IEEE Paper Template in A4 (V1)
advertisement
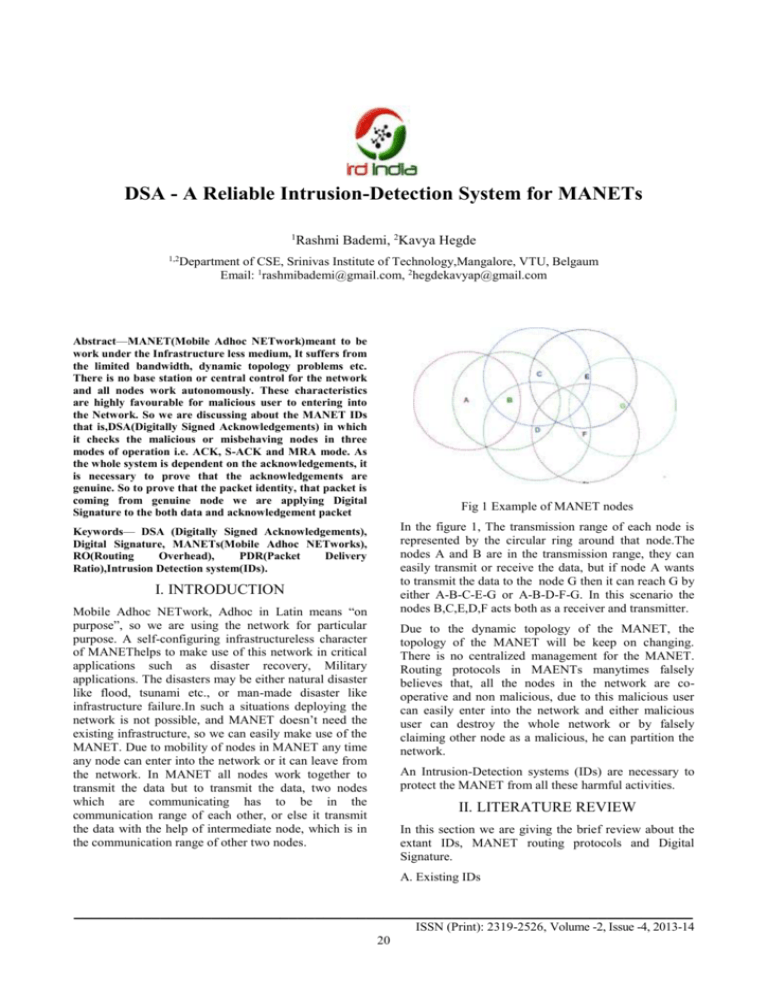
International Journal of Advanced Computer Engineering and Communication Technology (IJACECT) ________________________________________________________________________ DSA - A Reliable Intrusion-Detection System for MANETs 1 Rashmi Bademi, 2Kavya Hegde 1,2 Department of CSE, Srinivas Institute of Technology,Mangalore, VTU, Belgaum Email: 1rashmibademi@gmail.com, 2hegdekavyap@gmail.com Abstract—MANET(Mobile Adhoc NETwork)meant to be work under the Infrastructure less medium, It suffers from the limited bandwidth, dynamic topology problems etc. There is no base station or central control for the network and all nodes work autonomously. These characteristics are highly favourable for malicious user to entering into the Network. So we are discussing about the MANET IDs that is,DSA(Digitally Signed Acknowledgements) in which it checks the malicious or misbehaving nodes in three modes of operation i.e. ACK, S-ACK and MRA mode. As the whole system is dependent on the acknowledgements, it is necessary to prove that the acknowledgements are genuine. So to prove that the packet identity, that packet is coming from genuine node we are applying Digital Signature to the both data and acknowledgement packet Fig 1 Example of MANET nodes In the figure 1, The transmission range of each node is represented by the circular ring around that node.The nodes A and B are in the transmission range, they can easily transmit or receive the data, but if node A wants to transmit the data to the node G then it can reach G by either A-B-C-E-G or A-B-D-F-G. In this scenario the nodes B,C,E,D,F acts both as a receiver and transmitter. Keywords— DSA (Digitally Signed Acknowledgements), Digital Signature, MANETs(Mobile Adhoc NETworks), RO(Routing Overhead), PDR(Packet Delivery Ratio),Intrusion Detection system(IDs). I. INTRODUCTION Mobile Adhoc NETwork, Adhoc in Latin means “on purpose”, so we are using the network for particular purpose. A self-configuring infrastructureless character of MANEThelps to make use of this network in critical applications such as disaster recovery, Military applications. The disasters may be either natural disaster like flood, tsunami etc., or man-made disaster like infrastructure failure.In such a situations deploying the network is not possible, and MANET doesn’t need the existing infrastructure, so we can easily make use of the MANET. Due to mobility of nodes in MANET any time any node can enter into the network or it can leave from the network. In MANET all nodes work together to transmit the data but to transmit the data, two nodes which are communicating has to be in the communication range of each other, or else it transmit the data with the help of intermediate node, which is in the communication range of other two nodes. Due to the dynamic topology of the MANET, the topology of the MANET will be keep on changing. There is no centralized management for the MANET. Routing protocols in MAENTs manytimes falsely believes that, all the nodes in the network are cooperative and non malicious, due to this malicious user can easily enter into the network and either malicious user can destroy the whole network or by falsely claiming other node as a malicious, he can partition the network. An Intrusion-Detection systems (IDs) are necessary to protect the MANET from all these harmful activities. II. LITERATURE REVIEW In this section we are giving the brief review about the extant IDs, MANET routing protocols and Digital Signature. A. Existing IDs ________________________________________________________________________ ISSN (Print): 2319-2526, Volume -2, Issue -4, 2013-14 20 International Journal of Advanced Computer Engineering and Communication Technology (IJACECT) ________________________________________________________________________ In this section we are discussing about 4 existing IDs mainly, watchdog, TWOACK, 2ACK and AACK. acknowledging back to first node in a group of three consecutive nodes. Watch dog: Watchdog [1] [2] consists of mainly 2 parts, watchdog and pathrater. Watchdog actively detects if any malicious node is misbehaving in the network.The core theme of watchdog is that, it individually listens to its next hops transmission. If a Watchdog node overhears that its next node fails to forward the packet within a certain period of time, it increases its failure counter. After exceeding a predefined threshold, the Watchdog node reports it as misbehaving. After when the watchdog nodes reports particular node as a malicious,the Pathrater works with the routing protocols to avoid the reported nodes in future data transmission. AACK: AACK [1] is a hybrid scheme which is the combination of ACK and TACK (similar to TWOACK) scheme. ACKnowledgement scheme is an end-to-end ack scheme.After when the source node sends packet, every intermediate node passes the packet to destination and through the same path in reverse order,destination will acknowledges to the source within timeout, if source node doesnt get acknowledgement then it will switch to TACK mode by sending the TACK packet. TACK works similar to TWOACK, where three consecutive nodes work in a group, and the node which is two hop away from the first node will have to acknowledge back to first node. This process continues along the rest of the route. Watchdog scheme unable to detect malicious misbehaviors with the presence of 1) Ambiguous collisions.2) Receiver collisions.3) Limited transmission power. 4) False misbehavior report.5) Collusion. And 6) Partial dropping. B. MANET Routing Protocols TWOACK: In TWOACK [3] three consecutive nodes work in a group to detect misbehaving links in a network.Each node along theroute is required to send back an acknowledgment packet tothe node that is two hops away from it. This process continues from source till destination In this section we are discussing about the routing protocols and the DSR, an underlying routing protocol which is used in the system. There are three different routing protocols that can be used in MANET. They are proactive routingprotocol[5], reactive routing protocol[5], and hybrid routing protocol[5], which is the combination of both proactive and reactive routing protocols. We are discussing mainly about DSR[5], which comes under the reactive routing protocol. Reactive routing protocols discovers the route when it has the data to send Dynamic Source Routing Protocol (DSR) [5] is an on Demand, Source Routing protocol. On-demand means that the paths are discovered to the intended recipient when the source node has data to send. Fig 2 TWOACK Scheme The main two phases of DSR are Route Discovery and Route Maintenance. Consider fig 2 Node 1 first forwards Packet 1 to node 2,and then, node 2 forwards Packet 1 to node 3. When node 3 receives Packet 1, as it is two hops away from node 1, node 3 has to generate a TWOACK packet, which contains reverse route from node 1 to node 3, and sends it back to node A. The retrieval of this TWOACK packet at node 1 indicates that the transmission of Packet 1 from node 1 to node 3 is successful. Otherwise, if this TWOACK packet is not received in a predefined time period, both nodes 2 and 3 are reported as malicious. As every node need to generate the acknowledgement, network overhead increases, but it successfully recognises and solves the receiver collision [1] and limited transmission power [1] problems. When a node in the network has a data to send, first it checks its routing table for any possible routes to the destination, if there is no route for the particular destination or although the route is there but it is expired then the source node will launch the route discovery process. If any link on a route is broken, the source node is notified by an intermediate node that detects the link break when forwarding packet to the next node in the route path. The source node removes any route using this link from its cache, or removes the portion of the route that uses that broken link. The source must also try another path or do a new route discovery if it does not have another path. 2ACK:The 2ACK [4] scheme is an add-on technique for routing schemes which helps to detect routing misbehavior and to remit their adverse effect. The working processs of the 2ACK scheme is same as that of the TWOACK but only a fraction of the received data packets are acknowledged in the 2ACK scheme to reduce the routing overhead that is caused from the generation of 2ACK from every nodewhile C. Digital Signatures Digital Signature is the vital part of the cryptography [6]. Cryptography and encryption [1] [6]means the same, the encryption means that conversion of information from a readable state to apparent nonsense. ________________________________________________________________________ ISSN (Print): 2319-2526, Volume -2, Issue -4, 2013-14 21 International Journal of Advanced Computer Engineering and Communication Technology (IJACECT) ________________________________________________________________________ sent to source node. After when the source node gets the misbehavior report, it switches to MRA mode by sending MRA packet, to check the misbehavior report. 3) MRA: In MRA mode the source node sends the MRA packet to destination through another route to check whether the destination has received the reported missing packet or not. When the destination node receives an MRA packet, it searches its local knowledge base and compares if the reported packet was received. If it is already received, then it concludes that this is a false misbehavior report and whoever generated this report is marked as malicious. Otherwise, the misbehavior report is trusted and accepted. Fig 3: Example of Cryptography Figure 3, depicts the cryptographic method, where the key may be either same or different. Based on the use of key used cryptography is divided into 2 types, they are Symmetric key Cryptography and Asymmetric key cryptography. 4) Digital Signature: To provide the data security the data packets are encrypted and Acknowledgement packets are also encrypted. In turn the system provide security for both data and acknowledgement packets. In Symmetric-key cryptography [1] [6], the same key is used for both encryption and decryption. A significant disadvantage of symmetric ciphers is the key management necessary to use them securely. IV. PERFORMANCE EVALUATION In Asymmetric-key cryptography [1] [6], it uses two different but mathematically related keys, which are public key and private key. Asymmetric-key cryptography is also called as public key system. In public-key cryptosystems, we can freely distribute the public key whereas the private key must be secret. In a public-key encryption system, for encrypting the data the public key is used, and while the private or secret keyis used for decryption. In this section we are discussing mainly about simulation Configuration and simulation results. A. Simulation Methods The simulation is carried out to check, the Packet Delivery Ratio and energy consumed by the nodes in the network, when both the data and acknowledgement packets are encrypted. III. SCHEME DESCRIPTION: DSA B. Simulation Configuration Our simulation is carried out with the Network Simulator(NS) 2.34 environment and NS2 can be installed in any UNIX or LINUX flavoured OS (Operating System) such as Ubuntu. Our system is running on Ubuntu 9.10. The system will run on any Core 2Duo T7250 CPU and 3-GB RAM or higher versions, with Graphics card. Both the physical layer and the 802.11MAC layer are included during simulation. Our proposed system DSA solves the receiver collision, limited transmission power, and false misbehaviour problems. Our proposed system DSA, works in three modes of operation, namely ACK, secure ACK (SACK), and MRA. 1) ACK: ACK mode is the first step in our proposed system, which helps to reduce network overhead, when there is no misbehaving node in the network. ACK is an end-to-end acknowledgement scheme, in which the source node sends the data packet to destination, if destination node receives the data packet within time-out then it has to acknowledge back to the source. Otherwise source node will send an S-ACK packet and switch to SACK process. C. Performance Analysis In this section we are discussing about the performance of the DSA. 2) S-ACK: The purpose of the S-ACK is to detect misbehaving nodes in the presence of receiver collision or limited transmission power. In the (Secure – ACK) SACK mode, the source node sends the encrypted data packets over network, to maintain the integrity of the data, also to secure the data from unwanted user. The working of S-ACK is same as that of TWOACK system. In TWOACK every three consecutive nodes work in group for the detection of misbehaving nodes. In the three consecutive nodes the third node has to send an SACK acknowledgement packet to the first node. In a group of three consecutive nodes, if first node doesn’t receive the acknowledgement packet within timeout both second and third nodes are reported as malicious and misbehaviour report is generated by first node and Fig 4: Packet Delivery ratio Initially when there will be no malicious nodes in the network(Assuming no malicious nodes in the network)the PDR value will be high, after some time, ________________________________________________________________________ ISSN (Print): 2319-2526, Volume -2, Issue -4, 2013-14 22 International Journal of Advanced Computer Engineering and Communication Technology (IJACECT) ________________________________________________________________________ Energy Consumption due to the presence of malicious nodes in the network, the PDR value decreases, the main reason of decrease in PDR value is due to the increased packets in the networks and also due to the digital signatures, which is shown in Fig 4. REFERENCES [1] Elhadi M.Shakshuhi, Senior Member, IEEE, Nan Kang, and TarekR. Sheltami, Member, IEEE ” EAACKA Secure Intrusion-Detection System for MANETs,” in IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIALELECTRONICS, VOL. 60, NO. 3, MARCH 2013. [2] Nidal Nasser and Yunfeng Chen, ”Enhanced Intrusion Detection Systemfor Discovering Malicious Nodes in Mobile Ad hoc Networks,” in IEEE Communications for publication in the ICC 2007 proceedings. [3] Kashyap Balakrishnan, Jing Deng, Pramod K. Varshney ”TWOACK: Preventing Selfishness in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks”, in IEEE transaction2005. [4] Kejun Liu, Jing Deng, Member, IEEE, Pramod K. Varshney, Fellow, IEEE, and Kashyap Balakrishnan, Member, IEEE, ”An Acknowledgment-Based Approach for the Detection of Routing Misbehavior in MANETs,”in IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MOBILE COMPUTING, VOL. 6, NO. 5,MAY 2007. [5] Mr. L Raja, Capt. Dr. S SanthoshBaboo” Comparative study of reactive routing protocol in MANET”, in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science, Volume 2 Issue 3 March 2013. [6] R.L. Rivest, A. Shamir, and L. Adleman”A Method for Obtaining Digital Signatures and Public-Key Cryptosystems”. 800 600 400 AACK 200 DSA 0 6 8 10 12 14 16 Time Fig 5: Energy Consumption Consider the fig 5, where the energy consumption is high in DSA compared to AACK due to Digital Signature. V.CONCLUSION In this paper we have developed the Intrusion-Detection system for MANETs. A digital signature is applied to both data packets and acknowledgements to secure the data is being transmitted over network but the Digital Signature increases the Network overhead in the system. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT We would like to express our special thanks of gratitude to H.O.D Prof. Shivakumar G.S, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, SIT Mangalore. We also convey our thanks to all the staff members of SIT for helping in the project. ________________________________________________________________________ ISSN (Print): 2319-2526, Volume -2, Issue -4, 2013-14 23