Keywords
advertisement

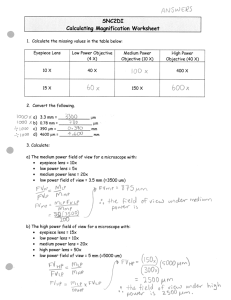
Keywords for Cell Structure Term Definition Magnification formula Magnification = power of objective lens x power of eyepiece lens Stage The stage holds the slide which contains the specimen to be viewed Diaphragm The diaphragm controls the amount of light reaching the specimen Fine focus The fine focus sharpens the image under high and low power. It moves the stage by small amounts Coarse focus The coarse focus focuses the image under low power Objective lens A lens attached to the nosepiece which magnifies the specimen Eyepiece lens The eyepiece lens magnifies the image, usually 10 times Magnification formula Magnification = power of objective lens x power of eyepiece lens Compound Microscope A microscope that uses two lenses for magnification Protoplasm The Protoplasm is all the living parts of the cell Function of the cell wall The cell wall gives strength to the cell Function of the vacuole The vacuole gives the cell strength and stores water, salts and sugars Cytoplasm The cytoplasm is the jelly like material outside the nucleus Ultrastructure of the cell Cell ultrastructure is the fine details of the cell that can be seen using an electron microscope Cell membrane The cell membrane is a thin membrane around the cell that is made of phospholipids and proteins Function of cell membrane Cell membranes retain the cell contents and they control what goes in and out of the cell Nucleus The nucleus is the control centre of the cell Chromatin Chromatin consists of DNA and proteins that makes up a chromosome when it is not dividing Nucleolus The nucleolus is an area of the nucleus where ribosomes are made Mitochondria The mitochondria supply energy to the cell. Respiration occurs here Chloroplasts Chloroplasts are only found in plant cells. They are the green structure where photosynthesis takes place. Cell Walls Cell walls are only found in plant cells. They are made of cellulose. Function of cell wall The function of the cell wall is to give strength and support to the plant cell. They are fully permeable. Ribosomes Ribosomes are tiny structures which are made of DNA and protein. Their function is to make proteins. Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryotic Cells do not have a nucleus or membrane bound organelles Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells have a nucleus and cell organelles Electron Microscope A microscope that achieves much greater magnification than a light microscope as it uses a parallel beam of electrons to illuminate the object instead of a beam of light