as the bones found in the paws of raccoon, though their function is quitedifferent. The similarity is evidence that the bat and the raccoon– A hunt for the same prey. B live in similar habitats. C are about the same size. D share a common ancestor. 2. Some snake embryos have small buds resembling limbs. These buds disappear at later stages of embryonic development. These observations suggest that these snakes – A will have offspring with limbs. B had a parent with working limbs. C have functional limbs as adults. D evolved from a limbed ancestor. 3. A chart comparing the base sequences of homologous segments of DNA from various primates is provided. The information in the chart can be used to conclude that which pair of organisms have the most recent common ancestor? DNA BASE SEQUENCE COMPARISON Gorilla AGG CCC CTT CCA ACC Chimpanzee AGG CCC CTT CCA ACC Baboon AGG CCC ACA CCA ACC Lemur AGG ACG CGC CCT AGT A Chimpanzees and baboons B Chimpanzees and lemurs C Gorillas and chimpanzees D Gorillas and baboons 4. All of the following can be told from the fossil record EXCEPT – A the order in which organisms appeared. B the number of organisms that existed. C the environment the organisms lived in. D the approximate age of past organisms. 5. Which of the following can be concluded from the evolutionary tree provided? A All three species became more complex over time. B The differences are greatest between species B and C. C There is evidence of large gaps in the fossil record. D The common ancestor was most similar to species C. Page 11 6. Which of the following best describes the relationship between natural selection and adaptation? A Organisms in an environment select the adaptations that provide a natural advantage. B The adaptations of a population of organisms are those selected over generations. C The adaptations of an organism influence the habitat they select for survival. D Nature selects adaptations that increase conflict and resource competition. 7. Natural selection works to produce change at which of the following levels? A Individuals B Communities C Populations D Characteristics 8. Which of the following best describes the effects of gene flow? As a result of gene flow – A new species arise more quickly B genetic variability increases C speciation does not occur D populations become genetically different 9. Which of the following phenomena usually only has an effect on very small populations? A. B. C. D. 10. Which of the following statements is true about mutations? Mutations ___________. A. B. C. D. 11. occur randomly and increase genetic variation. are usually harmful and cause organisms to die. are caused by changes in an organism’s environment. occur at a consistent rate in nearly every population. Which of the following statements best describes gene flow? As a result of gene flow _____________________. A. B. C. D. 12. gene flow genetic drift recombination mutations new species arise more quickly genetic variability increases speciation does not occur populations become genetically different Natural selection pressures will be greater in situations where which of the following is true? A. B. C. D. Resources are limited. Populations reproduce slowly. Populations vary genetically. Competition is minimal. Page 12