Unit 13 vocabulary
advertisement

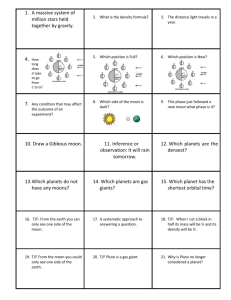
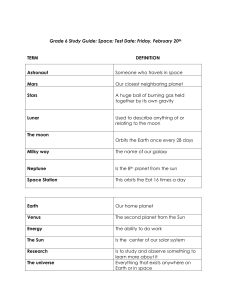
UNIT 13 VOCABULARY - SPACE 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) 16) 17) Asteroid: Piece of rock or metal made up of material similar to that which formed the planets that orbit the Sun Comets: Consists primarily of ice, dust, and rock whose orbit is a long narrow ellipse Galilean Moons: The four largest and brightest moons of Jupiter discovered by Galileo Gravity: The force of attraction that pulls objects toward each other Inner Planet: Any of the rocky, terrestrial planets of Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars whose orbits range is within the asteroid belt Outer Planet: Any of the larger, gaseous planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune whose orbits lie beyond the asteroid belt Meteor: Small meteoroid that burns upon entry of Earth's atmosphere Meteorite: Remains of meteoroids that strike the surface of Earth or the Moon Meteoroid: A natural chunk of rock or dust existing outside Earth's atmosphere Moon: A natural satellite that orbits a planet. Some planets have no moons; others have over 60 moons. Orbit: The path one object takes as it revolves around another object in space Planet: Any of the large celestial bodies that revolve around the Sun in the Solar System Satellite: A smaller body that orbits a larger body (the Moon) or Spacecraft that orbits Earth Solar System: The Sun together with the group of planets that are held by its attraction and revolve around it Sun: The luminous celestial body around which Earth and other planets revolve, and receive heat and light Rotation: "A 24-hour period on Earth, or, the time it takes the Earth to make one complete rotation on its axis Revolution: Earth's year-long elliptical orbit around the Sun (planets have different rotation and revolution times) UNIT 13 VOCABULARY - SPACE 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) 16) 17) Asteroid: Piece of rock or metal made up of material similar to that which formed the planets that orbit the Sun Comets: Consists primarily of ice, dust, and rock whose orbit is a long narrow ellipse Galilean Moons: The four largest and brightest moons of Jupiter discovered by Galileo Gravity: The force of attraction that pulls objects toward each other Inner Planet: Any of the rocky, terrestrial planets of Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars whose orbits range is within the asteroid belt Outer Planet: Any of the larger, gaseous planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune whose orbits lie beyond the asteroid belt Meteor: Small meteoroid that burns upon entry of Earth's atmosphere Meteorite: Remains of meteoroids that strike the surface of Earth or the Moon Meteoroid: A natural chunk of rock or dust existing outside Earth's atmosphere Moon: A natural satellite that orbits a planet. Some planets have no moons; others have over 60 moons. Orbit: The path one object takes as it revolves around another object in space Planet: Any of the large celestial bodies that revolve around the Sun in the Solar System Satellite: A smaller body that orbits a larger body (the Moon) or Spacecraft that orbits Earth Solar System: The Sun together with the group of planets that are held by its attraction and revolve around it Sun: The luminous celestial body around which Earth and other planets revolve, and receive heat and light Rotation: "A 24-hour period on Earth, or, the time it takes the Earth to make one complete rotation on its axis Revolution: Earth's year-long elliptical orbit around the Sun (planets have different rotation and revolution times)